Second-Site Mutagenesis of a Hypomorphic argonaute1 Allele Identifies SUPERKILLER3 as an Endogenous Suppressor of Transgene Posttranscriptional Gene Silencing
- PMID: 26286717
- PMCID: PMC4587451
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.15.00585
Second-Site Mutagenesis of a Hypomorphic argonaute1 Allele Identifies SUPERKILLER3 as an Endogenous Suppressor of Transgene Posttranscriptional Gene Silencing
Abstract
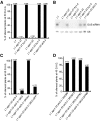
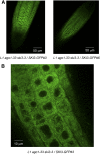
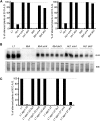
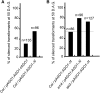
Second-site mutagenesis was performed on the argonaute1-33 (ago1-33) hypomorphic mutant, which exhibits reduced sense transgene posttranscriptional gene silencing (S-PTGS). Mutations in FIERY1, a positive regulator of the cytoplasmic 5'-to-3' EXORIBONUCLEASE4 (XRN4), and in SUPERKILLER3 (SKI3), a member of the SKI complex that threads RNAs directly to the 3'-to-5' exoribonuclease of the cytoplasmic exosome, compensated AGO1 partial deficiency and restored S-PTGS with 100% efficiency. Moreover, xrn4 and ski3 single mutations provoked the entry of nonsilenced transgenes into S-PTGS and enhanced S-PTGS on partially silenced transgenes, indicating that cytoplasmic 5'-to-3' and 3'-to-5' RNA degradation generally counteract S-PTGS, likely by reducing the amount of transgene aberrant RNAs that are used by the S-PTGS pathway to build up small interfering RNAs that guide transgene RNA cleavage by AGO1. Constructs generating improperly terminated transgene messenger RNAs (mRNAs) were not more sensitive to ski3 or xrn4 than regular constructs, suggesting that improperly terminated transgene mRNAs not only are degraded from both the 3' end but also from the 5' end, likely after decapping. The facts that impairment of either 5'-to-3' or 3'-to-5' RNA degradation is sufficient to provoke the entry of transgene RNA into the S-PTGS pathway, whereas simultaneous impairment of both pathways is necessary to provoke the entry of endogenous mRNA into the S-PTGS pathway, suggest poor RNA quality upon the transcription of transgenes integrated at random genomic locations.
© 2015 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RNA Quality Control as a Key to Suppressing RNA Silencing of Endogenous Genes in Plants.Mol Plant. 2016 Jun 6;9(6):826-36. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2016.03.011. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Mol Plant. 2016. PMID: 27045817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SUPERKILLER Complex Components Are Required for the RNA Exosome-Mediated Control of Cuticular Wax Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis Inflorescence Stems.Plant Physiol. 2016 Jun;171(2):960-73. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00450. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27208312 Free PMC article.
-
The Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein SmD1 Interplays with Splicing, RNA Quality Control, and Posttranscriptional Gene Silencing in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2016 Feb;28(2):426-38. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.01045. Epub 2016 Feb 3. Plant Cell. 2016. PMID: 26842463 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis FIERY1, XRN2, and XRN3 are endogenous RNA silencing suppressors.Plant Cell. 2007 Nov;19(11):3451-61. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.055319. Epub 2007 Nov 9. Plant Cell. 2007. PMID: 17993620 Free PMC article.
-
The diversity of post-transcriptional gene silencing mediated by small silencing RNAs in plants.Essays Biochem. 2020 Dec 7;64(6):919-930. doi: 10.1042/EBC20200006. Essays Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32885814 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA Quality Control as a Key to Suppressing RNA Silencing of Endogenous Genes in Plants.Mol Plant. 2016 Jun 6;9(6):826-36. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2016.03.011. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Mol Plant. 2016. PMID: 27045817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SUPERKILLER Complex Components Are Required for the RNA Exosome-Mediated Control of Cuticular Wax Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis Inflorescence Stems.Plant Physiol. 2016 Jun;171(2):960-73. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00450. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27208312 Free PMC article.
-
Interconnections between mRNA degradation and RDR-dependent siRNA production in mRNA turnover in plants.J Plant Res. 2017 Mar;130(2):211-226. doi: 10.1007/s10265-017-0906-8. Epub 2017 Feb 14. J Plant Res. 2017. PMID: 28197782 Review.
-
FIERY1 promotes microRNA accumulation by suppressing rRNA-derived small interfering RNAs in Arabidopsis.Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 27;10(1):4424. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12379-z. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31562313 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic action of the Arabidopsis spliceosome components PRP39a and SmD1b in promoting posttranscriptional transgene silencing.Plant Cell. 2023 May 29;35(6):1917-1935. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koad091. Plant Cell. 2023. PMID: 36970782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Béclin C, Boutet S, Waterhouse P, Vaucheret H (2002) A branched pathway for transgene-induced RNA silencing in plants. Curr Biol 12: 684–688 - PubMed
-
- Chekanova JA, Gregory BD, Reverdatto SV, Chen H, Kumar R, Hooker T, Yazaki J, Li P, Skiba N, Peng Q, et al. (2007) Genome-wide high-resolution mapping of exosome substrates reveals hidden features in the Arabidopsis transcriptome. Cell 131: 1340–1353 - PubMed
-
- Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16: 735–743 - PubMed
-
- Clough SJ, Tuteja JH, Li M, Marek LF, Shoemaker RC, Vodkin LO (2004) Features of a 103-kb gene-rich region in soybean include an inverted perfect repeat cluster of CHS genes comprising the I locus. Genome 47: 819–831 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

