Development of a Recombinant Xenogeneic Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Protein Vaccine To Protect Mice from Experimental Colitis
- PMID: 26466602
- PMCID: PMC4658592
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00331-15
Development of a Recombinant Xenogeneic Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Protein Vaccine To Protect Mice from Experimental Colitis
Abstract
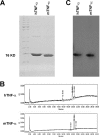
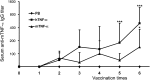
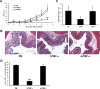
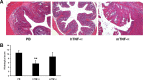
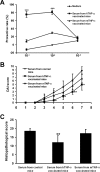
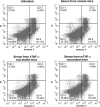
Previous studies have highlighted the efficacy of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) inhibitors, including monoclonal antibodies and soluble receptors, in the treatment and management of intestinal bowel disease (IBD). However, because of the immunogenicity of xenogeneic TNF-α inhibitors, antidrug antibodies (ADAs) can be triggered after repeated administration. An alternative way to target TNF-α is active immunization to elicit the production of high titers of neutralizing antibodies. In this study, we prepared a xenogeneic TNF-α protein vaccine and studied the protective effects in experimental colitis models. The xenogeneic TNF-α protein vaccine could overcome self-tolerance and induce TNF-α-specific neutralizing antibody. Moreover, the xenogeneic TNF-α protein vaccine could protect mice from acute and chronic colitis induced by dextran sodium sulfate (DSS). One possible explanation for this protective effect is the production of TNF-α-specific neutralizing antibody, which absorbed the biological activity of mouse TNF-α (mTNF-α) and failed to induce T lymphocyte apoptosis. In summary, use of the xenogeneic TNF-α protein vaccine may be a potent therapeutic strategy for IBD.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chitosan oligosaccharide as potential therapy of inflammatory bowel disease: therapeutic efficacy and possible mechanisms of action.Pharmacol Res. 2012 Jul;66(1):66-79. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2012.03.013. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Pharmacol Res. 2012. PMID: 22475725
-
Antibodies against tumor necrosis factor (TNF) induce T-cell apoptosis in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases via TNF receptor 2 and intestinal CD14⁺ macrophages.Gastroenterology. 2011 Dec;141(6):2026-38. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.08.032. Epub 2011 Aug 27. Gastroenterology. 2011. PMID: 21875498
-
Prepared and screened a modified TNF-alpha molecule as TNF-alpha autovaccine to treat LPS induced endotoxic shock and TNF-alpha induced cachexia in mouse.Cell Immunol. 2007 Apr;246(2):55-64. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2007.05.005. Epub 2007 Jun 25. Cell Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17592730
-
Predominant pathogenic role of tumor necrosis factor in experimental colitis in mice.Eur J Immunol. 1997 Jul;27(7):1743-50. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830270722. Eur J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9247586
-
Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor and nitrosative/oxidative stresses by Ziziphora clinopoides (Kahlioti); a molecular mechanism of protection against dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice.Toxicol Mech Methods. 2009 Feb;19(2):183-9. doi: 10.1080/15376510701533996. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2009. PMID: 19778264
Cited by
-
Aconitine induces cardiomyocyte damage by mitigating BNIP3-dependent mitophagy and the TNFα-NLRP3 signalling axis.Cell Prolif. 2020 Jan;53(1):e12701. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12701. Epub 2019 Oct 27. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 31657084 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

