Regulation of maintenance DNA methylation via histone ubiquitylation
- PMID: 26590302
- PMCID: PMC4882649
- DOI: 10.1093/jb/mvv113
Regulation of maintenance DNA methylation via histone ubiquitylation
Abstract
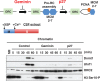
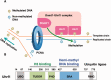
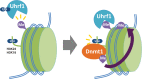
DNA methylation is one of the most stable but dynamically regulated epigenetic marks that act as determinants of cell fates during embryonic development through regulation of various forms of gene expression. DNA methylation patterns must be faithfully propagated throughout successive cell divisions in order to maintain cell-specific function. We have recently demonstrated that Uhrf1-dependent ubiquitylation of histone H3 at lysine 23 is critical for Dnmt1 recruitment to DNA replication sites, which catalyzes the conversion of hemi-methylated DNA to fully methylated DNA. In this review, we provide an overview of recent progress in understanding the mechanism underlying maintenance DNA methylation.
Keywords: DNA methylation; DNA methyltransferase 1, histone; Ubiquitin; cell cycle.
© The Authors 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Japanese Biochemical Society. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hemi-methylated DNA regulates DNA methylation inheritance through allosteric activation of H3 ubiquitylation by UHRF1.Elife. 2016 Sep 6;5:e17101. doi: 10.7554/eLife.17101. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27595565 Free PMC article.
-
Control of DNMT1 abundance in epigenetic inheritance by acetylation, ubiquitylation, and the histone code.Sci Signal. 2011 Jan 25;4(157):pe3. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2001764. Sci Signal. 2011. PMID: 21266713
-
DNA hypomethylation promotes UHRF1-and SUV39H1/H2-dependent crosstalk between H3K18ub and H3K9me3 to reinforce heterochromatin states.Mol Cell. 2025 Jan 16;85(2):394-412.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.11.009. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Mol Cell. 2025. PMID: 39631394
-
Coordinated Dialogue between UHRF1 and DNMT1 to Ensure Faithful Inheritance of Methylated DNA Patterns.Genes (Basel). 2019 Jan 18;10(1):65. doi: 10.3390/genes10010065. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30669400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular coupling of DNA methylation and histone methylation.Epigenomics. 2010 Oct;2(5):657-69. doi: 10.2217/epi.10.44. Epigenomics. 2010. PMID: 21339843 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Decoding histone ubiquitylation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 29;10:968398. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.968398. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36105353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ionizing Radiation-Induced Epigenetic Modifications and Their Relevance to Radiation Protection.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 20;21(17):5993. doi: 10.3390/ijms21175993. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32825382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting EP4 downstream c-Jun through ERK1/2-mediated reduction of DNMT1 reveals novel mechanism of solamargine-inhibited growth of lung cancer cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Feb;21(2):222-233. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12958. Epub 2016 Sep 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 27620163 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic cues modulating the generation of cell-type diversity in the cerebral cortex.J Neurochem. 2019 Apr;149(1):12-26. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14601. Epub 2018 Nov 22. J Neurochem. 2019. PMID: 30276807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p38 inhibition provides anti-DNA virus immunity by regulation of USP21 phosphorylation and STING activation.J Exp Med. 2017 Apr 3;214(4):991-1010. doi: 10.1084/jem.20161387. Epub 2017 Mar 2. J Exp Med. 2017. PMID: 28254948 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Holliday R., Pugh J.E. (1975) DNA modification mechanisms and gene activity during development. Science 187, 226–232 - PubMed
-
- Nafee T.M., Farrell W.E., Carroll W.D., Fryer A.A., Ismail K.M. (2008) Epigenetic control of fetal gene expression. BJOG 115, 158–168 - PubMed
-
- Goll M.G., Bestor T.H. (2005) Eukaryotic cytosine methyltransferases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 74, 481–514 - PubMed
-
- Chang S.C., Tucker T., Thorogood N.P., Brown C.J. (2006) Mechanisms of X chromosome inactivation. Front. Biosci. 11, 852–866 - PubMed
-
- Suzuki M.M., Bird A. (2008) DNA methylation landscape: Provocative insights from epigenomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 9, 465–476 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

