Small ubiquitin-related modifier 2/3 interacts with p65 and stabilizes it in the cytoplasm in HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 26458400
- PMCID: PMC4603762
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-015-1665-3
Small ubiquitin-related modifier 2/3 interacts with p65 and stabilizes it in the cytoplasm in HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: SUMOylation, an important post-translational modification, associates with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). p65, one of the most important subunits of NF-κB, is a key regulator in the development of HCC and has been reported to be SUMOylated by exogenous small ubiquitin-related modifier 3 (SUMO3) in HEK 293T cells. However, the relationship between p65 and SUMO2/3 in HCC remains unknown. This study was to investigate the interaction between p65 and SUMO2/3 and explore the potential roles involved in HCC.
Methods: The expressions of p65 and SUMO2/3 in the liver tissues were detected by using immunohistochemistry. We performed double-labeled immunofluorescence and co-immunoprecipitation assay to verify the interaction between p65 and SUMO2/3. The extraction of nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins was performed, and the subcellular localization of p65 was detected. The proliferation and migration of hepatoma cells were observed using MTT, colony formation, and transwell assays.
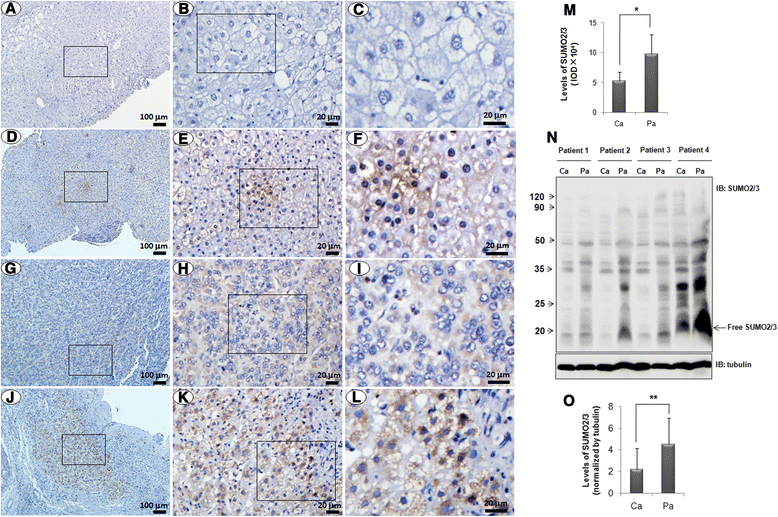
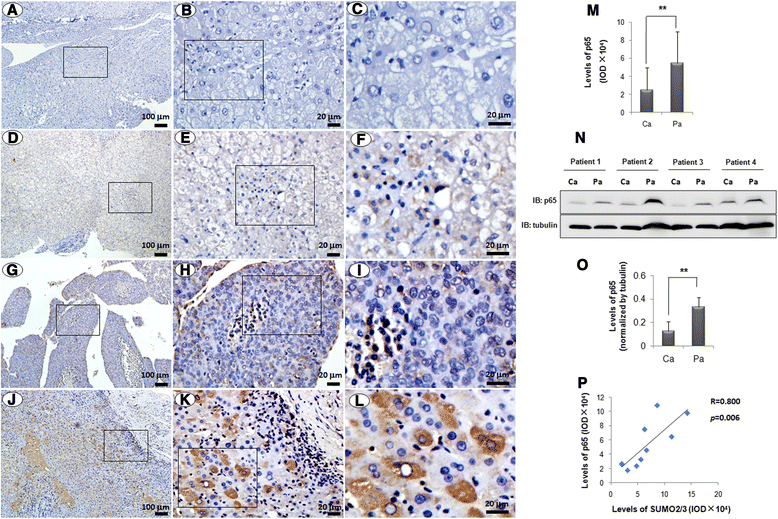
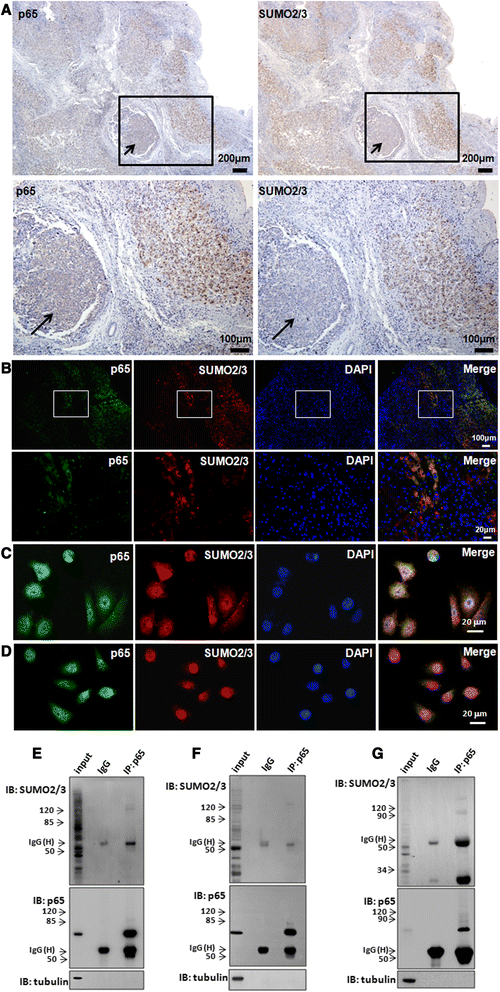
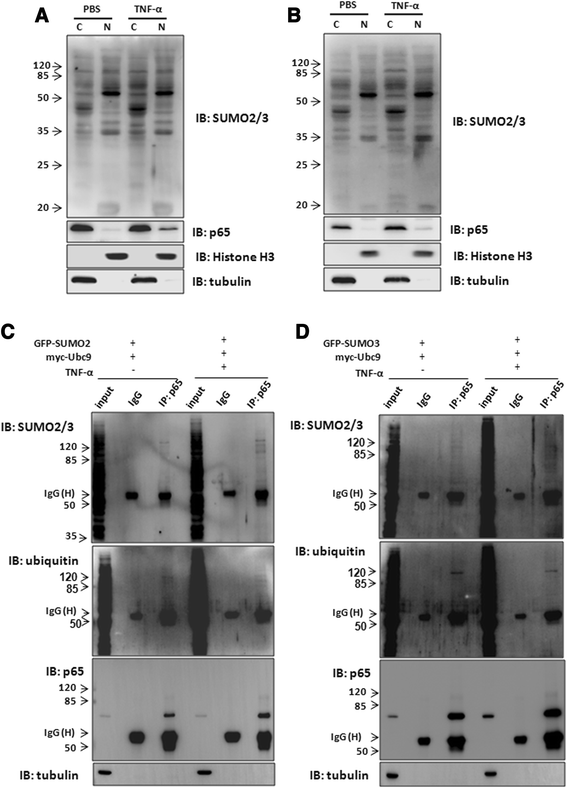
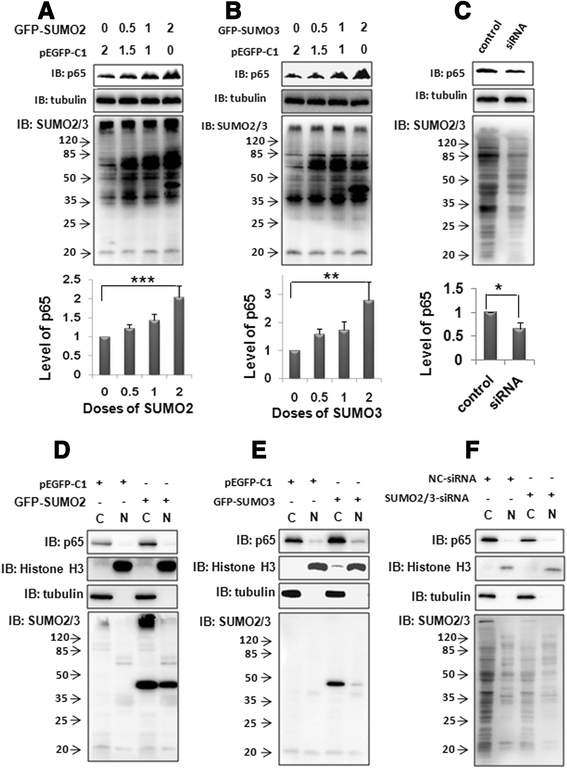
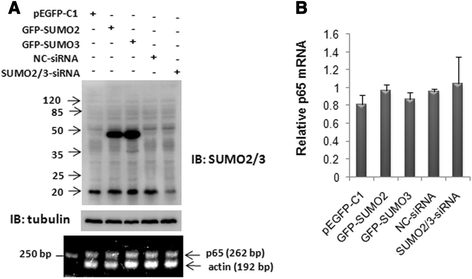
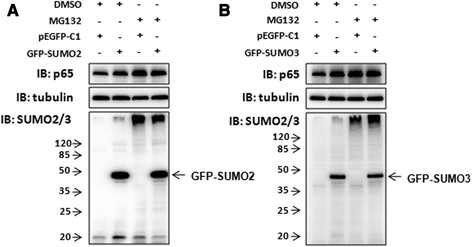
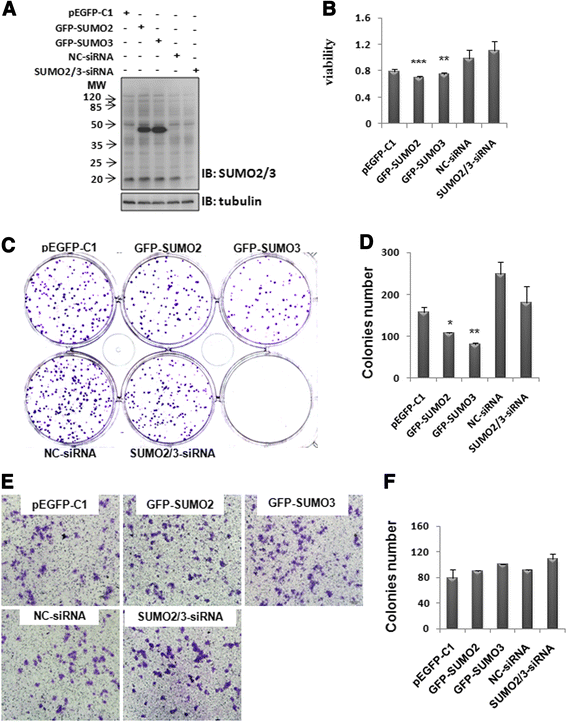
Results: We found a strong SUMO2/3-positive immunoreactivity in the cytoplasm in the non-tumor tissues of HCC. However, SUMO2/3 level was down regulated in the tumor tissues as compared with the adjacent non-tumor tissues. In accordance with this finding, p65 was up regulated in the adjacent non-tumor tissues and almost localized in the cytoplasm. There was a close correlation between SUMO2/3 and p65 expressions in the liver tissues (R = 0.800, p = 0.006). The interaction between p65 and SUMO2/3 was verified by co-immunoprecipitation and double-labeled immunofluorescent assays. TNF-α (10 ng/ml) treatment for 30 min not only up regulated the cytoplasmic conjugated SUMO2/3, but also enhanced SUMO2/3-p65 interaction. Furthermore, we found that SUMO2/3 up regulated the cytoplasmic p65 protein level in a dose-dependent manner, but not affected its mRNA level. The increase of p65 protein by SUMO2/3 was abolished by MG132 treatment, a reversible inhibitor of proteasome. Meanwhile, TNF-α-induced increase of SUMO2/3-conjugated p65 was along with the reduction of the ubiquitin-conjugated p65. The further study showed that SUMO2/3 over-expression decreased the proliferative ability of hepatoma cells, but did not affect the migration.
Conclusion: SUMO2/3-p65 interaction may be a novel mechanism involved in the transformation from chronic hepatitis B to HCC via stabilizing cytoplasmic p65, which might shed light on understanding the tumorigenesis and development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 is involved in hepatocellular carcinoma progression via mediating p65 nuclear translocation.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 19;7(16):22206-18. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8066. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26993772 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation of HSP27 by small ubiquitin-like modifier 2/3 promotes proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2017 Aug 3;18(8):552-559. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2017.1345382. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Cancer Biol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28665748 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of SUMO and NF-κB genes in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma patients: An observational study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jun 28;103(26):e38737. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038737. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38941371 Free PMC article.
-
Sumoylation in liver disease.Clin Chim Acta. 2020 Nov;510:347-353. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.07.044. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Clin Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32710938 Review.
-
Abnormal protein SUMOylation in liver disease: novel target for therapy.J Mol Med (Berl). 2024 Jun;102(6):719-731. doi: 10.1007/s00109-024-02440-w. Epub 2024 Apr 3. J Mol Med (Berl). 2024. PMID: 38565749 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Protein SUMOylation in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Potential Target of New Drug Discovery and Development.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 14;13(22):5700. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225700. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34830854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 is involved in hepatocellular carcinoma progression via mediating p65 nuclear translocation.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 19;7(16):22206-18. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8066. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26993772 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation of HSP27 by small ubiquitin-like modifier 2/3 promotes proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2017 Aug 3;18(8):552-559. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2017.1345382. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Cancer Biol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28665748 Free PMC article.
-
SENP1 promotes hypoxia-induced cancer stemness by HIF-1α deSUMOylation and SENP1/HIF-1α positive feedback loop.Gut. 2017 Dec;66(12):2149-2159. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313264. Epub 2017 Mar 3. Gut. 2017. PMID: 28258134 Free PMC article.
-
Sorafenib inhibits caspase-1 expression through suppressing TLR4/stat3/SUMO1 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Biol Ther. 2018;19(11):1057-1064. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1480280. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018. PMID: 30277836 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guo D, Li M, Zhang Y, Yang P, Eckenrode S, Hopkins D, Zheng W, Purohit S, Podolsky RH, Muir A, Wang J, Dong Z, Brusko T, Atkinson M, Pozzilli P, Zeidler A, Raffel LJ, Jacob CO, Park Y, Serrano-Rios M, Larrad MT, Zhang Z, Garchon HJ, Bach JF, Rotter JI, She JX, Wang CY. A functional variant of SUMO4, a new I kappa B alpha modifier, is associated with type 1 diabetes. Nat Genet. 2004;36:837–841. doi: 10.1038/ng1391. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

