Expression of NeuGc on Pig Corneas and Its Potential Significance in Pig Corneal Xenotransplantation
- PMID: 26418433
- PMCID: PMC4847538
- DOI: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000000635
Expression of NeuGc on Pig Corneas and Its Potential Significance in Pig Corneal Xenotransplantation
Abstract
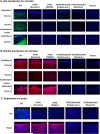
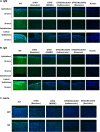
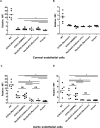
Purpose: Pigs expressing neither galactose-α1,3-galactose (Gal) nor N-glycolylneuraminic acid (NeuGc) take xenotransplantation one step closer to the clinic. Our aims were (1) to document the lack of NeuGc expression on corneas and aortas and cultured endothelial cells [aortic endothelial cells (AECs); corneal (CECs)] of GTKO/NeuGcKO pigs, and (2) to investigate whether the absence of NeuGc reduced human antibody binding to the tissues and cells.
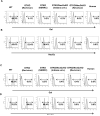
Methods: Wild-type (WT), GTKO, and GTKO/NeuGcKO pigs were used for the study. Human tissues and cultured cells were negative controls. Immunofluorescence staining was performed using anti-Gal and anti-NeuGc antibodies, and human IgM and IgG binding to tissues was determined. Flow cytometric analysis was used to determine Gal and NeuGc expression on cultured CECs and AECs and to measure human IgM/IgG binding to these cells.
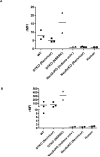
Results: Both Gal and NeuGc were detected on WT pig corneas and aortas. Although GTKO pigs expressed NeuGc, neither humans nor GTKO/NeuGcKO pigs expressed Gal or NeuGc. Human IgM/IgG binding to corneas and aortas from GTKO and GTKO/NeuGcKO pigs was reduced compared with binding to WT pigs. Human antibody binding to GTKO/NeuGcKO AECs was significantly less than that to GTKO AECs, but there was no significant difference in binding between GTKO and GTKO/NeuGcKO CECs.
Conclusions: The absence of NeuGc on GTKO aortic tissue and AECs is associated with reduced human antibody binding, and possibly will provide a better outcome in clinical xenotransplantation using vascularized organs. For clinical corneal xenotransplantation, the absence of NeuGc expression on GTKO/NeuGcKO pig corneas may not prove an advantage over GTKO corneas.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Initial in vitro studies on tissues and cells from GTKO/CD46/NeuGcKO pigs.Xenotransplantation. 2016 Mar;23(2):137-50. doi: 10.1111/xen.12229. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Xenotransplantation. 2016. PMID: 26988899 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of non-gal antigens in pig cornea: relevance to corneal xenotransplantation.Cornea. 2014 Apr;33(4):390-7. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000000069. Cornea. 2014. PMID: 24488129
-
Human antibody recognition of xenogeneic antigens (NeuGc and Gal) on porcine heart valves: could genetically modified pig heart valves reduce structural valve deterioration?Xenotransplantation. 2016 Sep;23(5):370-80. doi: 10.1111/xen.12254. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Xenotransplantation. 2016. PMID: 27511593
-
Recent investigations into pig antigen and anti-pig antibody expression.Int J Surg. 2015 Nov;23(Pt B):223-228. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2015.07.724. Epub 2015 Aug 22. Int J Surg. 2015. PMID: 26306769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corneal blindness and xenotransplantation.Xenotransplantation. 2014 Mar-Apr;21(2):99-114. doi: 10.1111/xen.12082. Epub 2014 Feb 21. Xenotransplantation. 2014. PMID: 25268248 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Corneal xenotransplantation: Where are we standing?Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021 Jan;80:100876. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2020.100876. Epub 2020 Aug 2. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 32755676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xenotransplantation: past, present, and future.Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2017 Dec;22(6):513-521. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0000000000000463. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2017. PMID: 28901971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) on primate complement-dependent cytotoxicity of genetically engineered pig cells: relevance to clinical xenotransplantation.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 16;10(1):11747. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68505-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32678137 Free PMC article.
-
Finding an Optimal Corneal Xenograft Using Comparative Analysis of Corneal Matrix Proteins Across Species.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 12;9(1):1876. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-38342-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30755666 Free PMC article.
-
Modifying the sugar icing on the transplantation cake.Glycobiology. 2016 Jun;26(6):571-81. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cww028. Epub 2016 Mar 1. Glycobiology. 2016. PMID: 26935763 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lutz AJ, Li P, Estrada JL, et al. Double knockout pigs deficient in N-glycolylneuraminic acid and galactose alpha-1,3-galactose reduce the humoral barrier to xenotransplantation. Xenotransplantation. 2013;20:27–35. - PubMed
-
- Zhu A, Hurst R. Anti-N-glycolylneuraminic acid antibodies identified in healthy human serum. Xenotransplantation. 2002;9:376–381. - PubMed
-
- Salama A, Evanno G, Harb J, et al. Potential deleterious role of anti-Neu5Gc antibodies in xenotransplantation. Xenotransplantation. 2015;22:85–94. - PubMed
-
- Miwa Y, Kobayashi T, Nagasaka T, et al. Are N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Hanganutziu-Deicher) antigens important in pig-to-human xenotransplantation? Xenotransplantation. 2004;11:247–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

