LINE-1 activity as molecular basis for genomic instability associated with light exposure at night
- PMID: 26442182
- PMCID: PMC4588535
- DOI: 10.1080/2159256X.2015.1037416
LINE-1 activity as molecular basis for genomic instability associated with light exposure at night
Abstract
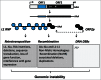
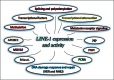
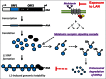
The original hypothesis that exposure to light at night increases risk of breast cancer via suppression of nocturnal melatonin production was proposed over 2 decades ago. In 2007, shift work that involves circadian disruption has been recognized by the World Health Organization as a probable human carcinogen. Our discovery of melatonin-dependent regulation of LINE-1 retrotransposon expression and mobilization is the latest addition to the list of cellular genes and processes that are affected by light exposure at night. This finding establishes an unexpected health relevant connection between this endogenous DNA damaging agent and environmental light exposure. It also offers an appealing hypothesis pertaining to the origin of genomic instability in the genomes of individuals with light at night- or age-associated disruption of melatonin signaling.
Keywords: DNA damage; LINE-1; aging; cancer; genomic instability; light exposure at night; melatonin; melatonin receptor; retroelements; shift-work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of L1 expression and retrotransposition by melatonin and its receptor: implications for cancer risk associated with light exposure at night.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jul;42(12):7694-707. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku503. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24914052 Free PMC article.
-
Association between light at night, melatonin secretion, sleep deprivation, and the internal clock: Health impacts and mechanisms of circadian disruption.Life Sci. 2017 Mar 15;173:94-106. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.02.008. Epub 2017 Feb 16. Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28214594 Review.
-
Circadian stage-dependent inhibition of human breast cancer metabolism and growth by the nocturnal melatonin signal: consequences of its disruption by light at night in rats and women.Integr Cancer Ther. 2009 Dec;8(4):347-53. doi: 10.1177/1534735409352320. Integr Cancer Ther. 2009. PMID: 20042410
-
Doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer is driven by light at night-induced disruption of the circadian melatonin signal.J Pineal Res. 2015 Aug;59(1):60-9. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12239. Epub 2015 Apr 20. J Pineal Res. 2015. PMID: 25857269 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian disruption, shift work and the risk of cancer: a summary of the evidence and studies in Seattle.Cancer Causes Control. 2006 May;17(4):539-45. doi: 10.1007/s10552-005-9010-9. Cancer Causes Control. 2006. PMID: 16596308 Review.
Cited by
-
Night Shift Work, DNA Methylation and Telomere Length: An Investigation on Hospital Female Nurses.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Jun 28;16(13):2292. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16132292. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31261650 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin: Regulation of Viral Phase Separation and Epitranscriptomics in Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 23;23(15):8122. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158122. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppression of Transposable Elements in Leukemic Stem Cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 1;7(1):7029. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07356-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28765607 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Light Exposure at Night (LAN) on Carcinogenesis via Decreased Nocturnal Melatonin Synthesis.Molecules. 2018 May 29;23(6):1308. doi: 10.3390/molecules23061308. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29844288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Truncated ORF1 proteins can suppress LINE-1 retrotransposition in trans.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 May 19;45(9):5294-5308. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx211. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28431148 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deharo D, Kines KJ, Sokolowski M, Dauchy RT, Streva VA, Hill SM, Hanifin JP, Brainard GC, Blask DE, Belancio VP. Regulation of L1 expression and retrotransposition by melatonin and its receptor: implications for cancer risk associated with light exposure at night. Nucleic Acids Res 2014; 42(12):7694-707; PMID:24914052 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bibillo A, Eickbush TH. The reverse transcriptase of the R2 non-LTR retrotransposon: continuous synthesis of cDNA on non-continuous RNA templates. J Mol Biol 2002; 316 459-73; PMID:11866511; http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2001.5369 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, Baldwin J, Devon K, Dewar K, Doyle M, FitzHugh W., et al.. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 2001; 409, 860-921; PMID:11237011; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35057062 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brouha B, Schustak J, Badge RM, Lutz-Prigge S, Farley AH, Moran JV, Kazazian HH. Jr. Hot L1s account for the bulk of retrotransposition in the human population. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003; 100 5280-5; PMID:12682288; http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0831042100 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sassaman DM, Dombroski BA, Moran JV, Kimberland ML, Naas TP, DeBerardinis RJ, Gabriel A, Swergold GD, Kazazian HH Jr. Many human L1 elements are capable of retrotransposition ; [see comments]. Nat Genet 1997; 16 37-43; PMID:9140393; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ng0597-37 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
