Coadministration of Atorvastatin and Amiodarone Increases the Risk of Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats
- PMID: 26544718
- PMCID: PMC5588350
- DOI: 10.1159/000442202
Coadministration of Atorvastatin and Amiodarone Increases the Risk of Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of atorvastatin administration on amiodarone-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats.
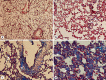
Materials and methods: Thirty-six male Wistar rats were randomly divided into 4 groups. The control group (CTL) received distilled water (0.3 ml intratracheally on days 0 and 2 and 0.5 ml orally from day 0 for 3 weeks). The atorvastatin group (AT), in addition to intratracheal distilled water, received 1 mg/kg of atorvastatin orally from day 0 for 3 weeks. The amiodarone group (AMI) received 2 intratracheal instillations of amiodarone (6.25 mg/kg in 0.3 ml of water) on days 0 and 2 and 0.5 ml of distilled water (like the CTL). The amiodarone plus atorvastatin group (AMI + AT) received both these drugs (same doses and methods as for the AMI and AT). After 28 days, the rate of lung fibrosis was estimated according to pathological criteria of lung sections and measurements of hydroxyproline in pieces of left lung tissue.
Results: The lung hydroxyproline content was higher in the treated groups (CTL: 0.35 ± 0.017, AT: 0.38 ± 0.012, AMI: 0.375 ± 0.018 and AMI + AT: 0.38 ± 0.012 unit/mg protein), but did not reach significance when compared with the CTL (p = 0.56). Amiodarone administration significantly increased the score of pulmonary fibrosis (0.5) in comparison with the AT (0.125) and CTL (0) (p < 0.5). The combination of amiodarone and atorvastatin exacerbated the pulmonary fibrosis (1.5; p < 0.01) compared to the AMI (0.5; p < 0.001), AT (0.125) and CTL (0).
Conclusion: In this study, the concomitant administration of amiodarone and atorvastatin increased pulmonary fibrosis in rats.
© 2015 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Amiodarone-induced pulmonary fibrosis in Fischer 344 rats.Toxicology. 1996 Jun 17;110(1-3):95-101. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(96)03339-2. Toxicology. 1996. PMID: 8658564
-
Pulmonary Responses Following Quercetin Administration in Rats After Intratracheal Instillation of Amiodarone.Niger J Physiol Sci. 2019 Jun 30;34(1):63-68. Niger J Physiol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31449273
-
A characterization of amiodarone-induced pulmonary toxicity in F344 rats and identification of surfactant protein-D as a potential biomarker for the development of the toxicity.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2000 Sep 15;167(3):182-90. doi: 10.1006/taap.2000.9000. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10986009
-
Altered surfactant homeostasis and alveolar epithelial cell stress in amiodarone-induced lung fibrosis.Toxicol Sci. 2014 Nov;142(1):285-97. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu177. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Toxicol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25163675
-
Effects of dietary vitamin E supplementation on pulmonary morphology and collagen deposition in amiodarone- and vehicle-treated hamsters.Toxicology. 1999 Apr 15;133(2-3):75-84. doi: 10.1016/s0300-483x(99)00009-8. Toxicology. 1999. PMID: 10378474
Cited by
-
Comparison of Oral, Intranasal and Aerosol Administration of Amiodarone in Rats as a Model of Pulmonary Phospholipidosis.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Jul 17;11(7):345. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11070345. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 31319538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics- 2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010;121:e46–e215. - PubMed
-
- Vassallo P, Trohman RG. Prescribing amiodarone: an evidence-based review of clinical indications. JAMA. 2007;298:1312–1322. - PubMed
-
- Schwaiblmair M, Berghaus T, Haeckel T, et al. Amiodarone-induced pulmonary toxicity: an underrecognized and severe adverse effect? Clin Res Cardiol. 2010;99:693–700. - PubMed
-
- Reasor M, Kacew S. An evaluation of possible mechanism underlying amiodarone-induced pulmonary toxicity. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1996;212:297–304. - PubMed
-
- Kudenchuk PJ, Pierson DJ, Greene HL, et al. Pulmonary effects of amiodarone. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1983;1:631. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

