Molecular dynamics simulation of the interactions between EHD1 EH domain and multiple peptides
- PMID: 26465136
- PMCID: PMC4609540
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B1500106
Molecular dynamics simulation of the interactions between EHD1 EH domain and multiple peptides
Abstract
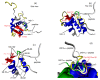
Objective: To provide essential information for peptide inhibitor design, the interactions of Eps15 homology domain of Eps15 homology domain-containing protein 1 (EHD1 EH domain) with three peptides containing NPF (asparagine-proline-phenylalanine), DPF (aspartic acid-proline-phenylalanine), and GPF (glycine-proline-phenylalanine) motifs were deciphered at the atomic level. The binding affinities and the underlying structure basis were investigated.
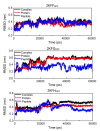
Methods: Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were performed on EHD1 EH domain/peptide complexes for 60 ns using the GROMACS package. The binding free energies were calculated and decomposed by molecular mechanics/generalized Born surface area (MM/GBSA) method using the AMBER package. The alanine scanning was performed to evaluate the binding hot spot residues using FoldX software.
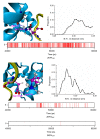
Results: The different binding affinities for the three peptides were affected dominantly by van der Waals interactions. Intermolecular hydrogen bonds provide the structural basis of contributions of van der Waals interactions of the flanking residues to the binding.
Conclusions: van der Waals interactions should be the main consideration when we design peptide inhibitors of EHD1 EH domain with high affinities. The ability to form intermolecular hydrogen bonds with protein residues can be used as the factor for choosing the flanking residues.
Keywords: Binding affinity; EHD1 EH domain; Inhibitor design; Molecular dynamics simulation; Peptide.
Conflict of interest statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural insight into the interaction of proteins containing NPF, DPF, and GPF motifs with the C-terminal EH-domain of EHD1.Protein Sci. 2009 Dec;18(12):2471-9. doi: 10.1002/pro.258. Protein Sci. 2009. PMID: 19798736 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism for the selective interaction of C-terminal Eps15 homology domain proteins with specific Asn-Pro-Phe-containing partners.J Biol Chem. 2010 Mar 19;285(12):8687-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.045666. Epub 2010 Jan 27. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20106972 Free PMC article.
-
Charge effects in the selection of NPF motifs by the EH domain of EHD1.Biochemistry. 2010 Apr 27;49(16):3381-92. doi: 10.1021/bi100065r. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20329706 Free PMC article.
-
EHD1 and Eps15 interact with phosphatidylinositols via their Eps15 homology domains.J Biol Chem. 2007 Jun 1;282(22):16612-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M609493200. Epub 2007 Apr 5. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17412695
-
Recent Advances in Computational Models for the Study of Protein-Peptide Interactions.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2016;105:27-57. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2016.06.002. Epub 2016 Aug 3. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2016. PMID: 27567483 Review.
Cited by
-
Simulating Peptide Monolayer Formation: GnRH-I on Silica.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 24;22(11):5523. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115523. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34073815 Free PMC article.
-
Atomistic simulations reveal impacts of missense mutations on the structure and function of SynGAP1.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Sep 23;25(6):bbae458. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae458. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39311700 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Interaction Mechanism of the Compounds From Cladophora sp to Recognize Prospective Larvicidal and Bactericidal Activities: In vitro and In Silico Approaches.Mol Biotechnol. 2023 Oct 16. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00902-z. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37843757
-
Unraveling modulation effects on albumin synthesis and inflammation by Striatin, a bioactive protein fraction isolated from Channa striata: In silico proteomics and in vitro approaches.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 24;10(19):e38386. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38386. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39398063 Free PMC article.
-
Designing a polyvalent vaccine targeting multiple strains of varicella zoster virus using integrated bioinformatics approaches.Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 17;14:1291868. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1291868. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38075876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berendsen HJC, Postma JPM, van Gunsteren WF, et al. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J Chem Phys. 1984;81(8):3684–3690. doi: 10.1063/1.448118. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

