Analysis of SCA8, SCA10, SCA12, SCA17 and SCA19 in patients with unknown spinocerebellar ataxia: a Thai multicentre study
- PMID: 26374734
- PMCID: PMC4571065
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-015-0425-y
Analysis of SCA8, SCA10, SCA12, SCA17 and SCA19 in patients with unknown spinocerebellar ataxia: a Thai multicentre study
Abstract
Background: About 50 % of Thai patients with adult-onset spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) was Machado-Joseph disease (MJD), SCA1, SCA2 and SCA6. The author investigated further on less common SCAs in the patients without any known mutations.
Methods: DNA samples of 82 index patients who were genetically excluded MJD, SCA1, SCA2, SCA6, SCA7 and dentatorubro-pallidoluysian atrophy (DRPLA) were examined. Analysis of SCA8, SCA10, SCA12, SCA17 and SCA19 genes were comprehensively performed. Normal range of trinucleotide repeat expansion sizes of TATA-box-binding protein gene (TBP) were also determined in 374 control subjects.
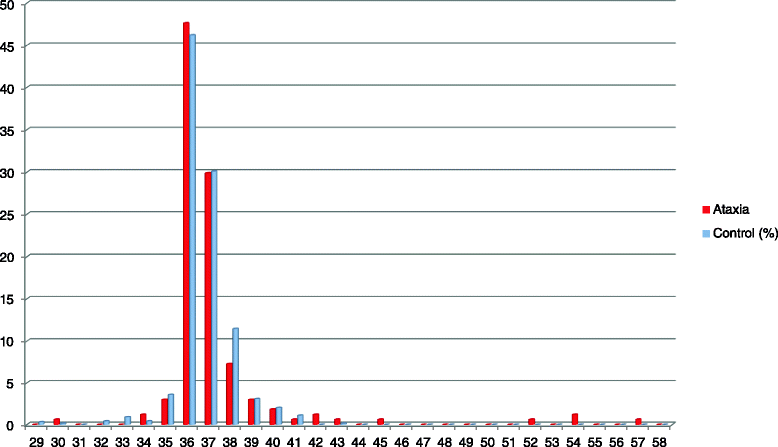
Results: Eight patients carried ≥42 CAG/CAA repeat allele in the TBP consistent with SCA17. The pathological repeat alleles ranged from 42 to 57 repeats. All patients had significant degree of cognitive dysfunction. Other non-ataxic phenotypes comprised of parkinsonism, chorea, dystonia and myoclonus. A sporadic patient carried a heterozygous 41-repeat allele developed chronic progressive cerebellar degeneration commenced at the age of 28 years. Whilst, 2 % of the control subjects (8/374) carried the 41-repeat allele. Five of the carriers were re-examined, and revealed that four of them had parkinsonism and/or cognitive impairment without cerebellar signs. Analysis of other types of SCAs was all negative.
Conclusions: This is the first study of SCA8, SCA10, SCA12, SCA17 and SCA19 in Thais. SCA17 appears to be an important cause of ataxia in Thailand. Although, the pathological cut-off point of the TBP repeat allele remains unclear, the finding suggests that the 41-repeat may be a pathological allele resulting late-onset or mild phenotype. Apart from ataxia, cognitive impairment and parkinsonism may be clinical presentations in these carriers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular genetics of hereditary spinocerebellar ataxia: mutation analysis of spinocerebellar ataxia genes and CAG/CTG repeat expansion detection in 225 Italian families.Arch Neurol. 2004 May;61(5):727-33. doi: 10.1001/archneur.61.5.727. Arch Neurol. 2004. PMID: 15148151
-
Possible reduced penetrance of expansion of 44 to 47 CAG/CAA repeats in the TATA-binding protein gene in spinocerebellar ataxia type 17.Arch Neurol. 2004 Feb;61(2):209-12. doi: 10.1001/archneur.61.2.209. Arch Neurol. 2004. PMID: 14967767
-
Frequency of SCA1, SCA2, SCA3/MJD, SCA6, SCA7, and DRPLA CAG trinucleotide repeat expansion in patients with hereditary spinocerebellar ataxia from Chinese kindreds.Arch Neurol. 2000 Apr;57(4):540-4. doi: 10.1001/archneur.57.4.540. Arch Neurol. 2000. PMID: 10768629
-
The wide spectrum of spinocerebellar ataxias (SCAs).Cerebellum. 2005;4(1):2-6. doi: 10.1080/14734220510007914. Cerebellum. 2005. PMID: 15895552 Review.
-
The hereditary spinocerebellar ataxias in Japan.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2003;100(1-4):198-205. doi: 10.1159/000072855. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2003. PMID: 14526181 Review.
Cited by
-
Spinocerebellar ataxias: prospects and challenges for therapy development.Nat Rev Neurol. 2018 Oct;14(10):590-605. doi: 10.1038/s41582-018-0051-6. Nat Rev Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30131520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dystonia and ataxia progression in spinocerebellar ataxias.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2017 Dec;45:75-80. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.10.007. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2017. PMID: 29089256 Free PMC article.
-
First report of a Japanese family with spinocerebellar ataxia type 10: The second report from Asia after a report from China.PLoS One. 2017 May 19;12(5):e0177955. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177955. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28542277 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency of SCA8, SCA10, SCA12, SCA36, FXTAS and C9orf72 repeat expansions in SCA patients negative for the most common SCA subtypes.BMC Neurol. 2018 Jan 9;18(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12883-017-1009-9. BMC Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29316893 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebellar Dysfunction and Ataxia in Patients with Epilepsy: Coincidence, Consequence, or Cause?Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov (N Y). 2016 Jun 23;6:376. doi: 10.7916/D8KH0NBT. eCollection 2016. Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov (N Y). 2016. PMID: 27375960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boonkongchuen P, Pongpakdee S, Jindahra P, Papsing C, Peerapatmongkol P, Wetchaphanphesat S, Paiboonpol S, Dejthevaporn C, Tanprawate S, Nudsasarn A, et al. Clinical analysis of adult-onset spinocerebellar ataxias in Thailand. BMC Neurol. 2014;14:75. doi: 10.1186/1471-2377-14-75. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moseley ML, Zu T, Ikeda Y, Gao W, Mosemiller AK, Daughters RS, Chen G, Weatherspoon MR, Clark HB, Ebner TJ, et al. Bidirectional expression of CUG and CAG expansion transcripts and intranuclear polyglutamine inclusions in spinocerebellar ataxia type 8. Nat Genet. 2006;38(7):758–69. doi: 10.1038/ng1827. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials