Intracellular Delivery of Molecular Cargo Using Cell-Penetrating Peptides and the Combination Strategies
- PMID: 26295227
- PMCID: PMC4581311
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms160819518
Intracellular Delivery of Molecular Cargo Using Cell-Penetrating Peptides and the Combination Strategies
Abstract
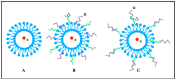
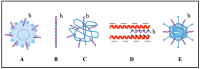
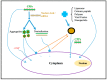
Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) can cross cellular membranes in a non-toxic fashion, improving the intracellular delivery of various molecular cargos such as nanoparticles, small molecules and plasmid DNA. Because CPPs provide a safe, efficient, and non-invasive mode of transport for various cargos into cells, they have been developed as vectors for the delivery of genetic and biologic products in recent years. Most common CPPs are positively charged peptides. While delivering negatively charged molecules (e.g., nucleic acids) to target cells, the internalization efficiency of CPPs is reduced and inhibited because the cationic charges on the CPPs are neutralized through the covering of CPPs by cargos on the structure. Even under these circumstances, the CPPs can still be non-covalently complexed with the negatively charged molecules. To address this issue, combination strategies of CPPs with other typical carriers provide a promising and novel delivery system. This review summarizes the latest research work in using CPPs combined with molecular cargos including liposomes, polymers, cationic peptides, nanoparticles, adeno-associated virus (AAV) and calcium for the delivery of genetic products, especially for small interfering RNA (siRNA). This combination strategy remedies the reduced internalization efficiency caused by neutralization.
Keywords: TAT peptide; calcium; cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs); combination delivery; liposome; nanoparticles.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Peptide vectors for the nonviral delivery of nucleic acids.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Jul 17;45(7):1048-56. doi: 10.1021/ar2002304. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 22455499
-
Intracellular Delivery of Nanoparticles with Cell Penetrating Peptides.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1324:357-68. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2806-4_24. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26202282
-
Cell Penetrating Peptide Conjugated Chitosan for Enhanced Delivery of Nucleic Acid.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Dec 4;16(12):28912-30. doi: 10.3390/ijms161226142. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26690119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell penetration: scope and limitations by the application of cell-penetrating peptides.J Pept Sci. 2014 Oct;20(10):760-84. doi: 10.1002/psc.2672. Epub 2014 Aug 11. J Pept Sci. 2014. PMID: 25112216 Review.
-
PepFects and NickFects for the Intracellular Delivery of Nucleic Acids.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1324:303-15. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2806-4_19. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26202277
Cited by
-
Nanoparticle-Based Delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 Genome-Editing Therapeutics.AAPS J. 2018 Oct 10;20(6):108. doi: 10.1208/s12248-018-0267-9. AAPS J. 2018. PMID: 30306365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trapped! A Critical Evaluation of Methods for Measuring Total Cellular Uptake versus Cytosolic Localization.Bioconjug Chem. 2019 Apr 17;30(4):1006-1027. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.9b00112. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Bioconjug Chem. 2019. PMID: 30882208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide-coated gold nanoparticles for modulation of angiogenesis in vivo.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Jun 7;11:2633-9. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S108661. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27354794 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi therapeutic strategies for acute respiratory distress syndrome.Transl Res. 2019 Dec;214:30-49. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2019.07.011. Epub 2019 Jul 27. Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31401266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
M918: A Novel Cell Penetrating Peptide for Effective Delivery of HIV-1 Nef and Hsp20-Nef Proteins into Eukaryotic Cell Lines.Curr HIV Res. 2018;16(4):280-287. doi: 10.2174/1570162X17666181206111859. Curr HIV Res. 2018. PMID: 30520377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eguchi A., Akuta T., Okuyama H., Senda T., Yokoi H., Inokuchi H., Fujita S., Hayakawa T., Takeda K., Hasegawa M., et al. Protein transduction domain of HIV-1 Tat protein promotes efficient delivery of DNA into mammalian cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:26204–26210. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M010625200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Coupade C., Fittipaldi A., Chagnas V., Michel M., Carlier S., Tasciotti E., Darmon A., Ravel D., Kearsey J., Giacca M., et al. Novel human-derived cell-penetrating peptides for specific subcellular delivery of therapeutic biomolecules. Biochem. J. 2005;390:407–418. doi: 10.1042/BJ20050401. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

