Adenosine receptor signaling: a key to opening the blood-brain door
- PMID: 26330053
- PMCID: PMC4557218
- DOI: 10.1186/s12987-015-0017-7
Adenosine receptor signaling: a key to opening the blood-brain door
Abstract
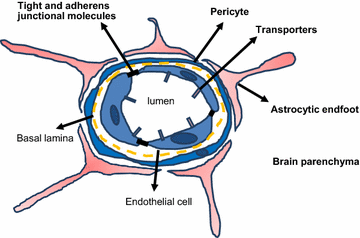
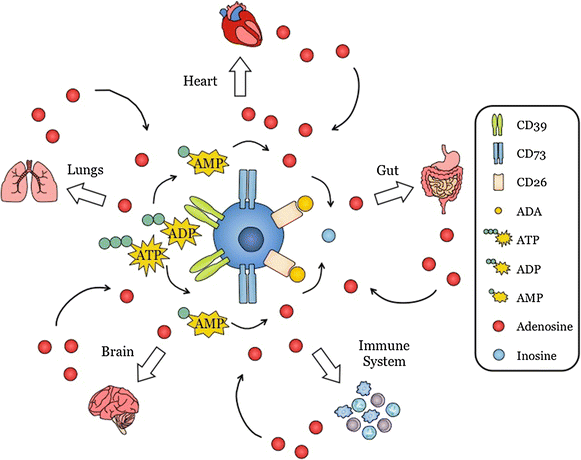
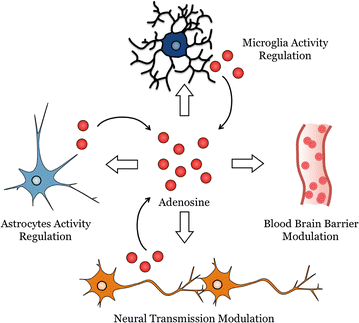
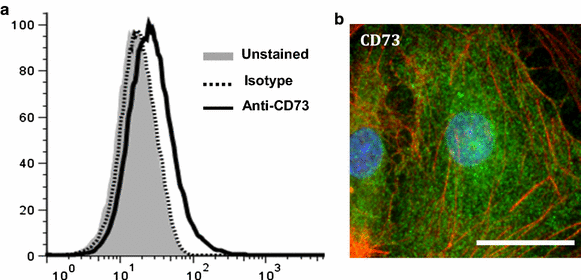
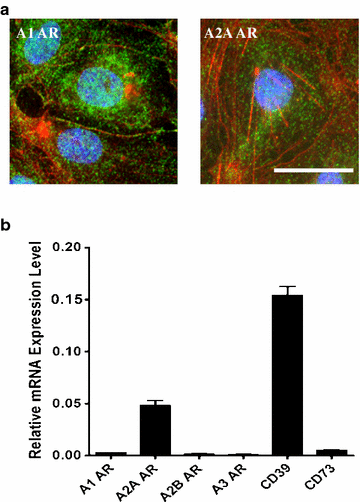
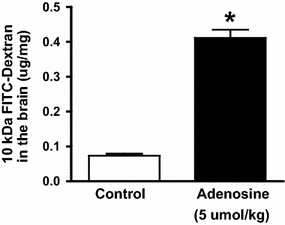
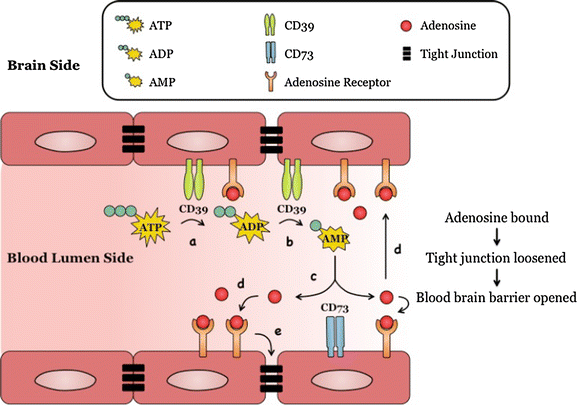
The aim of this review is to outline evidence that adenosine receptor (AR) activation can modulate blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability and the implications for disease states and drug delivery. Barriers of the central nervous system (CNS) constitute a protective and regulatory interface between the CNS and the rest of the organism. Such barriers allow for the maintenance of the homeostasis of the CNS milieu. Among them, the BBB is a highly efficient permeability barrier that separates the brain micro-environment from the circulating blood. It is made up of tight junction-connected endothelial cells with specialized transporters to selectively control the passage of nutrients required for neural homeostasis and function, while preventing the entry of neurotoxic factors. The identification of cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in the development and function of CNS barriers is required for a better understanding of CNS homeostasis in both physiological and pathological settings. It has long been recognized that the endogenous purine nucleoside adenosine is a potent modulator of a large number of neurological functions. More recently, experimental studies conducted with human/mouse brain primary endothelial cells as well as with mouse models, indicate that adenosine markedly regulates BBB permeability. Extracellular adenosine, which is efficiently generated through the catabolism of ATP via the CD39/CD73 ecto-nucleotidase axis, promotes BBB permeability by signaling through A1 and A2A ARs expressed on BBB cells. In line with this hypothesis, induction of AR signaling by selective agonists efficiently augments BBB permeability in a transient manner and promotes the entry of macromolecules into the CNS. Conversely, antagonism of AR signaling blocks the entry of inflammatory cells and soluble factors into the brain. Thus, AR modulation of the BBB appears as a system susceptible to tighten as well as to permeabilize the BBB. Collectively, these findings point to AR manipulation as a pertinent avenue of research for novel strategies aiming at efficiently delivering therapeutic drugs/cells into the CNS, or at restricting the entry of inflammatory immune cells into the brain in some diseases such as multiple sclerosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adenosine receptor signaling modulates permeability of the blood-brain barrier.J Neurosci. 2011 Sep 14;31(37):13272-80. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3337-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21917810 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming the blood-brain barrier for delivering drugs into the brain by using adenosine receptor nanoagonist.ACS Nano. 2014 Apr 22;8(4):3678-89. doi: 10.1021/nn5003375. Epub 2014 Apr 3. ACS Nano. 2014. PMID: 24673594
-
Purinergic signaling: A gatekeeper of blood-brain barrier permeation.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 7;14:1112758. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1112758. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36825149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies for Drug Delivery into the Brain: A Review on Adenosine Receptors Modulation for Central Nervous System Diseases Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Oct 10;15(10):2441. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15102441. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37896201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A2A Adenosine Receptor Regulates the Human Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability.Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Aug;52(1):664-78. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8879-2. Epub 2014 Sep 28. Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25262373 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CD73 Promotes Glioblastoma Pathogenesis and Enhances Its Chemoresistance via A2B Adenosine Receptor Signaling.J Neurosci. 2019 May 29;39(22):4387-4402. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1118-18.2019. Epub 2019 Mar 29. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30926752 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic Signaling and Related Biomarkers in Depression.Brain Sci. 2020 Mar 12;10(3):160. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10030160. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 32178222 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired tissue barriers as potential therapeutic targets for Parkinson's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Metab Brain Dis. 2018 Aug;33(4):1031-1043. doi: 10.1007/s11011-018-0239-x. Epub 2018 Apr 22. Metab Brain Dis. 2018. PMID: 29681010 Review.
-
A unified hypothesis of SUDEP: Seizure-induced respiratory depression induced by adenosine may lead to SUDEP but can be prevented by autoresuscitation and other restorative respiratory response mechanisms mediated by the action of serotonin on the periaqueductal gray.Epilepsia. 2023 Apr;64(4):779-796. doi: 10.1111/epi.17521. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Epilepsia. 2023. PMID: 36715572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting gliovascular connexins prevents inflammatory blood-brain barrier leakage and astrogliosis.JCI Insight. 2022 Aug 22;7(16):e135263. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.135263. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 35881483 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

