Comparison of stranded and non-stranded RNA-seq transcriptome profiling and investigation of gene overlap
- PMID: 26334759
- PMCID: PMC4559181
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-015-1876-7
Comparison of stranded and non-stranded RNA-seq transcriptome profiling and investigation of gene overlap
Abstract
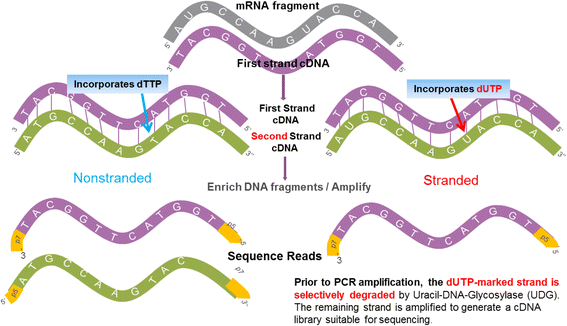
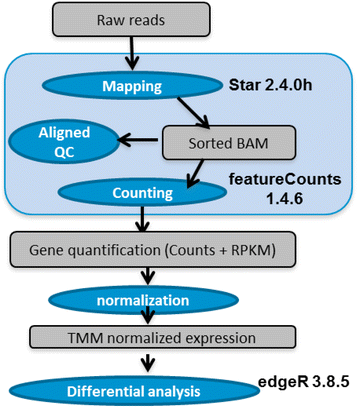
Background: While RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) is becoming a powerful technology in transcriptome profiling, one significant shortcoming of the first-generation RNA-seq protocol is that it does not retain the strand specificity of origin for each transcript. Without strand information it is difficult and sometimes impossible to accurately quantify gene expression levels for genes with overlapping genomic loci that are transcribed from opposite strands. It has recently become possible to retain the strand information by modifying the RNA-seq protocol, known as strand-specific or stranded RNA-seq. Here, we evaluated the advantages of stranded RNA-seq in transcriptome profiling of whole blood RNA samples compared with non-stranded RNA-seq, and investigated the influence of gene overlaps on gene expression profiling results based on practical RNA-seq datasets and also from a theoretical perspective.
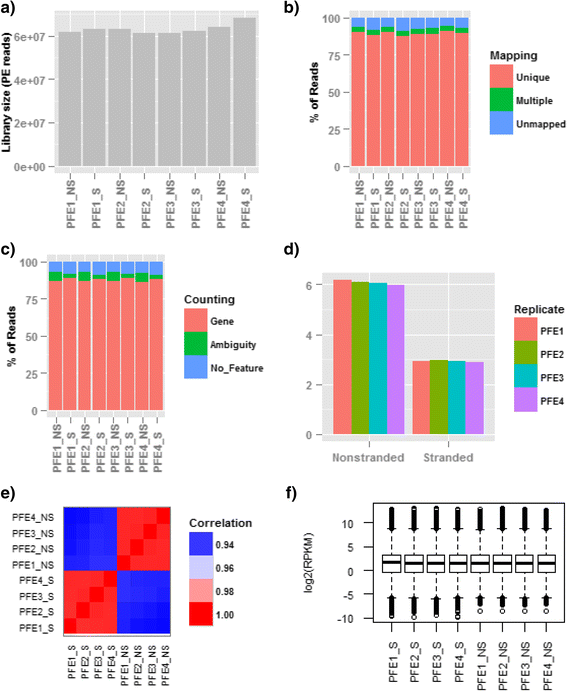
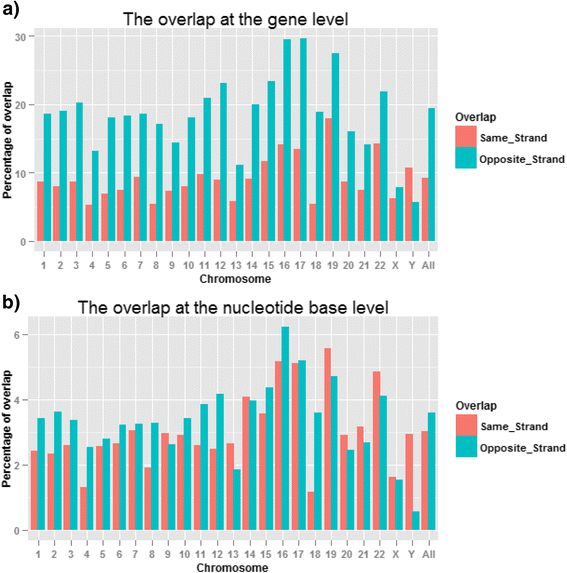
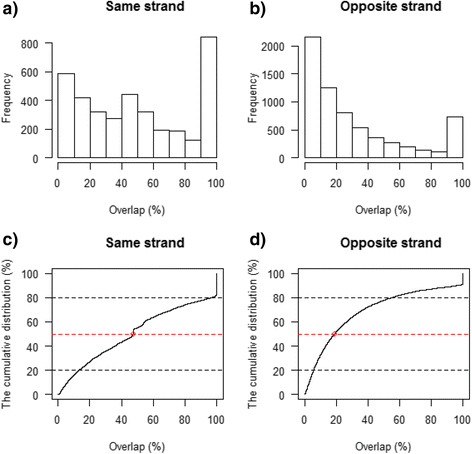
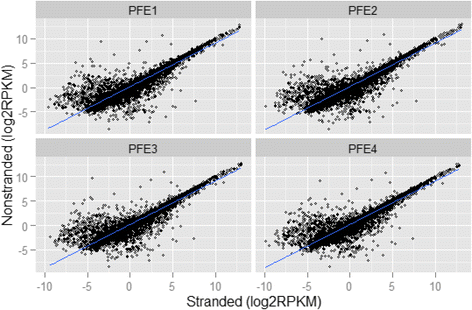
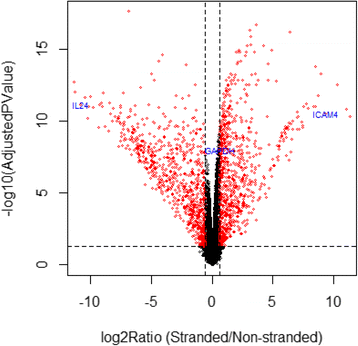
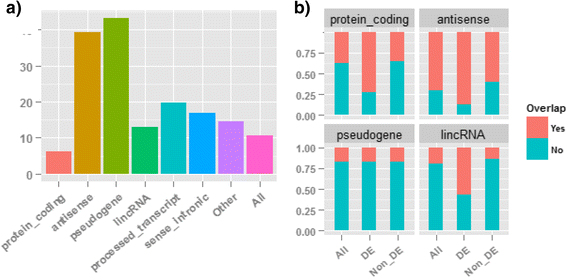
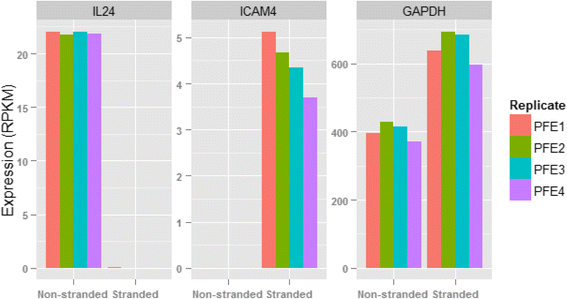
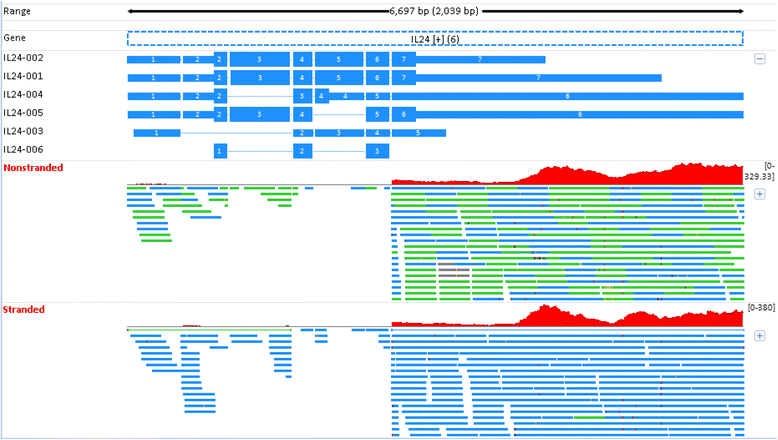
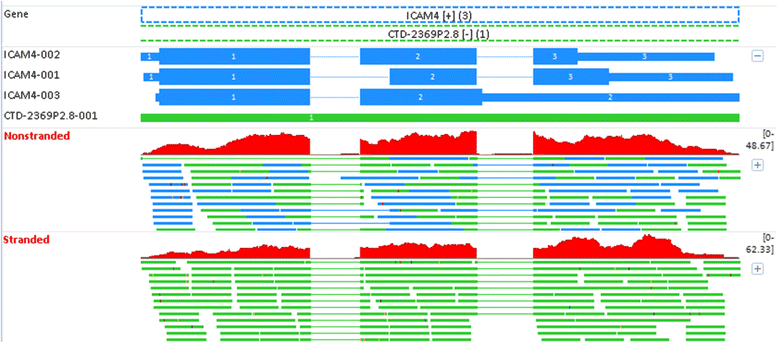
Results: Our results demonstrated a substantial impact of stranded RNA-seq on transcriptome profiling and gene expression measurements. As many as 1751 genes in Gencode Release 19 were identified to be differentially expressed when comparing stranded and non-stranded RNA-seq whole blood samples. Antisense and pseudogenes were significantly enriched in differential expression analyses. Because stranded RNA-seq retains strand information of a read, we can resolve read ambiguity in overlapping genes transcribed from opposite strands, which provides a more accurate quantification of gene expression levels compared with traditional non-stranded RNA-seq. In the human genome, it is not uncommon to find genomic loci where both strands encode distinct genes. Among the over 57,800 annotated genes in Gencode release 19, there are an estimated 19 % (about 11,000) of overlapping genes transcribed from the opposite strands. Based on our whole blood mRNA-seq datasets, the fraction of overlapping nucleotide bases on the same and opposite strands were estimated at 2.94 % and 3.1 %, respectively. The corresponding theoretical estimations are 3 % and 3.6 %, well in agreement with our own findings.
Conclusions: Stranded RNA-seq provides a more accurate estimate of transcript expression compared with non-stranded RNA-seq, and is therefore the recommended RNA-seq approach for future mRNA-seq studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comprehensive evaluation of AmpliSeq transcriptome, a novel targeted whole transcriptome RNA sequencing methodology for global gene expression analysis.BMC Genomics. 2015 Dec 16;16:1069. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2270-1. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26673413 Free PMC article.
-
Differentially expressed genes from RNA-Seq and functional enrichment results are affected by the choice of single-end versus paired-end reads and stranded versus non-stranded protocols.BMC Genomics. 2017 May 23;18(1):399. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3797-0. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28535780 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive evaluation of ensembl, RefSeq, and UCSC annotations in the context of RNA-seq read mapping and gene quantification.BMC Genomics. 2015 Feb 18;16(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1308-8. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25765860 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing and annotating the genome using RNA-seq data.Sci China Life Sci. 2017 Feb;60(2):116-125. doi: 10.1007/s11427-015-0349-4. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Sci China Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 27294835 Review.
-
Transcriptome analysis using next-generation sequencing.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2013 Feb;24(1):22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2012.09.004. Epub 2012 Sep 25. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23020966 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA-seq and ChIP-seq as Complementary Approaches for Comprehension of Plant Transcriptional Regulatory Mechanism.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 25;21(1):167. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010167. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31881735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome sequencing of turmeric provides evolutionary insights into its medicinal properties.Commun Biol. 2021 Oct 15;4(1):1193. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02720-y. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34654884 Free PMC article.
-
De novo assembly of transcriptomes and differential gene expression analysis using short-read data from emerging model organisms - a brief guide.Front Zool. 2024 Jun 20;21(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12983-024-00538-y. Front Zool. 2024. PMID: 38902827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative evaluation of RNA-Seq library preparation methods for strand-specificity and low input.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 17;9(1):13477. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49889-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31530843 Free PMC article.
-
The Necessity of Using Strand-Specific cDNA for Achieving Accurate Transcriptome Analysis Result.Adv Biomed Res. 2023 Apr 27;12:108. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_102_22. eCollection 2023. Adv Biomed Res. 2023. PMID: 37288031 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

