Top Down Proteomics Reveals Mature Proteoforms Expressed in Subcellular Fractions of the Echinococcus granulosus Preadult Stage
- PMID: 26465659
- PMCID: PMC4638118
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00642
Top Down Proteomics Reveals Mature Proteoforms Expressed in Subcellular Fractions of the Echinococcus granulosus Preadult Stage
Abstract
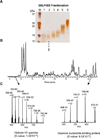
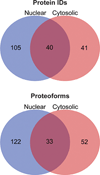
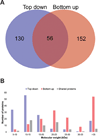
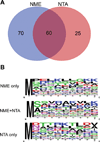
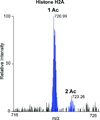
Echinococcus granulosus is the causative agent of cystic hydatid disease, a neglected zoonosis responsible for high morbidity and mortality. Several molecular mechanisms underlying parasite biology remain poorly understood. Here, E. granulosus subcellular fractions were analyzed by top down and bottom up proteomics for protein identification and characterization of co-translational and post-translational modifications (CTMs and PTMs, respectively). Nuclear and cytosolic extracts of E. granulosus protoscoleces were fractionated by 10% GELFrEE and proteins under 30 kDa were analyzed by LC-MS/MS. By top down analysis, 186 proteins and 207 proteoforms were identified, of which 122 and 52 proteoforms were exclusively detected in nuclear and cytosolic fractions, respectively. CTMs were evident as 71% of the proteoforms had methionine excised and 47% were N-terminal acetylated. In addition, in silico internal acetylation prediction coupled with top down MS allowed the characterization of 9 proteins differentially acetylated, including histones. Bottom up analysis increased the overall number of identified proteins in nuclear and cytosolic fractions to 154 and 112, respectively. Overall, our results provided the first description of the low mass proteome of E. granulosus subcellular fractions and highlighted proteoforms with CTMs and PTMS whose characterization may lead to another level of understanding about molecular mechanisms controlling parasitic flatworm biology.
Keywords: hydatid disease; low mass proteome; post-translational modifications; subcellular fractions; top down proteomics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proteomics analysis of Echinococcus granulosus protoscolex stage.Vet Parasitol. 2016 Mar 15;218:43-5. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2015.12.026. Epub 2016 Jan 3. Vet Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 26872926
-
Excretory/secretory products in the Echinococcus granulosus metacestode: is the intermediate host complacent with infection caused by the larval form of the parasite?Int J Parasitol. 2016 Dec;46(13-14):843-856. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2016.07.009. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Int J Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 27771257
-
Excretory/secretory products from in vitro-cultured Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2012 May;183(1):15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2012.01.001. Epub 2012 Jan 13. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2012. PMID: 22261090
-
Profiling proteoforms: promising follow-up of proteomics for biomarker discovery.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2014 Feb;11(1):121-9. doi: 10.1586/14789450.2014.878652. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24437377 Review.
-
Recent advances in characterization of Echinococcus antigen B.Parasitol Int. 2006;55 Suppl:S57-62. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2005.11.008. Epub 2005 Dec 19. Parasitol Int. 2006. PMID: 16360336 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of the B-Cell Epitopes of Echinococcus granulosus Histones H4 and H2A Recognized by Sera From Patients With Liver Cysts.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jun 13;12:901994. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.901994. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35770070 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Approaches to Study Cysteine Oxidation: Applications in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Jun 9;14:678837. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.678837. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34177463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Top-Down Proteomics and Farm Animal and Aquatic Sciences.Proteomes. 2016 Dec 21;4(4):38. doi: 10.3390/proteomes4040038. Proteomes. 2016. PMID: 28248248 Free PMC article.
-
Terminomics Methodologies and the Completeness of Reductive Dimethylation: A Meta-Analysis of Publicly Available Datasets.Proteomes. 2019 Mar 29;7(2):11. doi: 10.3390/proteomes7020011. Proteomes. 2019. PMID: 30934878 Free PMC article.
-
Multidimensional Separations in Top-Down Proteomics.Anal Sci Adv. 2023 Jul;4(5-6):181-203. doi: 10.1002/ansa.202300016. Epub 2023 May 29. Anal Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 38188188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moro P, Schantz PM. Echinococcosis: a review. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2009;13:125–133. - PubMed
-
- Carmena D, Cardona GA. Echinococcosis in wild carnivorous species: epidemiology, genotypic diversity, and implications for veterinary public health. Vet. Parasitol. 2014;202:69–94. - PubMed
-
- Thompson RC, Lymbery AJ. Let’s not forget the thinkers. Trends Parasitol. 2013;29:581–584. - PubMed
-
- Tsai IJ, Zarowiecki M, Holroyd N, Garciarrubio A, Sanchez-Flores A, Brooks KL, Tracey A, Bobes RJ, Fragoso G, Sciutto E, Aslett M, Beasley H, Bennett HM, Cai J, Camicia F, Clark R, Cucher M, De Silva N, Day TA, Deplazes P, Estrada K, Fernández C, Holland PW, Hou J, Hu S, Huckvale T, Hung SS, Kamenetzky L, Keane JA, Kiss F, Koziol U, Lambert O, Liu K, Luo X, Luo Y, Macchiaroli N, Nichol S, Paps J, Parkinson J, Pouchkina-Stantcheva N, Riddiford N, Rosenzvit M, Salinas G, Wasmuth JD, Zamanian M, Zheng Y, Cai X, Soberón X, Olson PD, Laclette JP, Brehm K, Berriman M, Consortium TsG. The genomes of four tapeworm species reveal adaptations to parasitism. Nature. 2013;496:57–63. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

