Real-time analysis of dual-display phage immobilization and autoantibody screening using quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring
- PMID: 26316752
- PMCID: PMC4547655
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S84800
Real-time analysis of dual-display phage immobilization and autoantibody screening using quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring
Abstract
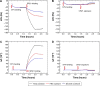
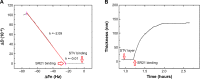
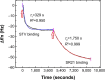
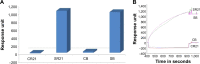
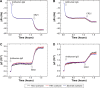
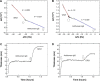
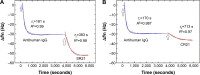
Over the last three decades, phage display technology has been used for the display of target-specific biomarkers, peptides, antibodies, etc. Phage display-based assays are mostly limited to the phage ELISA, which is notorious for its high background signal and laborious methodology. These problems have been recently overcome by designing a dual-display phage with two different end functionalities, namely, streptavidin (STV)-binding protein at one end and a rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantigenic target at the other end. Using this dual-display phage, a much higher sensitivity in screening specificities of autoantibodies in complex serum sample has been detected compared to single-display phage system on phage ELISA. Herein, we aimed to develop a novel, rapid, and sensitive dual-display phage to detect autoantibodies presence in serum samples using quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring as a sensing platform. The vertical functionalization of the phage over the STV-modified surfaces resulted in clear frequency and dissipation shifts revealing a well-defined viscoelastic signature. Screening for autoantibodies using antihuman IgG-modified surfaces and the dual-display phage with STV magnetic bead complexes allowed to isolate the target entities from complex mixtures and to achieve a large response as compared to negative control samples. This novel dual-display strategy can be a potential alternative to the time consuming phage ELISA protocols for the qualitative analysis of serum autoantibodies and can be taken as a departure point to ultimately achieve a point of care diagnostic system.
Keywords: dissipation monitoring; dual-display phage; quartz crystal microbalance; rheumatoid arthritis; streptavidin-binding protein; surface plasmon resonance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunomagnetic separation of human myeloperoxidase using an antibody-mimicking peptide identified by phage display.J Biotechnol. 2017 Sep 10;257:118-121. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.12.010. Epub 2016 Dec 15. J Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 27989733
-
Construction of helper plasmid-mediated dual-display phage for autoantibody screening in serum.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;98(14):6365-73. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-5713-8. Epub 2014 Apr 25. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24764015 Free PMC article.
-
Quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) as a device for the screening of phage libraries.Biosens Bioelectron. 1999 Feb;14(2):139-44. doi: 10.1016/s0956-5663(98)00111-0. Biosens Bioelectron. 1999. PMID: 10101836
-
cDNA phage display for the discovery of theranostic autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis.Immunol Res. 2017 Feb;65(1):307-325. doi: 10.1007/s12026-016-8839-1. Immunol Res. 2017. PMID: 27503624 Review.
-
Identification of Soft Matter Binding Peptide Ligands Using Phage Display.Bioconjug Chem. 2015 Oct 21;26(10):2002-15. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00377. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Bioconjug Chem. 2015. PMID: 26275106 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a Phage Display Panning Strategy Utilizing Crude Antigens: Isolation of MERS-CoV Nucleoprotein human antibodies.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 15;9(1):6088. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42628-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30988390 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arap MA. Phage display technology. Applications and innovations. Genet Mol Biol. 2005;28(1):1–9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

