Chemosensitization of multidrug resistant Candida albicans by the oxathiolone fused chalcone derivatives
- PMID: 26300857
- PMCID: PMC4525051
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00783
Chemosensitization of multidrug resistant Candida albicans by the oxathiolone fused chalcone derivatives
Abstract
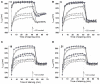
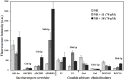
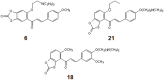
Three structurally related oxathiolone fused chalcone derivatives appeared effective chemosensitizers, able to restore in part sensitivity to fluconazole of multidrug-resistant C. albicans strains. Compound 21 effectively chemosensitized cells resistant due to the overexpression of the MDR1 gene, compound 6 reduced resistance of cells overexpressing the ABC-type drug transporters CDR1/CDR2 and derivative 18 partially reversed fluconazole resistance mediated by both types of yeast drug efflux pumps. The observed effect of sensitization of resistant strains of Candida albicans to fluconazole activity in the presence of active compounds most likely resulted from inhibition of the pump-mediated efflux, as was revealed by the results of studies involving the fluorescent probes, Nile Red, Rhodamine 6G and diS-C3(3).
Keywords: Candida albicans; antifungals; chalcones; chemosensitization; multidrug resistance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synthetic Organotellurium Compounds Sensitize Drug-Resistant Candida albicans Clinical Isolates to Fluconazole.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Dec 27;61(1):e01231-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01231-16. Print 2017 Jan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27821447 Free PMC article.
-
Extracts from Argentinian native plants reverse fluconazole resistance in Candida species by inhibiting the efflux transporters Mdr1 and Cdr1.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Oct 12;22(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03745-4. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 36224581 Free PMC article.
-
[Investigation of mutations in transcription factors of efflux pump genes in fluconazole-resistant Candida albicans strains overexpressing the efflux pumps].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2015 Oct;49(4):609-18. doi: 10.5578/mb.10105. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2015. PMID: 26649419 Turkish.
-
Antifungal drug resistance in pathogenic fungi.Med Mycol. 1998;36 Suppl 1:119-28. Med Mycol. 1998. PMID: 9988500 Review.
-
The genetic basis of fluconazole resistance development in Candida albicans.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Jul 18;1587(2-3):240-8. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4439(02)00087-x. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12084466 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting efflux pumps to overcome antifungal drug resistance.Future Med Chem. 2016 Aug;8(12):1485-501. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2016-0050. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Future Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27463566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dermatophyte Resistance to Antifungal Drugs: Mechanisms and Prospectus.Front Microbiol. 2018 May 29;9:1108. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01108. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29896175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fungicidal action of geraniol against Candida albicans is potentiated by abrogated CaCdr1p drug efflux and fluconazole synergism.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 29;13(8):e0203079. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203079. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30157240 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Organotellurium Compounds Sensitize Drug-Resistant Candida albicans Clinical Isolates to Fluconazole.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Dec 27;61(1):e01231-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01231-16. Print 2017 Jan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27821447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balzi E., Chen W., Ulaszewski S., Capieaux E., Goffeau A. (1987). The multidrug resistance gene PDR1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 16871–16879. - PubMed
-
- Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (2008). Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts-Second Edition. Approved Standard M27-A3. Wayne, PA: CLSI.
-
- Conseil G., Baubichon-Cortay H., Dayan G., Jault J. M., Barron D., Di Pietro A. (1998). Flavonoids: a class of modulators with bifunctional interactions at vicinal ATP- and steroid-binding sites on mouse P-glycoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95, 9831–9836. 10.1073/pnas.95.17.9831 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

