Opposing effects of Apoe/Apoa1 double deletion on amyloid-β pathology and cognitive performance in APP mice
- PMID: 26510953
- PMCID: PMC4731410
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awv293
Opposing effects of Apoe/Apoa1 double deletion on amyloid-β pathology and cognitive performance in APP mice
Abstract
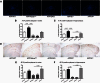
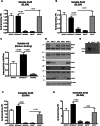
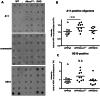
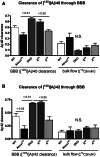
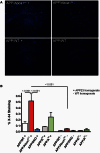
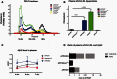
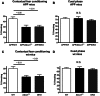
ATP binding cassette transporter A1 (encoded by ABCA1) regulates cholesterol efflux from cells to apolipoproteins A-I and E (ApoA-I and APOE; encoded by APOA1 and APOE, respectively) and the generation of high density lipoproteins. In Abca1 knockout mice (Abca1(ko)), high density lipoproteins and ApoA-I are virtually lacking, and total APOE and APOE-containing lipoproteins in brain substantially decreased. As the ε4 allele of APOE is the major genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer's disease, ABCA1 role as a modifier of APOE lipidation is of significance for this disease. Reportedly, Abca1 deficiency in mice expressing human APP accelerates amyloid deposition and behaviour deficits. We used APP/PS1dE9 mice crossed to Apoe and Apoa1 knockout mice to generate Apoe/Apoa1 double-knockout mice. We hypothesized that Apoe/Apoa1 double-knockout mice would mimic the phenotype of APP/Abca1(ko) mice in regards to amyloid plaques and cognitive deficits. Amyloid pathology, peripheral lipoprotein metabolism, cognitive deficits and dendritic morphology of Apoe/Apoa1 double-knockout mice were compared to APP/Abca1(ko), APP/PS1dE9, and single Apoa1 and Apoe knockouts. Contrary to our prediction, the results demonstrate that double deletion of Apoe and Apoa1 ameliorated the amyloid pathology, including amyloid plaques and soluble amyloid. In double knockout mice we show that (125)I-amyloid-β microinjected into the central nervous system cleared at a rate twice faster compared to Abca1 knockout mice. We tested the effect of Apoe, Apoa1 or Abca1 deficiency on spreading of exogenous amyloid-β seeds injected into the brain of young pre-depositing APP mice. The results show that lack of Abca1 augments dissemination of exogenous amyloid significantly more than the lack of Apoe. In the periphery, Apoe/Apoa1 double-knockout mice exhibited substantial atherosclerosis and very high levels of low density lipoproteins compared to APP/PS1dE9 and APP/Abca1(ko). Plasma level of amyloid-β42 measured at several time points for each mouse was significantly higher in Apoe/Apoa1 double-knockout then in APP/Abca1(ko) mice. This result demonstrates that mice with the lowest level of plasma lipoproteins, APP/Abca1(ko), have the lowest level of peripheral amyloid-β. Unexpectedly, and independent of amyloid pathology, the deletion of both apolipoproteins worsened behaviour deficits of double knockout mice and their performance was undistinguishable from those of Abca1 knockout mice. Finally we observed that the dendritic complexity in the CA1 region of hippocampus but not in CA2 is significantly impaired by Apoe/Apoa1 double deletion as well as by lack of ABCA1.
In conclusion: (i) plasma lipoproteins may affect amyloid-β clearance from the brain by the 'peripheral sink' mechanism; and (ii) deficiency of brain APOE-containing lipoproteins is of significance for dendritic complexity and cognition.
Keywords: ABCA1; APOA1; APOE; Alzheimer’s disease; behaviour.
© The Author (2015). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Comment in
-
Lipidated APOE has effects on cognitive function that are independent of amyloid-β pathology.Brain. 2015 Dec;138(Pt 12):3470-2. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv300. Brain. 2015. PMID: 26598491 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
ABCA1 Deficiency Affects Basal Cognitive Deficits and Dendritic Density in Mice.J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;56(3):1075-1085. doi: 10.3233/JAD-161056. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 28106559 Free PMC article.
-
Abca1 deficiency affects Alzheimer's disease-like phenotype in human ApoE4 but not in ApoE3-targeted replacement mice.J Neurosci. 2012 Sep 19;32(38):13125-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1937-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22993429 Free PMC article.
-
ABCA1 is Necessary for Bexarotene-Mediated Clearance of Soluble Amyloid Beta from the Hippocampus of APP/PS1 Mice.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016 Mar;11(1):61-72. doi: 10.1007/s11481-015-9627-8. Epub 2015 Jul 15. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26175148 Free PMC article.
-
ATP-binding cassette transporter A1: from metabolism to neurodegeneration.Neurobiol Dis. 2014 Dec;72 Pt A:13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.05.007. Epub 2014 May 17. Neurobiol Dis. 2014. PMID: 24844148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of A beta deposition in APP transgenic mice by an apolipoprotein E null background.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;920:171-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06919.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000. PMID: 11193147 Review.
Cited by
-
Revelation of Pivotal Genes Pertinent to Alzheimer's Pathogenesis: A Methodical Evaluation of 32 GEO Datasets.J Mol Neurosci. 2022 Feb;72(2):303-322. doi: 10.1007/s12031-021-01919-2. Epub 2021 Oct 19. J Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 34668150 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal In Vitro Raman Spectroscopy for Monitoring Replication Kinetics of Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in Glial Cells.ACS Omega. 2020 Nov 4;5(45):29547-29560. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c04525. eCollection 2020 Nov 17. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 33225186 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to gain novel Alzheimer's disease diagnostics and therapeutics using modulators of ABCA transporters.Free Neuropathol. 2021;2:2-33. doi: 10.17879/freeneuropathology-2021-3528. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Free Neuropathol. 2021. PMID: 34977908 Free PMC article.
-
ABCA1 Deficiency Affects Basal Cognitive Deficits and Dendritic Density in Mice.J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;56(3):1075-1085. doi: 10.3233/JAD-161056. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 28106559 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting innate immunity for neurodegenerative disorders of the central nervous system.J Neurochem. 2016 Sep;138(5):653-93. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13667. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 27248001 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

