A systematic mRNA control mechanism for germline stem cell homeostasis and cell fate specification
- PMID: 26303971
- PMCID: PMC4915122
- DOI: 10.5483/bmbrep.2016.49.2.135
A systematic mRNA control mechanism for germline stem cell homeostasis and cell fate specification
Abstract
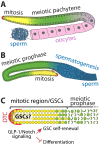
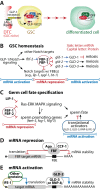
Germline stem cells (GSCs) are the best understood adult stem cell types in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, and have provided an important model system for studying stem cells and their cell fate in vivo, in mammals. In this review, we propose a mechanism that controls GSCs and their cell fate through selective activation, repression and mobilization of the specific mRNAs. This mechanism is acutely controlled by known signal transduction pathways (e.g., Notch signaling and Ras-ERK MAPK signaling pathways) and P granule (analogous to mammalian germ granule)-associated mRNA regulators (FBF-1, FBF-2, GLD-1, GLD-2, GLD-3, RNP-8 and IFE-1). Importantly, all regulators are highly conserved in many multi-cellular animals. Therefore, GSCs from a simple animal may provide broad insight into vertebrate stem cells (e.g., hematopoietic stem cells) and their cell fate specification. [BMB Reports 2016; 49(2): 93-98].
Figures
Similar articles
-
Germline Stem Cell Differentiation Entails Regional Control of Cell Fate Regulator GLD-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2016 Mar;202(3):1085-103. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.185678. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 26757772 Free PMC article.
-
Germline stem cells and their regulation in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;786:29-46. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-6621-1_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23696350
-
A conserved RNA-binding protein controls germline stem cells in Caenorhabditis elegans.Nature. 2002 Jun 6;417(6889):660-3. doi: 10.1038/nature754. Epub 2002 May 22. Nature. 2002. PMID: 12050669
-
Scratching the niche that controls Caenorhabditis elegans germline stem cells.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2009 Dec;20(9):1107-13. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2009.09.005. Epub 2009 Sep 16. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19765664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of germline stem cell regulation.Annu Rev Genet. 2005;39:173-95. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.39.073003.105855. Annu Rev Genet. 2005. PMID: 16285857 Review.
Cited by
-
Cap-Independent mRNA Translation in Germ Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 5;20(1):173. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010173. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30621249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subunits of the DNA polymerase alpha-primase complex promote Notch-mediated proliferation with discrete and shared functions in C. elegans germline.FEBS J. 2018 Jul;285(14):2590-2604. doi: 10.1111/febs.14512. Epub 2018 May 28. FEBS J. 2018. PMID: 29775245 Free PMC article.
-
A simple and rapid method for combining fluorescent in situ RNA hybridization (FISH) and immunofluorescence in the C. elegans germline.MethodsX. 2016 May 6;3:378-85. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2016.05.001. eCollection 2016. MethodsX. 2016. PMID: 27257608 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing full-text publications for deep insights into C. elegans and Drosophila biomaps.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 13;25(1):1080. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10997-6. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39538127 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Germ Cell mRNPs by eIF4E:4EIP Complexes: Multiple Mechanisms, One Goal.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jul 7;8:562. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00562. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32733883 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

