Protective Mechanisms of Flavonoids in Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 26576219
- PMCID: PMC4630416
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/314560
Protective Mechanisms of Flavonoids in Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
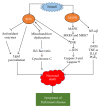
Parkinson's disease is a chronic, debilitating neurodegenerative movement disorder characterized by progressive degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta region in human midbrain. To date, oxidative stress is the well accepted concept in the etiology and progression of Parkinson's disease. Hence, the therapeutic agent is targeted against suppressing and alleviating the oxidative stress-induced cellular damage. Within the past decades, an explosion of research discoveries has reported on the protective mechanisms of flavonoids, which are plant-based polyphenols, in the treatment of neurodegenerative disease using both in vitro and in vivo models. In this paper, we have reviewed the literature on the neuroprotective mechanisms of flavonoids in protecting the dopaminergic neurons hence reducing the symptoms of this movement disorder. The mechanism reviewed includes effect of flavonoids in activation of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, suppressing the lipid peroxidation, inhibition of inflammatory mediators, flavonoids as a mitochondrial target therapy, and modulation of gene expression in neuronal cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of antioxidants in Parkinson's disease.Nutr Neurosci. 2012 May;15(3):120-6. doi: 10.1179/1476830511Y.0000000033. Nutr Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22732354 Review.
-
Accumulation of mitochondrial DNA deletions within dopaminergic neurons triggers neuroprotective mechanisms.Brain. 2013 Aug;136(Pt 8):2369-78. doi: 10.1093/brain/awt196. Brain. 2013. PMID: 23884809
-
Neuroprotective and Therapeutic Strategies against Parkinson's Disease: Recent Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 8;17(6):904. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060904. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27338353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress in Parkinson's disease.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Oct 15;765:154-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.08.033. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26297973 Review.
-
Auraptene Mitigates Parkinson's Disease-Like Behavior by Protecting Inhibition of Mitochondrial Respiration and Scavenging Reactive Oxygen Species.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 11;20(14):3409. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143409. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31336718 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Jia-Jian-Di-Huang-Yin-Zi decoction exerts neuroprotective effects on dopaminergic neurons and their microenvironment.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 29;8(1):9886. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27852-w. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29959371 Free PMC article.
-
New Neuroprotective Effect of Lemon IntegroPectin on Neuronal Cellular Model.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Apr 25;10(5):669. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050669. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33923111 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Polyscias fruticosa (L.) Harms Leaf Extract for Parkinson's Disease Treatment by Drosophila melanogaster Model.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 May 19;2022:5262677. doi: 10.1155/2022/5262677. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35633880 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Plant-Derived Flavonoids on Neurodegenerative Diseases.Neurotox Res. 2016 Jul;30(1):41-52. doi: 10.1007/s12640-016-9600-1. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Neurotox Res. 2016. PMID: 26951456 Review.
-
The Beneficial Role of Natural Endocrine Disruptors: Phytoestrogens in Alzheimer's Disease.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Sep 3;2021:3961445. doi: 10.1155/2021/3961445. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34527172 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Double K. L. Neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism and Related Disorders. 2012;18(supplement 1):S52–S54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

