Dual Agonist Surrobody Simultaneously Activates Death Receptors DR4 and DR5 to Induce Cancer Cell Death
- PMID: 26516157
- PMCID: PMC4707094
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0400
Dual Agonist Surrobody Simultaneously Activates Death Receptors DR4 and DR5 to Induce Cancer Cell Death
Abstract
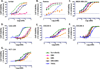
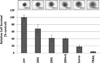
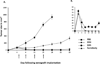
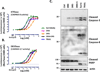
Death receptors of the TNF family are found on the surface of most cancer cells and their activation typically kills cancer cells through the stimulation of the extrinsic apoptotic pathway. The endogenous ligand for death receptors 4 and 5 (DR4 and DR5) is TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand, TRAIL (Apo2L). As most untransformed cells are not susceptible to TRAIL-induced apoptosis, death receptor activators have emerged as promising cancer therapeutic agents. One strategy to stimulate death receptors in cancer patients is to use soluble human recombinant TRAIL protein, but this agent has limitations of a short half-life and decoy receptor sequestration. Another strategy that attempted to evade decoy receptor sequestration and to provide improved pharmacokinetic properties was to generate DR4 or DR5 agonist antibodies. The resulting monoclonal agonist antibodies overcame the limitations of short half-life and avoided decoy receptor sequestration, but are limited by activating only one of the two death receptors. Here, we describe a DR4 and DR5 dual agonist produced using Surrobody technology that activates both DR4 and DR5 to induce apoptotic death of cancer cells in vitro and in vivo and also avoids decoy receptor sequestration. This fully human anti-DR4/DR5 Surrobody displays superior potency to DR4- and DR5-specific antibodies, even when combined with TRAIL-sensitizing proapoptotic agents. Moreover, cancer cells were less likely to acquire resistance to Surrobody than either anti-DR4 or anti-DR5 monospecific antibodies. Taken together, Surrobody shows promising preclinical proapoptotic activity against cancer cells, meriting further exploration of its potential as a novel cancer therapeutic agent.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pro-survival effects by NF-κB, Akt and ERK(1/2) and anti-apoptosis actions by Six1 disrupt apoptotic functions of TRAIL-Dr4/5 pathway in ovarian cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Dec;84:1078-1087. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.10.028. Epub 2016 Oct 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27780136
-
Prediction of proapoptotic anticancer therapeutic response in vivo based on cell death visualization and TRAIL death ligand-receptor interaction.Cancer Biol Ther. 2011 Aug 15;12(4):335-48. doi: 10.4161/cbt.12.4.17174. Epub 2011 Aug 15. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21785270
-
DR4 specific TRAIL variants are more efficacious than wild-type TRAIL in pancreatic cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2014;15(12):1658-66. doi: 10.4161/15384047.2014.972183. Cancer Biol Ther. 2014. PMID: 25482930 Free PMC article.
-
TRAIL receptor signalling and modulation: Are we on the right TRAIL?Cancer Treat Rev. 2009 May;35(3):280-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2008.11.006. Epub 2008 Dec 30. Cancer Treat Rev. 2009. PMID: 19117685 Review.
-
Modulation of death receptors by cancer therapeutic agents.Cancer Biol Ther. 2008 Feb;7(2):163-73. doi: 10.4161/cbt.7.2.5335. Epub 2007 Nov 21. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18059181 Review.
Cited by
-
Agonist antibody discovery: Experimental, computational, and rational engineering approaches.Drug Discov Today. 2022 Jan;27(1):31-48. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2021.09.008. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Drug Discov Today. 2022. PMID: 34571277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design and engineering of bispecific antibodies: insights and practical considerations.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jan 25;12:1352014. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1352014. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38333084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A functional genetic screen defines the AKT-induced senescence signaling network.Cell Death Differ. 2020 Feb;27(2):725-741. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0384-8. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Cell Death Differ. 2020. PMID: 31285545 Free PMC article.
-
Antibodies and Derivatives Targeting DR4 and DR5 for Cancer Therapy.Antibodies (Basel). 2017 Oct 25;6(4):16. doi: 10.3390/antib6040016. Antibodies (Basel). 2017. PMID: 31548531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The making of bispecific antibodies.MAbs. 2017 Feb/Mar;9(2):182-212. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2016.1268307. MAbs. 2017. PMID: 28071970 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Herbst RS, Eckhardt SG, Kurzrock R, Ebbinghaus S, O'Dwyer PJ, Gordon MS, et al. Phase I dose-escalation study of recombinant human Apo2L/TRAIL, a dual proapoptotic receptor agonist, in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:2839–2846. - PubMed
-
- Soria JC, Smit E, Khayat D, Besse B, Yang X, Hsu CP, et al. Phase 1b study of dulanermin (recombinant human Apo2L/TRAIL) in combination with paclitaxel, carboplatin, and bevacizumab in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1527–1533. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Davis JS, Wu X. Immunoglobulin Fc domain fusion to TRAIL significantly prolongs its plasma half-life and enhances its antitumor activity. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13:643–650. - PubMed
-
- Adams C, Totpal K, Lawrence D, Marsters S, Pitti R, Yee S, et al. Structural and functional analysis of the interaction between the agonistic monoclonal antibody Apomab and the proapoptotic receptor DR5. Cell death and differentiation. 2008;15:751–761. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

