Repair Pathway Choices and Consequences at the Double-Strand Break
- PMID: 26437586
- PMCID: PMC4862604
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2015.07.009
Repair Pathway Choices and Consequences at the Double-Strand Break
Abstract
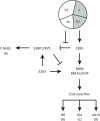
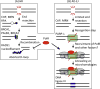
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are cytotoxic lesions that threaten genomic integrity. Failure to repair a DSB has deleterious consequences, including genomic instability and cell death. Indeed, misrepair of DSBs can lead to inappropriate end-joining events, which commonly underlie oncogenic transformation due to chromosomal translocations. Typically, cells employ two main mechanisms to repair DSBs: homologous recombination (HR) and classical nonhomologous end joining (C-NHEJ). In addition, alternative error-prone DSB repair pathways, namely alternative end joining (alt-EJ) and single-strand annealing (SSA), have been recently shown to operate in many different conditions and to contribute to genome rearrangements and oncogenic transformation. Here, we review the mechanisms regulating DSB repair pathway choice, together with the potential interconnections between HR and the annealing-dependent error-prone DSB repair pathways.
Keywords: DNA repair; Polθ; alternative end joining; homologous recombination; synthetic lethality.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modernizing the nonhomologous end-joining repertoire: alternative and classical NHEJ share the stage.Annu Rev Genet. 2013;47:433-55. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-110711-155540. Epub 2013 Sep 11. Annu Rev Genet. 2013. PMID: 24050180 Review.
-
Alternative end-joining repair pathways are the ultimate backup for abrogated classical non-homologous end-joining and homologous recombination repair: Implications for the formation of chromosome translocations.Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2015 Nov;793:166-75. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2015.07.001. Epub 2015 Jul 4. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2015. PMID: 26520387 Review.
-
New Facets of DNA Double Strand Break Repair: Radiation Dose as Key Determinant of HR versus c-NHEJ Engagement.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 6;24(19):14956. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914956. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of nonhomologous DNA end joining, conservative homologous recombination, and single-strand annealing in the cell cycle-dependent repair of DNA double-strand breaks induced by H(2)O(2) in mammalian cells.Radiat Res. 2008 Dec;170(6):784-93. doi: 10.1667/RR1375.1. Radiat Res. 2008. PMID: 19138034
-
Single-strand annealing, conservative homologous recombination, nonhomologous DNA end joining, and the cell cycle-dependent repair of DNA double-strand breaks induced by sparsely or densely ionizing radiation.Radiat Res. 2009 Mar;171(3):265-73. doi: 10.1667/RR0784.1. Radiat Res. 2009. PMID: 19267553
Cited by
-
PUMA facilitates EMI1-promoted cytoplasmic Rad51 ubiquitination and inhibits DNA repair in stem and progenitor cells.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Mar 31;6(1):129. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00510-w. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 33785736 Free PMC article.
-
Noncanonical views of homology-directed DNA repair.Genes Dev. 2016 May 15;30(10):1138-54. doi: 10.1101/gad.280545.116. Genes Dev. 2016. PMID: 27222516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of PARylation in DNA Damage Repair Pathways.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016 Jun;14(3):131-139. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2016.05.001. Epub 2016 May 27. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27240471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CCAR2 functions downstream of the Shieldin complex to promote double-strand break end-joining.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Dec 6;119(49):e2214935119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2214935119. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36442094 Free PMC article.
-
The Fanconi anaemia pathway: new players and new functions.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Jun;17(6):337-49. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.48. Epub 2016 May 5. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27145721 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

