Caenorhabditis elegans ALG-1 antimorphic mutations uncover functions for Argonaute in microRNA guide strand selection and passenger strand disposal
- PMID: 26351692
- PMCID: PMC4586838
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1506576112
Caenorhabditis elegans ALG-1 antimorphic mutations uncover functions for Argonaute in microRNA guide strand selection and passenger strand disposal
Abstract
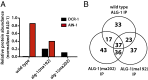
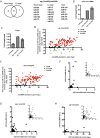
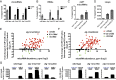
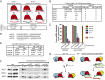
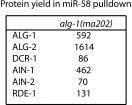
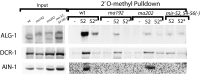
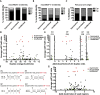
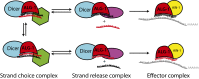
MicroRNAs are regulators of gene expression whose functions are critical for normal development and physiology. We have previously characterized mutations in a Caenorhabditis elegans microRNA-specific Argonaute ALG-1 (Argonaute-like gene) that are antimorphic [alg-1(anti)]. alg-1(anti) mutants have dramatically stronger microRNA-related phenotypes than animals with a complete loss of ALG-1. ALG-1(anti) miRISC (microRNA induced silencing complex) fails to undergo a functional transition from microRNA processing to target repression. To better understand this transition, we characterized the small RNA and protein populations associated with ALG-1(anti) complexes in vivo. We extensively characterized proteins associated with wild-type and mutant ALG-1 and found that the mutant ALG-1(anti) protein fails to interact with numerous miRISC cofactors, including proteins known to be necessary for target repression. In addition, alg-1(anti) mutants dramatically overaccumulated microRNA* (passenger) strands, and immunoprecipitated ALG-1(anti) complexes contained nonstoichiometric yields of mature microRNA and microRNA* strands, with some microRNA* strands present in the ALG-1(anti) Argonaute far in excess of the corresponding mature microRNAs. We show complex and microRNA-specific defects in microRNA strand selection and microRNA* strand disposal. For certain microRNAs (for example mir-58), microRNA guide strand selection by ALG-1(anti) appeared normal, but microRNA* strand release was inefficient. For other microRNAs (such as mir-2), both the microRNA and microRNA* strands were selected as guide by ALG-1(anti), indicating a defect in normal specificity of the strand choice. Our results suggest that wild-type ALG-1 complexes recognize structural features of particular microRNAs in the context of conducting the strand selection and microRNA* ejection steps of miRISC maturation.
Keywords: ALG-1; Argonaute; microRNA; microRNA*; passenger.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A specific type of Argonaute phosphorylation regulates binding to microRNAs during C. elegans development.Cell Rep. 2022 Dec 13;41(11):111822. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111822. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36516777 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling neurodevelopmental disorder-associated human AGO1 mutations in Caenorhabditis elegans Argonaute alg-1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Mar 5;121(10):e2308255121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2308255121. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38412125 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in conserved residues of the C. elegans microRNA Argonaute ALG-1 identify separable functions in ALG-1 miRISC loading and target repression.PLoS Genet. 2014 Apr 24;10(4):e1004286. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004286. eCollection 2014 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24763381 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA strand selection: Unwinding the rules.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2021 May;12(3):e1627. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1627. Epub 2020 Sep 20. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2021. PMID: 32954644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of microRNAs in the Caenorhabditis elegans nervous system.J Genet Genomics. 2013 Sep 20;40(9):445-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Aug 7. J Genet Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24053946 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Molecular Genetic Explorations of Caenorhabditis elegans MicroRNAs.Genetics. 2018 Jul;209(3):651-673. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.300291. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29967059 Free PMC article.
-
KH domain containing RNA-binding proteins coordinate with microRNAs to regulate Caenorhabditis elegans development.G3 (Bethesda). 2021 Feb 9;11(2):jkab013. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab013. G3 (Bethesda). 2021. PMID: 33585875 Free PMC article.
-
An RNAi screen for conserved kinases that enhance microRNA activity after dauer in Caenorhabditis elegans.G3 (Bethesda). 2024 Mar 6;14(3):jkae007. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkae007. G3 (Bethesda). 2024. PMID: 38226857 Free PMC article.
-
A specific type of Argonaute phosphorylation regulates binding to microRNAs during C. elegans development.Cell Rep. 2022 Dec 13;41(11):111822. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111822. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36516777 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in understanding microRNA function and regulation in C. elegans.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Feb 15;154(Pt A):4-13. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2023.03.011. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 37055330 Review.
References
-
- Maniataki E, De Planell Saguer MDA, Mourelatos Z. Immunoprecipitation of microRNPs and directional cloning of microRNAs. Methods Mol Biol. 2005;309:283–294. - PubMed
-
- Iwasaki S, et al. Defining fundamental steps in the assembly of the Drosophila RNAi enzyme complex. Nature. 2015;521(7553):533–536. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

