The Notch ligand E3 ligase, Mind Bomb1, regulates glutamate receptor localization in Drosophila
- PMID: 26596173
- PMCID: PMC4698086
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcn.2015.11.004
The Notch ligand E3 ligase, Mind Bomb1, regulates glutamate receptor localization in Drosophila
Abstract
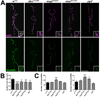
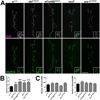
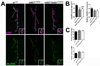
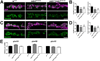
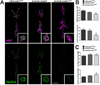
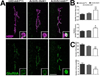
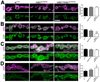
The postsynaptic density (PSD) is a protein-rich network important for the localization of postsynaptic glutamate receptors (GluRs) and for signaling downstream of these receptors. Although hundreds of PSD proteins have been identified, many are functionally uncharacterized. We conducted a reverse genetic screen for mutations that affected GluR localization using Drosophila genes that encode homologs of mammalian PSD proteins. 42.8% of the mutants analyzed exhibited a significant change in GluR localization at the third instar larval neuromuscular junction (NMJ), a model synapse that expresses homologs of AMPA receptors. We identified the E3 ubiquitin ligase, Mib1, which promotes Notch signaling, as a regulator of synaptic GluR localization. Mib1 positively regulates the localization of the GluR subunits GluRIIA, GluRIIB, and GluRIIC. Mutations in mib1 and ubiquitous expression of Mib1 that lacks its ubiquitin ligase activity result in the loss of synaptic GluRIIA-containing receptors. In contrast, overexpression of Mib1 in all tissues increases postsynaptic levels of GluRIIA. Cellular levels of Mib1 are also important for the structure of the presynaptic motor neuron. While deficient Mib1 signaling leads to overgrowth of the NMJ, ubiquitous overexpression of Mib1 results in a reduction in the number of presynaptic motor neuron boutons and branches. These synaptic changes may be secondary to attenuated glutamate release from the presynaptic motor neuron in mib1 mutants as mib1 mutants exhibit significant reductions in the vesicle-associated protein cysteine string protein and in the frequency of spontaneous neurotransmission.
Keywords: Drosophila neuromuscular junction; Glutamate receptors; Postsynaptic density; Synapse; Synaptic transmission.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
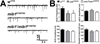
Similar articles
-
Pre and postsynaptic roles for Drosophila CASK.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011 Oct;48(2):171-82. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2011.07.009. Epub 2011 Jul 28. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21820054
-
Dbo/Henji Modulates Synaptic dPAK to Gate Glutamate Receptor Abundance and Postsynaptic Response.PLoS Genet. 2016 Oct 13;12(10):e1006362. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006362. eCollection 2016 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27736876 Free PMC article.
-
Kismet positively regulates glutamate receptor localization and synaptic transmission at the Drosophila neuromuscular junction.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 20;9(11):e113494. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113494. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25412171 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic development: insights from Drosophila.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007 Feb;17(1):35-42. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2007.01.001. Epub 2007 Jan 16. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17229568 Review.
-
Functional organization of postsynaptic glutamate receptors.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2018 Sep;91:82-94. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2018.05.002. Epub 2018 May 16. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29777761 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase mindbomb1 controls planar cell polarity-dependent convergent extension movements during zebrafish gastrulation.Elife. 2022 Feb 10;11:e71928. doi: 10.7554/eLife.71928. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35142609 Free PMC article.
-
microRNAs Sculpt Neuronal Communication in a Tight Balance That Is Lost in Neurological Disease.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Dec 12;11:455. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00455. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30618607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-Developmental Roles of Notch Signaling in the Nervous System.Biomolecules. 2020 Jul 1;10(7):985. doi: 10.3390/biom10070985. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32630239 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bangash MA, Park JM, Melnikova T, Wang D, Jeon SK, Lee D, Syeda S, Kim J, Kouser M, Schwartz J, Cui Y, Zhao X, Speed HE, Kee SE, Tu JC, Hu JH, Petralia RS, Linden DJ, Powell CM, Savonenko A, Xiao B, Worley PF. Enhanced polyubiquitination of Shank3 and NMDA receptor in a mouse model of autism. Cell. 2011;145:758–772. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

