Ribavirin contributes to eradicate hepatitis C virus through polarization of T helper 1/2 cell balance into T helper 1 dominance
- PMID: 26557951
- PMCID: PMC4635144
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i25.2590
Ribavirin contributes to eradicate hepatitis C virus through polarization of T helper 1/2 cell balance into T helper 1 dominance
Abstract
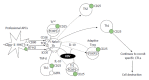
The mechanism of action of ribavirin (RBV) as an immunomodulatory and antiviral agent and its clinical significance in the future treatment of patients with hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection are reviewed. RBV up-regulates type 1 and/or 2 cytokines to modulate the T helper (Th) 1/2 cell balance to Th1 dominance. Examination of co-stimulatory signaling indicated that RBV down-modulates inducible co-stimulator on Th cells, which contributes to differentiating naïve Th cells into Th2 cells while reducing their interleukin-10 production. The effects on T-regulatory (Treg) cells were also investigated, and RBV inhibited the differentiation of naïve Th cells into adaptive Treg cells by down-modulating forkhead box-P3. These findings indicate that RBV mainly down-regulates the activity of Th2 cells, resulting in the maintenance of Th1 activity that contributes to abrogating HCV-infected hepatocytes. Although an interferon-free treatment regimen exhibits almost the same efficacy without serious complications, regimens with RBV will be still be used because of their ability to facilitate the cellular immune response, which may contribute to reducing the development of hepatocellular carcinogenesis in patients infected with HCV.
Keywords: Forkhead box-P3; Hepatitis C virus infection; Inducible co-stimulator; Interleukin-10; Ribavirin; T helper 1/2 cell balance; T-regulatory lymphocytes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ribavirin downmodulates inducible costimulator on CD4+ T cells and their interleukin-10 secretion to assist in hepatitis C virus clearance.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012 Apr;27(4):823-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.06882.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 21871023
-
The antiviral compound ribavirin modulates the T helper (Th) 1/Th2 subset balance in hepatitis B and C virus-specific immune responses.J Gen Virol. 1998 Oct;79 ( Pt 10):2381-91. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-79-10-2381. J Gen Virol. 1998. PMID: 9780043
-
Immunomodulatory activities of IFN-gamma1b in combination with type I IFN: implications for the use of IFN-gamma1b in the treatment of chronic HCV infections.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2006 Jul;26(7):473-83. doi: 10.1089/jir.2006.26.473. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2006. PMID: 16800786
-
Ribavirin induced hemolysis: a novel mechanism of action against chronic hepatitis C virus infection.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Nov 21;20(43):16184-90. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16184. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25473172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Hepatitis C virus infection in renal diseases: state of knowledge, therapeutic problems and perspectives].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2000 Apr;8(46):303-6. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2000. PMID: 10897663 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
The ABC7 regimen: a new approach to metastatic breast cancer using seven common drugs to inhibit epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and augment capecitabine efficacy.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2017 Jul 11;9:495-514. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S139963. eCollection 2017. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2017. PMID: 28744157 Free PMC article.
-
Mpox (formerly monkeypox): pathogenesis, prevention, and treatment.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Dec 27;8(1):458. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01675-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 38148355 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mohd Hanafiah K, Groeger J, Flaxman AD, Wiersma ST. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection: new estimates of age-specific antibody to HCV seroprevalence. Hepatology. 2013;57:1333–1342. - PubMed
-
- Gerlach JT, Diepolder HM, Zachoval R, Gruener NH, Jung MC, Ulsenheimer A, Schraut WW, Schirren CA, Waechtler M, Backmund M, et al. Acute hepatitis C: high rate of both spontaneous and treatment-induced viral clearance. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:80–88. - PubMed
-
- Thein HH, Yi Q, Dore GJ, Krahn MD. Estimation of stage-specific fibrosis progression rates in chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a meta-analysis and meta-regression. Hepatology. 2008;48:418–431. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

