Distinct predictive performance of Rac1 and Cdc42 in cell migration
- PMID: 26634649
- PMCID: PMC4669460
- DOI: 10.1038/srep17527
Distinct predictive performance of Rac1 and Cdc42 in cell migration
Abstract
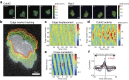
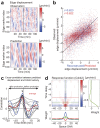
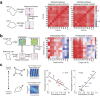
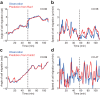
We propose a new computation-based approach for elucidating how signaling molecules are decoded in cell migration. In this approach, we performed FRET time-lapse imaging of Rac1 and Cdc42, members of Rho GTPases which are responsible for cell motility, and quantitatively identified the response functions that describe the conversion from the molecular activities to the morphological changes. Based on the identified response functions, we clarified the profiles of how the morphology spatiotemporally changes in response to local and transient activation of Rac1 and Cdc42, and found that Rac1 and Cdc42 activation triggers laterally propagating membrane protrusion. The response functions were also endowed with property of differentiator, which is beneficial for maintaining sensitivity under adaptation to the mean level of input. Using the response function, we could predict the morphological change from molecular activity, and its predictive performance provides a new quantitative measure of how much the Rho GTPases participate in the cell migration. Interestingly, we discovered distinct predictive performance of Rac1 and Cdc42 depending on the migration modes, indicating that Rac1 and Cdc42 contribute to persistent and random migration, respectively. Thus, our proposed predictive approach enabled us to uncover the hidden information processing rules of Rho GTPases in the cell migration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Fret-based single-molecule probes for monitoring induced activation of Rac, Cdc42 signaling pathways in living cells].Fen Zi Xi Bao Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2008 Oct;41(5):349-58. Fen Zi Xi Bao Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 19127770 Chinese.
-
Different roles of the small GTPases Rac1, Cdc42, and RhoG in CALEB/NGC-induced dendritic tree complexity.J Neurochem. 2016 Oct;139(1):26-39. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13735. Epub 2016 Aug 4. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 27412363
-
Rho GTPases in embryonic development.Small GTPases. 2014;5(2):8. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.29716. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 25483305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optical Tools To Study the Isoform-Specific Roles of Small GTPases in Immune Cells.J Immunol. 2016 Apr 15;196(8):3479-93. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501655. Epub 2016 Mar 7. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26951800 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Cdc42 and Rac1 activities in pheochromocytoma, the adrenal medulla tumor.Small GTPases. 2017 Apr 3;8(2):122-127. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1202634. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Small GTPases. 2017. PMID: 27355516 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-phasic bi-directional chemotactic responses of the growth cone.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 3;6:36256. doi: 10.1038/srep36256. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27808115 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic dissection of Rac1 and Cdc42 gradient shaping.Nat Commun. 2018 Nov 16;9(1):4816. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07286-8. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30446664 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent cell migration emerges from a coupling between protrusion dynamics and polarized trafficking.Elife. 2022 Mar 18;11:e69229. doi: 10.7554/eLife.69229. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35302488 Free PMC article.
-
Rational identification of a Cdc42 inhibitor presents a new regimen for long-term hematopoietic stem cell mobilization.Leukemia. 2019 Mar;33(3):749-761. doi: 10.1038/s41375-018-0251-5. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Leukemia. 2019. PMID: 30254339 Free PMC article.
-
Indispensable role of STIL in the regulation of cancer cell motility through the lamellipodial accumulation of ARHGEF7-PAK1 complex.Oncogene. 2020 Feb;39(9):1931-1943. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-1115-9. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 31754215
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

