Copy number variations in the genome of the Qatari population
- PMID: 26490036
- PMCID: PMC4618522
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-015-1991-5
Copy number variations in the genome of the Qatari population
Abstract
Background: The populations of the Arabian Peninsula remain the least represented in public genetic databases, both in terms of single nucleotide variants and of larger genomic mutations. We present the first high-resolution copy number variation (CNV) map for a Gulf Arab population, using a hybrid approach that integrates array genotyping intensity data and next-generation sequencing reads to call CNVs in the Qatari population.
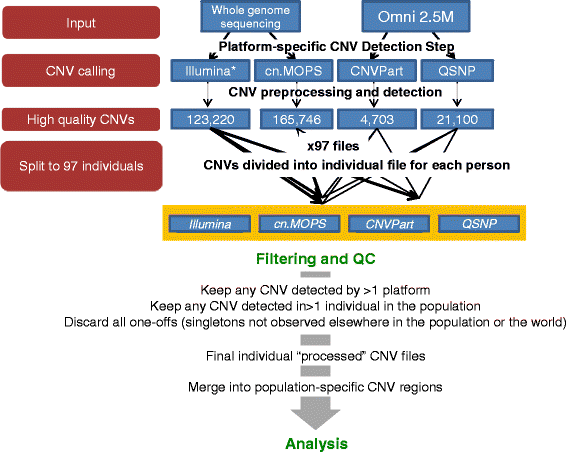
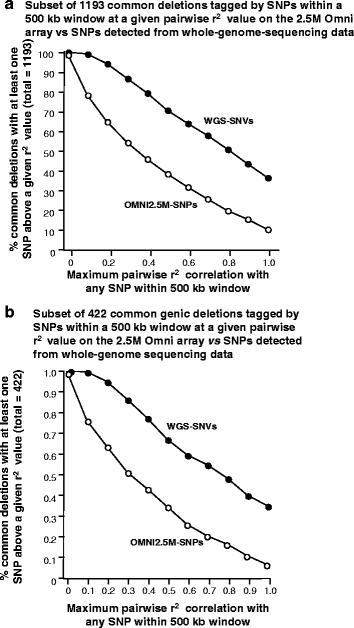
Methods: CNVs were detected in 97 unrelated Qatari individuals by running two calling algorithms on each of two primary datasets: high-resolution genotyping (Illumina Omni 2.5M) and high depth whole-genome sequencing (Illumina PE 100bp). The four call-sets were integrated to identify high confidence CNV regions, which were subsequently annotated for putative functional effect and compared to public databases of CNVs in other populations. The availability of genome sequence was leveraged to identify tagging SNPs in high LD with common deletions in this population, enabling their imputation from genotyping experiments in the future.
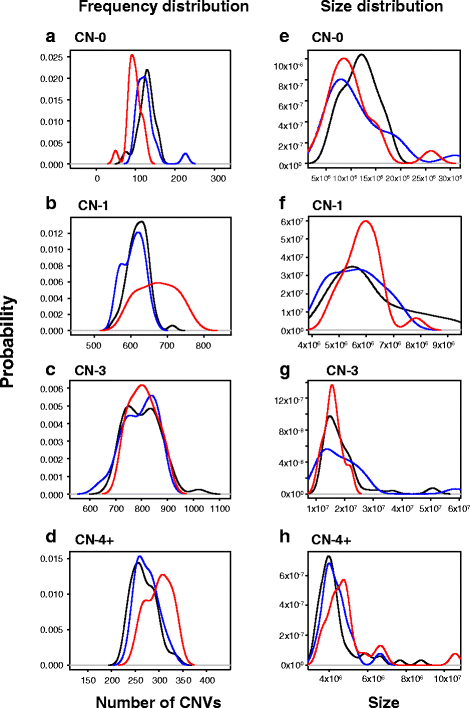
Results: Genotyping intensities and genome sequencing data from 97 Qataris were analyzed with four different algorithms and integrated to discover 16,660 high confidence CNV regions (CNVRs) in the total population, affecting ~28 Mb in the median Qatari genome. Up to 40% of all CNVs affected genes, including novel CNVs affecting Mendelian disease genes, segregating at different frequencies in the 3 major Qatari subpopulations, including those with Bedouin, Persian/South Asian, and African ancestry. Consistent with high consanguinity levels in the Bedouin subpopulation, we found an increased burden for homozygous deletions in this group. In comparison to known CNVs in the comprehensive Database of Genomic Variants, we found that 5% of all CNVRs in Qataris were completely novel, with an enrichment of CNVs affecting several known chromosomal disorder loci and genes known to regulate sugar metabolism and type 2 diabetes in the Qatari cohort. Finally, we leveraged the availability of genome sequence to find suitable tagging SNPs for common deletions in this population.
Conclusion: We combine four independently generated datasets from 97 individuals to study CNVs for the first time at high-resolution in a Gulf Arab population.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide copy number variation (CNV) detection in Nelore cattle reveals highly frequent variants in genome regions harboring QTLs affecting production traits.BMC Genomics. 2016 Jun 13;17:454. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2752-9. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27297173 Free PMC article.
-
Copy number variation in human genomes from three major ethno-linguistic groups in Africa.BMC Genomics. 2020 Apr 10;21(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6669-y. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32272904 Free PMC article.
-
Copy number variants in the sheep genome detected using multiple approaches.BMC Genomics. 2016 Jun 8;17:441. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2754-7. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27277319 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of germline copy number variation in susceptibility of human diseases.J Genet Genomics. 2018 Jan 20;45(1):3-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2018.01.001. Epub 2018 Jan 5. J Genet Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29396143 Review.
-
Progress in the detection of human genome structural variations.Sci China C Life Sci. 2009 Jun;52(6):560-7. doi: 10.1007/s11427-009-0078-4. Epub 2009 Jun 26. Sci China C Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19557334 Review.
Cited by
-
Thousands of Qatari genomes inform human migration history and improve imputation of Arab haplotypes.Nat Commun. 2021 Oct 12;12(1):5929. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25287-y. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34642339 Free PMC article.
-
panelcn.MOPS: Copy-number detection in targeted NGS panel data for clinical diagnostics.Hum Mutat. 2017 Jul;38(7):889-897. doi: 10.1002/humu.23237. Epub 2017 May 16. Hum Mutat. 2017. PMID: 28449315 Free PMC article.
-
Copy Number Variations in Tilapia Genomes.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2017 Feb;19(1):11-21. doi: 10.1007/s10126-017-9733-0. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2017. PMID: 28168542
-
A map of copy number variations in the Tunisian population: a valuable tool for medical genomics in North Africa.NPJ Genom Med. 2021 Jan 8;6(1):3. doi: 10.1038/s41525-020-00166-5. NPJ Genom Med. 2021. PMID: 33420067 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation spectrum of congenital heart disease in a consanguineous Turkish population.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2022 Jun;10(6):e1944. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1944. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2022. PMID: 35481623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rodriguez-Flores JL, Fuller J, Hackett NR, Salit J, Malek JA, Al-Dous E, Chouchane L, Zirie M, Jayoussi A, Mahmoud MA, et al. Exome sequencing of only seven qataris identifies potentially deleterious variants in the qatari population. PLoS One. 2012;7:e47614. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047614. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez-Flores JL, Fakhro K, Hackett NR, Salit J, Fuller J, Gosto-Perez F, Gharbiah M, Malek JA, Zirie M, Jayyousi A, et al. Exome sequencing identifies potential risk variants for Mendelian disorders at high prevalence in Qatar. Hum Mutat. 2014;35:105–16. doi: 10.1002/humu.22460. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

