Antibodies against High Mobility Group Box protein-1 (HMGB1) versus other anti-nuclear antibody fine-specificities and disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 26596890
- PMCID: PMC4657231
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-015-0856-2
Antibodies against High Mobility Group Box protein-1 (HMGB1) versus other anti-nuclear antibody fine-specificities and disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Introduction: The non-histone nuclear protein high mobility group box protein-1 (HMGB1) is typically associated with nucleosomes, but may shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm, and under some conditions also be released extracellularly and participate in systemic inflammation. Monoclonal HMGB1-targeting antibodies can ameliorate murine polyarthritis and lupus-like disease. Interestingly, autoantibodies against HMGB1 have also been described in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), but their clinical implications remain elusive. The main aims of this study were to detect serum anti-HMGB1 antibodies in patients with SLE and relate them to other types of antinuclear antibodies (ANA), and to disease activity.
Methods: 188 Swedish SLE patients meeting the 1982 American College of Rheumatology classification criteria and/or the 2012 Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria participated in the study. Anti-HMGB1 antibody levels were analysed in patient and control (n = 112) sera by an in-house ELISA using recombinant histidine-tagged HMGB1. SLE sera were also analysed for ANA by immunofluorescence (IF) microscopy (IF-ANA) using fixed HEp-2 cells, and by a line-blot assay for antigen fine-specificities. To quantify antibodies to double-stranded DNA, a fluoroenzyme-immunoassay was employed.
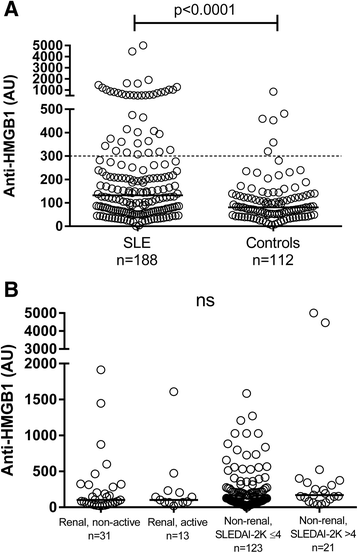
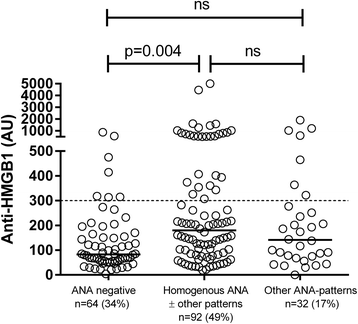
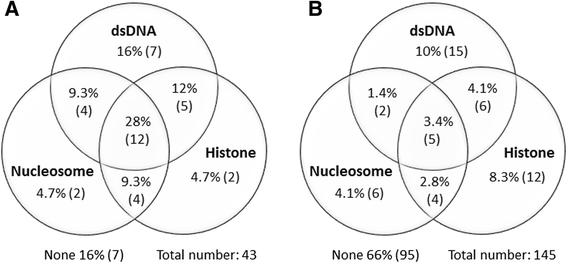
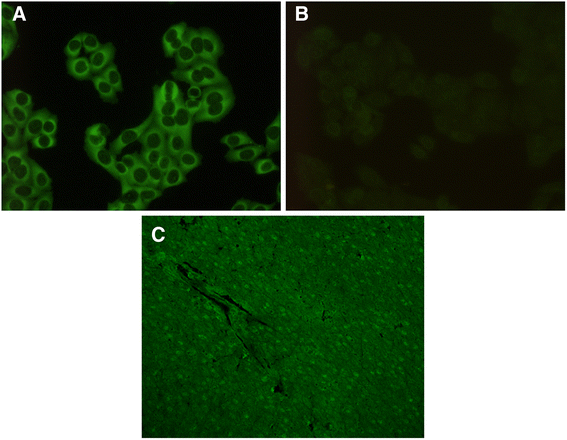
Results: At inclusion, 23 % of the SLE patients were anti-HMGB1 antibody positive compared to 5 % of the controls. Anti-HMGB1 antibodies occurred in 49 % of the IF-ANA positive SLE patients, and in 34 % of IF-ANA negative cases (p = 0.004). Levels of anti-HMGB1 antibodies correlated with anti-dsDNA antibody levels (r = 0.49; p < 0.001). Significant, but less pronounced correlations were found regarding anti-HMGB1 and SLE disease activity index (SLEDAI-2K: r = 0.15; p = 0.04), classical complement function (r = -0.24; p = 0.002) and complement protein C4 (r = -0.23; p = 0.002). Average anti-HMGB1 antibody levels were significantly higher among patients with homogenous ± other IF-ANA staining patterns (median 180 AU) compared to IF-ANA negative cases (median 83 AU) (p = 0.004). Rabbit anti-HMGB1 antibodies gave rise to cytoplasmic, but not nuclear, staining of HEp-2 cells.
Conclusions: We confirm that anti-HMGB1 antibodies are common in SLE and correlate with disease activity variables. Although anti-HMGB1 antibodies measured by ELISA often coincide with nuclear IF-ANA staining, our results indicate that anti-HMGB1 antibodies do not give rise to nuclear staining of the predominantly used commercial HEp-2 cell slides.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of anti-CLIC2 and anti-HMGB1 autoantibodies with higher disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus patients.J Postgrad Med. 2017 Oct-Dec;63(4):257-261. doi: 10.4103/jpgm.JPGM_499_16. J Postgrad Med. 2017. PMID: 28862243 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal anti-nuclear antibody (ANA) seroconversion in systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective study of Swedish cases with recent-onset disease.Clin Exp Immunol. 2020 Mar;199(3):245-254. doi: 10.1111/cei.13402. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Clin Exp Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31778219 Free PMC article.
-
Autoantibodies to box A of high mobility group box 1 in systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Exp Immunol. 2017 Jun;188(3):412-419. doi: 10.1111/cei.12951. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28245520 Free PMC article.
-
[Modern look at the problems of investigation of antinuclear antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus (literature review).].Klin Lab Diagn. 2018;63(6):340-348. doi: 10.18821/0869-2084-2018-63-6-340-348. Klin Lab Diagn. 2018. PMID: 30702224 Review. Russian.
-
The complex role of DNA, histones and HMGB1 in the pathogenesis of SLE.Autoimmunity. 2014 Dec;47(8):487-93. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2014.921811. Epub 2014 Jun 11. Autoimmunity. 2014. PMID: 24916843 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Use of Poly-L-Lysine as a Capture Agent to Enhance the Detection of Antinuclear Antibodies by ELISA.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 9;11(9):e0161818. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161818. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27611194 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-HMGB1 antibody is a potential characteristic autoantibody for Sjögren's syndrome.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 11;12(1):6020. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10007-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35411013 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Toll-Like Receptors Activity and TLR Ligands in Patients with Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases.Front Immunol. 2016 Dec 9;7:578. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00578. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 28018345 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-Like Receptor as a Potential Biomarker in Renal Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 13;21(18):6712. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186712. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32933213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HMGB1 in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2020 May 27;11:1057. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01057. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32536928 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sjowall C, Sturm M, Dahle C, Bengtsson AA, Jonsen A, Sturfelt G, et al. Abnormal antinuclear antibody titers are less common than generally assumed in established cases of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2008;35(10):1994–2000. - PubMed
-
- Acosta-Merida A, Isenberg DA. Antinuclear antibodies seroconversion in 100 patients with lupus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013;31(4):656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

