Breaking resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to an attenuated vesicular stomatitis virus through a novel activity of IKK inhibitor TPCA-1
- PMID: 26331681
- PMCID: PMC4619123
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.08.003
Breaking resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to an attenuated vesicular stomatitis virus through a novel activity of IKK inhibitor TPCA-1
Abstract
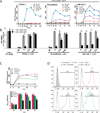
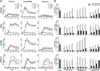
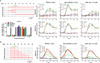
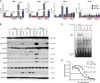
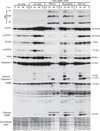
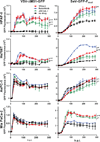
Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) is an effective oncolytic virus against most human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cell lines. However, some PDAC cell lines are highly resistant to oncolytic VSV-ΔM51 infection. To better understand the mechanism of resistance, we tested a panel of 16 small molecule inhibitors of different cellular signaling pathways, and identified TPCA-1 (IKK-β inhibitor) and ruxolitinib (JAK1/2 inhibitor), as strong enhancers of VSV-ΔM51 replication and virus-mediated oncolysis in all VSV-resistant PDAC cell lines. Both TPCA-1 and ruxolitinib similarly inhibited STAT1 and STAT2 phosphorylation and decreased expression of antiviral genes MxA and OAS. Moreover, an in situ kinase assay provided biochemical evidence that TPCA-1 directly inhibits JAK1 kinase activity. Together, our data demonstrate that TPCA-1 is a unique dual inhibitor of IKK-β and JAK1 kinase, and provide a new evidence that upregulated type I interferon signaling plays a major role in resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to oncolytic viruses.
Keywords: IKK inhibitor; Interferon signaling; Janus kinase (JAK); NF-kappa B (NF-κB); Oncolytic virus; Pancreatic cancer; Ruxolitinib; TPCA-1; Vesicular stomatitis virus.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expanding the Spectrum of Pancreatic Cancers Responsive to Vesicular Stomatitis Virus-Based Oncolytic Virotherapy: Challenges and Solutions.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 9;13(5):1171. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051171. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel biomarkers of resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to oncolytic vesicular stomatitis virus.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 20;7(38):61601-61618. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11202. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27533247 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to oncolytic vesicular stomatitis virus: role of type I interferon signaling.Virology. 2013 Feb 5;436(1):221-34. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2012.11.014. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Virology. 2013. PMID: 23246628 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of type I interferon-mediated antiviral action in human glioma cells by the IKK inhibitors BMS-345541 and TPCA-1.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2012 Aug;32(8):368-77. doi: 10.1089/jir.2012.0002. Epub 2012 Apr 17. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2012. PMID: 22509977 Free PMC article.
-
Oncotargeting by Vesicular Stomatitis Virus (VSV): Advances in Cancer Therapy.Viruses. 2018 Feb 23;10(2):90. doi: 10.3390/v10020090. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 29473868 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cooperative effects of RIG-I-like receptor signaling and IRF1 on DNA damage-induced cell death.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Apr 18;13(4):364. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04797-7. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35436994 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the Spectrum of Pancreatic Cancers Responsive to Vesicular Stomatitis Virus-Based Oncolytic Virotherapy: Challenges and Solutions.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 9;13(5):1171. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051171. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of IκB Kinase Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy to Circumvent Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 24;14(21):5215. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215215. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358633 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance Mechanisms Influencing Oncolytic Virotherapy, a Systematic Analysis.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Oct 12;9(10):1166. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9101166. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34696274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting IκappaB kinases for cancer therapy.Semin Cancer Biol. 2019 Jun;56:12-24. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2018.02.007. Epub 2018 Feb 24. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019. PMID: 29486318 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

