Cooperative and independent functions of FGF and Wnt signaling during early inner ear development
- PMID: 26443994
- PMCID: PMC4594887
- DOI: 10.1186/s12861-015-0083-8
Cooperative and independent functions of FGF and Wnt signaling during early inner ear development
Abstract
Background: In multiple vertebrate organisms, including chick, Xenopus, and zebrafish, Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) and Wnt signaling cooperate during formation of the otic placode. However, in the mouse, although FGF signaling induces Wnt8a expression during induction of the otic placode, it is unclear whether these two signaling pathways functionally cooperate. Sprouty (Spry) genes encode intracellular antagonists of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling, including FGF signaling. We previously demonstrated that the Sprouty1 (Spry1) and Sprouty2 (Spry2) genes antagonize FGF signaling during induction of the otic placode. Here, we investigate cross talk between FGF/SPRY and Wnt signaling during otic placode induction and assess whether these two signaling pathways functionally cooperate during early inner ear development in the mouse.
Methods: Embryos were generated carrying combinations of a Spry1 null allele, Spry2 null allele, β-catenin null allele, or a Wnt reporter transgene. Otic phenotypes were assessed by in situ hybridization, semi-quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR, immunohistochemistry, and morphometric analysis of sectioned tissue.
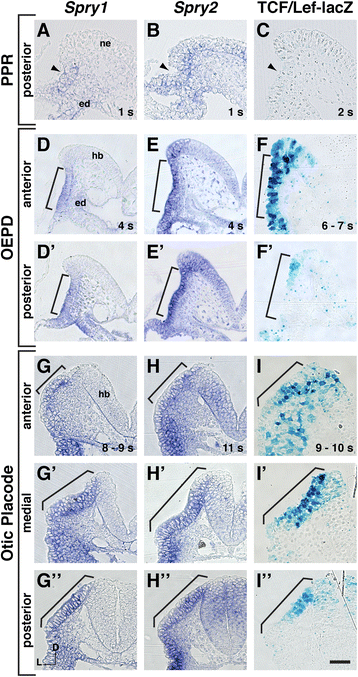
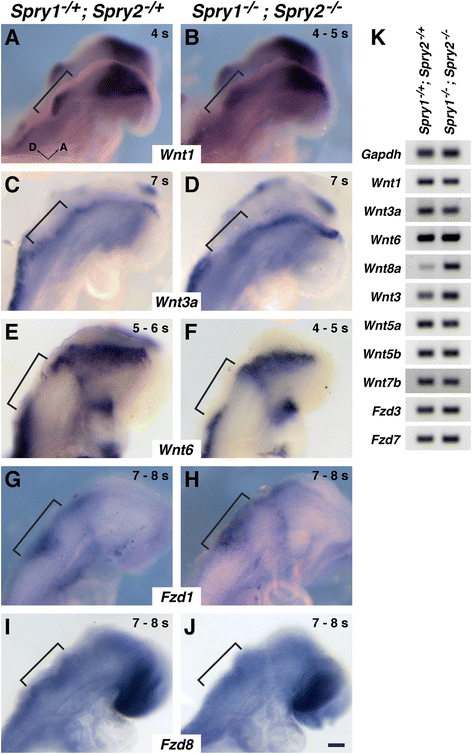
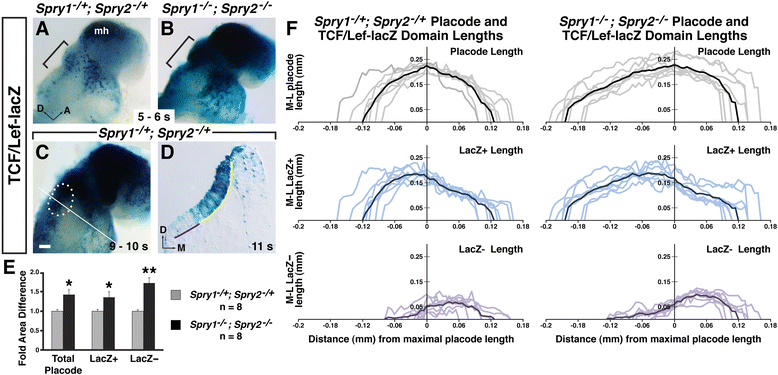
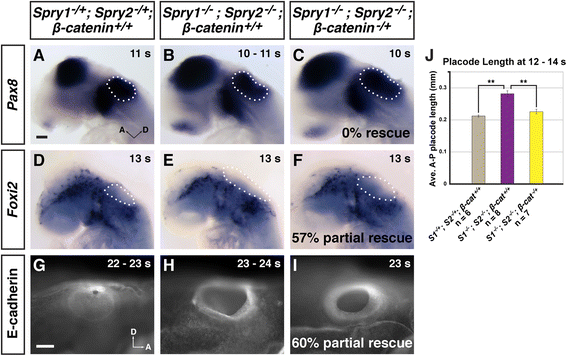
Results: Comparison of Spry1, Spry2, and Wnt reporter expression in pre-otic and otic placode cells indicates that FGF signaling precedes and is active in more cells than Wnt signaling. We provide in vivo evidence that FGF signaling activates the Wnt signaling pathway upstream of TCF/Lef transcriptional activation. FGF regulation of Wnt signaling is functional, since early inner ear defects in Spry1 and Spry2 compound mutant embryos can be genetically rescued by reducing the activity of the Wnt signaling pathway. Interestingly, we find that although the entire otic placode increases in size in Spry1 and Spry2 compound mutant embryos, the size of the Wnt-reporter-positive domain does not increase to the same extent as the Wnt-reporter-negative domain.
Conclusions: This study provides genetic evidence that FGF and Wnt signaling cooperate during early inner ear development in the mouse. Furthermore, our data suggest that although specification of the otic placode may be globally regulated by FGF signaling, otic specification of cells in which both FGF and Wnt signaling are active may be more tightly regulated.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sprouty1 and Sprouty2 limit both the size of the otic placode and hindbrain Wnt8a by antagonizing FGF signaling.Dev Biol. 2011 May 1;353(1):94-104. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.02.022. Epub 2011 Feb 26. Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21362415 Free PMC article.
-
Compensatory regulation of the size of the inner ear in response to excess induction of otic progenitors by fibroblast growth factor signaling.Dev Dyn. 2014 Oct;243(10):1317-27. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.24148. Epub 2014 Jun 12. Dev Dyn. 2014. PMID: 24847848 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Wnt8a during formation and patterning of the mouse inner ear.Mech Dev. 2013 Feb;130(2-3):160-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2012.09.009. Epub 2012 Oct 4. Mech Dev. 2013. PMID: 23041177
-
Expression and functions of FGF ligands during early otic development.Int J Dev Biol. 2007;51(6-7):473-81. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.072334ts. Int J Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17891710 Review.
-
The first steps towards hearing: mechanisms of otic placode induction.Int J Dev Biol. 2007;51(6-7):463-72. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.072320to. Int J Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17891709 Review.
Cited by
-
Temporal and regulatory dynamics of the inner ear transcriptome during development in mice.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 7;12(1):21196. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-25808-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36476755 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Wnt Signaling Enhances Inner Ear Organoid Development in 3D Culture.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 8;11(9):e0162508. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162508. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27607106 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-194 Regulates the Development and Differentiation of Sensory Patches and Statoacoustic Ganglion of Inner Ear by Fgf4.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Mar 23;24:1712-1723. doi: 10.12659/msm.906277. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 29570699 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms governing development of the hindbrain choroid plexus and auditory projection: A validation of the seminal observations of Wilhelm His.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022 Oct 3;13:306-313. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2022.09.011. eCollection 2022 Dec. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36247525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A gene network regulated by FGF signalling during ear development.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 21;7(1):6162. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05472-0. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28733657 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parr BA, Shea MJ, Vassileva G, McMahon AP. Mouse Wnt genes exhibit discrete domains of expression in the early embryonic CNS and limb buds. Development. 1993;119:247–61. - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi TP, Bradley A, McMahon AP, Jones S. A Wnt5a pathway underlies outgrowth of multiple structures in the vertebrate embryo. Development. 1999;126:1211–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

