Vessel Wall Imaging of the Intracranial and Cervical Carotid Arteries
- PMID: 26437991
- PMCID: PMC4635720
- DOI: 10.5853/jos.2015.17.3.238
Vessel Wall Imaging of the Intracranial and Cervical Carotid Arteries
Abstract
Vessel wall imaging can depict the morphologies of atherosclerotic plaques, arterial walls, and surrounding structures in the intracranial and cervical carotid arteries beyond the simple luminal changes that can be observed with traditional luminal evaluation. Differentiating vulnerable from stable plaques and characterizing atherosclerotic plaques are vital parts of the early diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of stroke and the neurological adverse effects of atherosclerosis. Various techniques for vessel wall imaging have been developed and introduced to differentiate and analyze atherosclerotic plaques in the cervical carotid artery. High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (HR-MRI) is the most important and popular vessel wall imaging technique for directly evaluating the vascular wall and intracranial artery disease. Intracranial artery atherosclerosis, dissection, moyamoya disease, vasculitis, and reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome can also be diagnosed and differentiated by using HR-MRI. Here, we review the radiologic features of intracranial artery disease and cervical carotid artery atherosclerosis on HR-MRI and various other vessel wall imaging techniques (e.g., ultrasound, computed tomography, magnetic resonance, and positron emission tomography-computed tomography).
Keywords: Cervical carotid artery; High-resolution magnetic resonance; Intracranial artery; Vessel wall imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
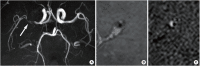

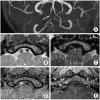
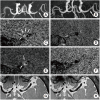
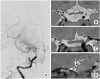
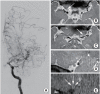
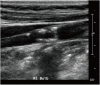
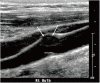
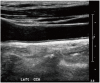
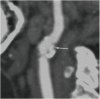
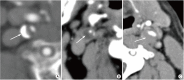
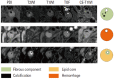
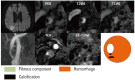
Similar articles
-
Added Value of Vessel Wall Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Differentiation of Moyamoya Vasculopathies in a Non-Asian Cohort.Stroke. 2016 Jul;47(7):1782-8. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.013320. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Stroke. 2016. PMID: 27272486 Free PMC article.
-
Vessel and Vessel Wall Imaging.Front Neurol Neurosci. 2016;40:109-123. doi: 10.1159/000448308. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Front Neurol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27960184 Review.
-
Vessel wall imaging for intracranial vascular disease evaluation.J Neurointerv Surg. 2016 Nov;8(11):1154-1159. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2015-012127. Epub 2016 Jan 14. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016. PMID: 26769729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of the Diagnostic Performances of Ultrasound, High-Resolution Magnetic Resonance Imaging, and Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography in a Rabbit Carotid Vulnerable Plaque Atherosclerosis Model.J Ultrasound Med. 2020 Nov;39(11):2201-2209. doi: 10.1002/jum.15331. Epub 2020 May 12. J Ultrasound Med. 2020. PMID: 32395879
-
Clinical interpretation of high-resolution vessel wall MRI of intracranial arterial diseases.Br J Radiol. 2016 Nov;89(1067):20160496. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20160496. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Br J Radiol. 2016. PMID: 27585640 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stroke due to large vessel atherosclerosis: Five new things.Neurol Clin Pract. 2016 Jun;6(3):252-258. doi: 10.1212/CPJ.0000000000000247. Neurol Clin Pract. 2016. PMID: 29443138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smaller outer diameter of atherosclerotic middle cerebral artery associated with RNF213 c.14576G>A Variant (rs112735431).Surg Neurol Int. 2017 Jun 5;8:104. doi: 10.4103/sni.sni_59_17. eCollection 2017. Surg Neurol Int. 2017. PMID: 28695051 Free PMC article.
-
Optical Coherence Tomography of Spontaneous Basilar Artery Dissection in a Patient With Acute Ischemic Stroke.Front Neurol. 2018 Oct 16;9:858. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00858. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30459699 Free PMC article.
-
High-on-Aspirin Platelet Reactivity Differs Between Recurrent Ischemic Stroke Associated With Extracranial and Intracranial Atherosclerosis.J Clin Neurol. 2022 Jul;18(4):421-427. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2022.18.4.421. J Clin Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35796267 Free PMC article.
-
Superficial Temporal Artery-middle Cerebral Artery Anastomosis for Ischemic Stroke due to Dissection of the Intracranial Internal Carotid Artery with Middle Cerebral Artery Extension.NMC Case Rep J. 2018 Mar 9;5(2):39-44. doi: 10.2176/nmccrj.cr.2017-0063. eCollection 2018 Apr. NMC Case Rep J. 2018. PMID: 29725566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kernan WN, Ovbiagele B, Black HR, Bravata DM, Chimowitz MI, Ezekowitz MD, et al. Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2014;45:2160–2236. - PubMed
-
- Johnston SC, Mendis S, Mathers CD. Global variation in stroke burden and mortality: estimates from monitoring, surveillance, and modelling. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:345–354. - PubMed
-
- Dieleman N, van der Kolk AG, Zwanenburg JJ, Harteveld AA, Biessels GJ, Luijten PR, et al. Imaging intracranial vessel wall pathology with magnetic resonance imaging: current prospects and future directions. Circulation. 2014;130:192–201. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

