Clinicopathological Significance of MicroRNA-20b Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Regulation of HIF-1α and VEGF Effect on Cell Biological Behaviour
- PMID: 26612965
- PMCID: PMC4646993
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/325176
Clinicopathological Significance of MicroRNA-20b Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Regulation of HIF-1α and VEGF Effect on Cell Biological Behaviour
Abstract
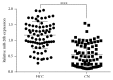
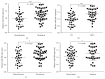
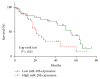
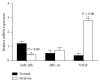
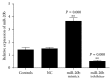
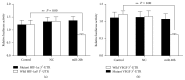
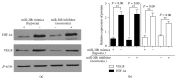
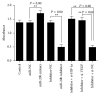
miRNA-20b has been shown to be aberrantly expressed in several tumor types. However, the clinical significance of miRNA-20b in the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is poorly understood, and the exact role of miRNA-20b in HCC remains unclear. The aim of the present study was to investigate the association of the expression of miR-20b with clinicopathological characteristics and overall survival of HCC patients analyzed by Kaplan-Meier analysis and Cox proportional hazards regression models. Meanwhile, the HIF-1α and VEGF targets of miR-20b have been confirmed. We found not only miR-20b regulation of HIF-1α and VEGF in normal but also regulation of miR-20b in hypoxia. This mechanism would help the tumor cells adapt to the different environments thus promoting the tumor invasion and development. The whole study suggests that miR-20b, HIF-1α, and VEGF serve as a potential therapeutic agent for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential distribution of miR-20a and miR-20b may underly metastatic heterogeneity of breast cancers.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(5):1901-6. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2012.13.5.1901. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012. PMID: 22901144
-
MicroRNA-20b Downregulates HIF-1α and Inhibits the Proliferation and Invasion of Osteosarcoma Cells.Oncol Res. 2016;23(5):257-66. doi: 10.3727/096504016X14562725373752. Oncol Res. 2016. PMID: 27098149 Free PMC article.
-
miR-20b modulates VEGF expression by targeting HIF-1 alpha and STAT3 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Jul;224(1):242-9. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22126. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20232316
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha in lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016 Jun;36(3):321-327. doi: 10.1007/s11596-016-1586-7. Epub 2016 Jul 5. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27376798 Review.
-
Protein expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review with meta-analysis.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct;38(5):598-603. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2014.04.004. Epub 2014 May 15. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24835771 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Silibinin on the Expression of Mir-20b, Bcl2L11, and Erbb2 in Breast Cancer Cell Lines.Mol Biotechnol. 2023 Dec;65(12):1979-1990. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00702-5. Epub 2023 Mar 11. Mol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36905464
-
miR-20b Inhibits T Cell Proliferation and Activation via NFAT Signaling Pathway in Thymoma-Associated Myasthenia Gravis.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:9595718. doi: 10.1155/2016/9595718. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27833920 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-20b (miR-20b) Promotes the Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, and Tumorigenicity in Esophageal Cancer Cells via the Regulation of Phosphatase and Tensin Homologue Expression.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 4;11(10):e0164105. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164105. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2022 Jan 19;17(1):e0262879. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0262879 PMID: 27701465 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
miR-15a and miR-20b sensitize hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib through repressing CDC37L1 and consequent PPIA downregulation.Cell Death Discov. 2022 Jun 27;8(1):297. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01094-2. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 35760798 Free PMC article.
-
Micromanaging aerobic respiration and glycolysis in cancer cells.Mol Metab. 2019 May;23:98-126. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.01.014. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Mol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30837197 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

