Bioinformatics-Based Identification of MicroRNA-Regulated and Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Genes
- PMID: 26359667
- PMCID: PMC4567271
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137551
Bioinformatics-Based Identification of MicroRNA-Regulated and Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Genes
Abstract
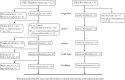
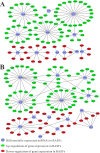
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) act as epigenetic markers and regulate the expression of their target genes, including those characterized as regulators in autoimmune diseases. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is one of the most common autoimmune diseases. The potential roles of miRNA-regulated genes in RA pathogenesis have greatly aroused the interest of clinicians and researchers in recent years. In the current study, RA-related miRNAs records were obtained from PubMed through conditional literature retrieval. After analyzing the selected records, miRNA targeted genes were predicted. We identified 14 RA-associated miRNAs, and their sub-analysis in 5 microarray or RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) datasets was performed. The microarray and RNA-seq data of RA were also downloaded from NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and Sequence Read Archive (SRA), analyzed, and annotated. Using a bioinformatics approach, we identified a series of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) by comparing studies on RA and the controls. The RA-related gene expression profile was thus obtained and the expression of miRNA-regulated genes was analyzed. After functional annotation analysis, we found GO molecular function (MF) terms significantly enriched in calcium ion binding (GO: 0005509). Moreover, some novel dysregulated target genes were identified in RA through integrated analysis of miRNA/mRNA expression. The result revealed that the expression of a number of genes, including ROR2, ABI3BP, SMOC2, etc., was not only affected by dysregulated miRNAs, but also altered in RA. Our findings indicate that there is a close association between negatively correlated mRNA/miRNA pairs and RA. These findings may be applied to identify genetic markers for RA diagnosis and treatment in the future.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deduction of Novel Genes Potentially Involved in Osteoblasts of Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Next-Generation Sequencing and Bioinformatic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 11;18(11):2396. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112396. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29137139 Free PMC article.
-
A Systems Biology Approach for miRNA-mRNA Expression Patterns Analysis in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2021;24(2):195-212. doi: 10.2174/1386207323666200605150024. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2021. PMID: 32503403
-
Identification of microRNA-mRNA interactions in atrial fibrillation using microarray expression profiles and bioinformatics analysis.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Jun;13(6):4535-40. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5106. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27082053 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: From pathogenesis to clinical impact.Autoimmun Rev. 2019 Nov;18(11):102391. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102391. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Autoimmun Rev. 2019. PMID: 31520804 Review.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis and miRNAs: A Critical Review through a Functional View.J Immunol Res. 2018 Mar 29;2018:2474529. doi: 10.1155/2018/2474529. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 29785401 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synovial fibroblast-derived exosomal microRNA-106b suppresses chondrocyte proliferation and migration in rheumatoid arthritis via down-regulation of PDK4.J Mol Med (Berl). 2020 Mar;98(3):409-423. doi: 10.1007/s00109-020-01882-2. Epub 2020 Feb 20. J Mol Med (Berl). 2020. PMID: 32152704
-
A Microdialysis in Adjuvant Arthritic Rats for Pharmacokinetics⁻Pharmacodynamics Modeling Study of Geniposide with Determination of Drug Concentration and Efficacy Levels in Dialysate.Molecules. 2018 Apr 24;23(5):987. doi: 10.3390/molecules23050987. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29695042 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic Acid-Platinum (II) Complex [RT-Pt(II)] Protects Against Rheumatoid Arthritis in Mice via MEK/Nuclear Factor kappa B (NF-κB) Pathway Downregulation.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Aug 3;26:e924787. doi: 10.12659/MSM.924787. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32741960 Free PMC article.
-
Multivariate genome-wide association analysis identifies novel and relevant variants associated with anterior cruciate ligament rupture risk in the dog model.BMC Genet. 2018 Jun 26;19(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12863-018-0626-7. BMC Genet. 2018. PMID: 29940858 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of avicularin on rheumatoid arthritis and its associated mechanisms.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Dec;16(6):5343-5349. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6872. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30542493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Levy L, Fautrel B, Barnetche T, Schaeverbeke T. (2008) Incidence and risk of fatal myocardial infarction and stroke events in rheumatoid arthritis patients. A systematic review of the literature. Clinical and experimental rheumatology 26: 673–679. - PubMed
-
- Khurana R, Wolf R, Berney S, Caldito G, Hayat S, Berney SM. (2008) Risk of development of lung cancer is increased in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a large case control study in US veterans. The Journal of rheumatology 35: 1704–1708. - PubMed
-
- Young A, Koduri G. (2007) Extra-articular manifestations and complications of rheumatoid arthritis. Best practice & research Clinical rheumatology 21: 907–927. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

