Further Optimization and Evaluation of Bioavailable, Mixed-Efficacy μ-Opioid Receptor (MOR) Agonists/δ-Opioid Receptor (DOR) Antagonists: Balancing MOR and DOR Affinities
- PMID: 26524472
- PMCID: PMC4772774
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01270
Further Optimization and Evaluation of Bioavailable, Mixed-Efficacy μ-Opioid Receptor (MOR) Agonists/δ-Opioid Receptor (DOR) Antagonists: Balancing MOR and DOR Affinities
Abstract
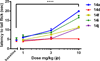
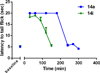
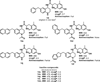
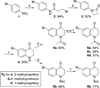
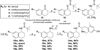
In a previously described peptidomimetic series, we reported the development of bifunctional μ-opioid receptor (MOR) agonist and δ-opioid receptor (DOR) antagonist ligands with a lead compound that produced antinociception for 1 h after intraperitoneal administration in mice. In this paper, we expand on our original series by presenting two modifications, both of which were designed with the following objectives: (1) probing bioavailability and improving metabolic stability, (2) balancing affinities between MOR and DOR while reducing affinity and efficacy at the κ-opioid receptor (KOR), and (3) improving in vivo efficacy. Here, we establish that, through N-acetylation of our original peptidomimetic series, we are able to improve DOR affinity and increase selectivity relative to KOR while maintaining the desired MOR agonist/DOR antagonist profile. From initial in vivo studies, one compound (14a) was found to produce dose-dependent antinociception after peripheral administration with an improved duration of action of longer than 3 h.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Opioid peptidomimetics: leads for the design of bioavailable mixed efficacy μ opioid receptor (MOR) agonist/δ opioid receptor (DOR) antagonist ligands.J Med Chem. 2013 Mar 14;56(5):2139-49. doi: 10.1021/jm400050y. Epub 2013 Feb 27. J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23419026 Free PMC article.
-
Benzylideneoxymorphone: A new lead for development of bifunctional mu/delta opioid receptor ligands.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017 Feb 1;27(3):666-669. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.11.057. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017. PMID: 28011222 Free PMC article.
-
Development of novel LP1-based analogues with enhanced delta opioid receptor profile.Bioorg Med Chem. 2017 Sep 1;25(17):4745-4752. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.07.021. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Bioorg Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28734666
-
Progress in the development of more effective and safer analgesics for pain management.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Dec 1;183:111701. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111701. Epub 2019 Sep 16. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31550662 Review.
-
Potential for Kappa-Opioid Receptor Agonists to Engineer Nonaddictive Analgesics: A Narrative Review.Anesth Analg. 2021 Feb 1;132(2):406-419. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000005309. Anesth Analg. 2021. PMID: 33332902 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mu-Opioid receptor biased ligands: A safer and painless discovery of analgesics?Drug Discov Today. 2017 Nov;22(11):1719-1729. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2017.07.002. Epub 2017 Jul 22. Drug Discov Today. 2017. PMID: 28743488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Mu-Delta Opioid Agonist Demonstrates Enhanced Efficacy With Reduced Tolerance and Dependence in Mouse Neuropathic Pain Models.J Pain. 2020 Jan-Feb;21(1-2):146-160. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2019.05.017. Epub 2019 Jun 12. J Pain. 2020. PMID: 31201990 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Molecular Strategies and Targets for Opioid Drug Discovery for the Treatment of Chronic Pain.Yale J Biol Med. 2017 Mar 29;90(1):97-110. eCollection 2017 Mar. Yale J Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28356897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptidomimetics and Their Applications for Opioid Peptide Drug Discovery.Biomolecules. 2022 Sep 5;12(9):1241. doi: 10.3390/biom12091241. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36139079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and Pharmacological Evaluation of Novel C-8 Substituted Tetrahydroquinolines as Balanced-Affinity Mu/Delta Opioid Ligands for the Treatment of Pain.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018 Jul 18;9(7):1840-1848. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00139. Epub 2018 May 2. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29677442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mosberg HI, Yeomans L, Harland AA, Bender AM, Sobczyk-Kojiro K, Anand JP, Clark MJ, Jutkiewicz EM, Traynor JR. Opioid peptidomimetics: leads for the design of bioavailable mixed efficacy µ opioid receptor (MOR) agonist/δ opioid receptor (DOR) antagonist ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2013;56:2139–2149. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mosberg HI, Yeomans L, Anand JP, Porter V, Sobczyk-Kojiro K, Traynor JR, Jutkiewicz EM. Development of a bioavailable µ opioid receptor (MOPr) agonist, δ opioid receptor (DOPr) antagonist peptide that evokes antinociception without development of acute tolerance. J. Med. Chem. 2014;57:3148–3153. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wells JL, Bartlett JL, Ananthan S, Bilsky EJ. In vivo pharmacological characterization of SoRI 9409, a nonpeptidic opioid mu-agonist/delta-antagonist that produces limited antinociceptive tolerance and attenuates morphine physical dependence. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001;297:597–605. - PubMed
-
- Dove LS, Lembo A, Randall CW, Fogel R, Andrae D, Davenport JM, McIntyre G, Almenoff JS, Covington PS. Eluxadoline benefits patients with irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea in a phase 2 study. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:329–338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Research Materials

