Hippo transducer TAZ promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition and supports pancreatic cancer progression
- PMID: 26416426
- PMCID: PMC4742153
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5772
Hippo transducer TAZ promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition and supports pancreatic cancer progression
Abstract
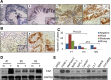
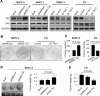
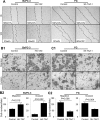
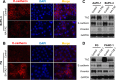
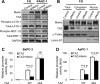
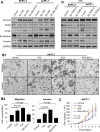
Transcriptional co-activator with PDZ binding motif (TAZ) is a transducer of the Hippo pathway and promotes cancer development and progression. In the present study, we sought to determine the roles and underlying mechanisms of elevated expression and activation of TAZ in pancreatic cancer development and progression. The mechanistic role of TAZ and Hippo signaling in promotion of pancreatic cancer development and progression was examined using cell culture, molecular biology, and mouse models. The relevance of our experimental and mechanistic findings was validated using human pancreatic tumor specimens. We found that TAZ expression was markedly higher in pancreatic tumors than in normal pancreatic tissue. Further analysis of the correlation of TAZ expression with tissue microarray clinicopathologic parameters revealed that this expression was positively associated with tumor differentiation. Also, TAZ expression was higher in pancreatic cancer cell lines than in pancreatic ductal epithelial cells. TAZ activation in pancreatic cancer cells promoted their proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Further mechanistic studies demonstrated that aberrant expression and activation of TAZ in pancreatic cancer cells resulted from suppression of the expression of Merlin, a positive regulator upstream of the Hippo pathway, and that the oncogenic function of TAZ in pancreatic cancer cells was mediated by TEA/ATTS domain transcription factors. Therefore, TAZ functioned as an oncogene and promoted pancreatic cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition and progression. TAZ thus may be a target for effective therapeutic strategies for pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: EMT; TAZ; metastasis; pancreatic cancer; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no known conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Hippo transducer TAZ promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell maintenance in oral cancer.Mol Oncol. 2015 Jun;9(6):1091-105. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2015.01.007. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Mol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25704916 Free PMC article.
-
TAZQ233del Hijacks Hippo pathway to promote mesenchymal-epithelial transition in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Sep 18;503(4):2240-2247. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.144. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29953851
-
MEKK3 Sustains EMT and Stemness in Pancreatic Cancer by Regulating YAP and TAZ Transcriptional Activity.Anticancer Res. 2018 Apr;38(4):1937-1946. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.12431. Anticancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29599309
-
Central role of Yes-associated protein and WW-domain-containing transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif in pancreatic cancer development.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Apr 21;25(15):1797-1816. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i15.1797. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31057295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Hippo Signaling Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer.Anticancer Res. 2019 Jul;39(7):3317-3321. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13474. Anticancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31262852 Review.
Cited by
-
A Potential Role of YAP/TAZ in the Interplay Between Metastasis and Metabolic Alterations.Front Oncol. 2020 Jun 11;10:928. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00928. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32596154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-125a-5p inhibits colorectal cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and migration by targeting TAZ.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 May 7;12:3481-3489. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S191247. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31190857 Free PMC article.
-
Activated hippo signal pathway inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in NK/T cell lymphoma cells.Cancer Med. 2019 Jul;8(8):3892-3904. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2174. Epub 2019 May 23. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31124291 Free PMC article.
-
PKM2 regulates neural invasion of and predicts poor prognosis for human hilar cholangiocarcinoma.Mol Cancer. 2015 Nov 14;14:193. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0462-6. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26576639 Free PMC article.
-
Deubiquitinating Enzyme USP9X Suppresses Tumor Growth via LATS Kinase and Core Components of the Hippo Pathway.Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 15;77(18):4921-4933. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-3413. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28720576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

