Receptor Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase α-Mediated Enhancement of Rheumatoid Synovial Fibroblast Signaling and Promotion of Arthritis in Mice
- PMID: 26414708
- PMCID: PMC4770259
- DOI: 10.1002/art.39442
Receptor Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase α-Mediated Enhancement of Rheumatoid Synovial Fibroblast Signaling and Promotion of Arthritis in Mice
Abstract
Objective: During rheumatoid arthritis (RA), fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) critically promote disease pathogenesis by aggressively invading the extracellular matrix of the joint. The focal adhesion kinase (FAK) signaling pathway is emerging as a contributor to the anomalous behavior of RA FLS. The receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase α (RPTPα), which is encoded by the PTPRA gene, is a key promoter of FAK signaling. The aim of this study was to investigate whether RPTPα mediates FLS aggressiveness and RA pathogenesis.
Methods: Through RPTPα knockdown, we assessed FLS gene expression by quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, invasion and migration by Transwell assays, survival by annexin V and propidium iodide staining, adhesion and spreading by immunofluorescence microscopy, and activation of signaling pathways by Western blotting of FLS lysates. Arthritis development was examined in RPTPα-knockout (KO) mice using the K/BxN serum-transfer model. The contribution of radiosensitive and radioresistant cells to disease was evaluated by reciprocal bone marrow transplantation.
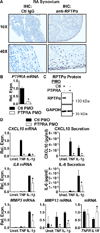
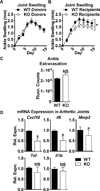
Results: RPTPα was enriched in the RA synovial lining. RPTPα knockdown impaired RA FLS survival, spreading, migration, invasiveness, and responsiveness to platelet-derived growth factor, tumor necrosis factor, and interleukin-1 stimulation. These phenotypes correlated with increased phosphorylation of Src on inhibitory Y(527) and decreased phosphorylation of FAK on stimulatory Y(397) . Treatment of RA FLS with an inhibitor of FAK phenocopied the knockdown of RPTPα. RPTPα-KO mice were protected from arthritis development, which was due to radioresistant cells.
Conclusion: By regulating the phosphorylation of Src and FAK, RPTPα mediates proinflammatory and proinvasive signaling in RA FLS, correlating with the promotion of disease in an FLS-dependent model of RA.
© 2016, American College of Rheumatology.
Figures


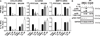
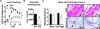
Similar articles
-
TGFβ responsive tyrosine phosphatase promotes rheumatoid synovial fibroblast invasiveness.Ann Rheum Dis. 2016 Jan;75(1):295-302. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205790. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016. PMID: 25378349 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1 beta alleviates the proinflammatory effect of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes through inhibiting extracellular signal-regulated kinase, p38 and nuclear factor-kappaB activation.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Oct 24;16(5):472. doi: 10.1186/s13075-014-0472-6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25367151 Free PMC article.
-
A novel function of artesunate on inhibiting migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients.Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 Jun 24;21(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s13075-019-1935-6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31234900 Free PMC article.
-
Restoring synovial homeostasis in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020 Jun;16(6):316-333. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-0413-5. Epub 2020 May 11. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32393826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stable activation of fibroblasts in rheumatic arthritis-causes and consequences.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016 Dec;55(suppl 2):ii64-ii67. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kew347. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016. PMID: 27856663 Review.
Cited by
-
The Importance of Tyrosine Phosphorylation Control of Cellular Signaling Pathways in Respiratory Disease: pY and pY Not.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018 Nov;59(5):535-547. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0049TR. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29812954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PTPα promotes fibroproliferative responses after acute lung injury.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2022 Jul 1;323(1):L69-L83. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00436.2021. Epub 2022 Jun 7. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35670474 Free PMC article.
-
Ssu72 Dual-Specific Protein Phosphatase: From Gene to Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 6;22(7):3791. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073791. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33917542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does a rare mutation in PTPRA contribute to the development of Parkinson's disease in an Australian multi-incident family?PLoS One. 2022 Jul 28;17(7):e0271499. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271499. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35900966 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting protein phosphatases in cancer immunotherapy and autoimmune disorders.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023 Apr;22(4):273-294. doi: 10.1038/s41573-022-00618-w. Epub 2023 Jan 24. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023. PMID: 36693907 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ospelt C, Neidhart M, Gay RE, Gay S. Synovial activation in rheumatoid arthritis. Frontiers in bioscience: a journal and virtual library. 2004;9:2323–2334. - PubMed
-
- Neumann E, Lefevre S, Zimmermann B, Gay S, Muller-Ladner U. Rheumatoid arthritis progression mediated by activated synovial fibroblasts. Trends Mol Med. 2010;16(10):458–468. - PubMed
-
- Noss EH, Brenner MB. The role and therapeutic implications of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in inflammation and cartilage erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunological reviews. 2008;223:252–270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

