MicroRNAs: Emerging Novel Clinical Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinomas
- PMID: 26295264
- PMCID: PMC4555081
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm4081631
MicroRNAs: Emerging Novel Clinical Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinomas
Abstract
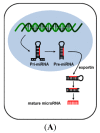
The discovery of small non-coding RNAs known as microRNAs has refined our view of the complexity of gene expression regulation. In hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the fifth most frequent cancer and the third leading cause of cancer death worldwide, dysregulation of microRNAs has been implicated in all aspects of hepatocarcinogenesis. In addition, alterations of microRNA expression have also been reported in non-cancerous liver diseases including chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis. MicroRNAs have been proposed as clinically useful diagnostic biomarkers to differentiate HCC from different liver pathologies and healthy controls. Unique patterns of microRNA expression have also been implicated as biomarkers for prognosis as well as to predict and monitor therapeutic responses in HCC. Since dysregulation has been detected in various specimens including primary liver cancer tissues, serum, plasma, and urine, microRNAs represent novel non-invasive markers for HCC screening and predicting therapeutic responses. However, despite a significant number of studies, a consensus on which microRNA panels, sample types, and methodologies for microRNA expression analysis have to be used has not yet been established. This review focuses on potential values, benefits, and limitations of microRNAs as new clinical markers for diagnosis, prognosis, prediction, and therapeutic monitoring in HCC.
Keywords: biomarker; diagnosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; microRNA; prognosis; therapeutic monitoring.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Circulating microRNA-200 Family as Diagnostic Marker in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 8;10(10):e0140066. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140066. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26447841 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic roles of circulating miRNA-223-3p in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 24;15(4):e0232211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232211. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32330203 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 29;13(3):514. doi: 10.3390/cancers13030514. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33572780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum MicroRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis of Hepatitis C Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Egyptian Patients.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 9;10(9):e0137706. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137706. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26352740 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs and liver disease: viral hepatitis, liver fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.Postgrad Med J. 2014 Feb;90(1060):106-12. doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2013-131883. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Postgrad Med J. 2014. PMID: 24243965 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic implication of a circulating serum-based three-microRNA signature in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Genet. 2022 Nov 15;13:929787. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.929787. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36457743 Free PMC article.
-
hsa-mir-183 is frequently methylated and related to poor survival in human hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Mar 7;23(9):1568-1575. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i9.1568. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28321157 Free PMC article.
-
Genomics, microRNA, epigenetics, and proteomics for future diagnosis, treatment and monitoring response in upper GI cancers.Clin Transl Med. 2016 Mar;5(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s40169-016-0093-6. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Clin Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27053248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-122 in patients with hepatitis B and hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019 Aug;10(4):789-796. doi: 10.21037/jgo.2019.02.14. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31392060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA 885-5p Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis by Repressing AEG1.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Jan 31;13:981-988. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S228576. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32099401 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

