Overexpression of Leucine-Rich Repeat-Containing G Protein-Coupled Receptor 5 (LGR5) Represents a Typical Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway-Activated Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 26280006
- PMCID: PMC4531428
- DOI: 10.1159/000343873
Overexpression of Leucine-Rich Repeat-Containing G Protein-Coupled Receptor 5 (LGR5) Represents a Typical Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway-Activated Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common and most frequently lethal cancers worldwide. Although many advances have been made in the analysis of multistage hepatocarcinogenesis, we still lack information to guide adequate clinical management options for HCC. A large number of genetic alterations occur during hepatocarcinogenesis, and many genetic studies have indicated that one of the most frequently mutated oncogenes found in HCC is β-catenin.
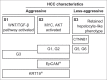
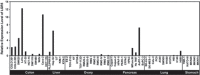
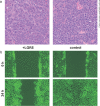
Summary: Molecular subclassification of HCC based on gene expression signatures has identified a typical hepatocyte-like subclass of HCC harboring β-catenin mutations; this subclass is characterized by better histological differentiation and a less aggressive nature. We previously identified overexpression of the leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 5 (LGR5), also known as GPR49, in HCC with β-catenin mutations. LGR5 has been indicated as one of the downstream target genes of the Wnt signaling pathway; however, the functional role of LGR5 in cancer is largely unknown. We demonstrated that HCC cells transfected with LGR5 exhibited higher colony forming activity and were more resistant to a cytotoxic drug than the control HCC cells were. Overexpression of LGR5 also retarded cell migration. LGR5-transfected HCC cells formed nodule-type tumors in the livers of immunodeficient mice, whereas control cells formed more invasive tumors. Results of our recent research suggest that aberrant expression of LGR5 could regulate the epithelial cell phenotype and promotes HCC cell survival. HCC cells overexpressing LGR5 seem to represent a typical phenotype of a less aggressive HCC.
Key messages: Recent efforts on the molecular classification of HCC have led us to new strategies for dealing with HCC. These specific signatures may predict the risk of recurrence or the patient survival rate, which affect the outlook and may suggest treatment strategies for HCC patients.
Keywords: HCC molecular subclassification; HCC typical phenotype; LGR5; LGR5-overexpressing cells; WNT/β-catenin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpression of leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 5 predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018 Jul;25(5):904-908. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.12.014. Epub 2017 Dec 30. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30108439 Free PMC article.
-
Leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 5 regulates epithelial cell phenotype and survival of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Exp Cell Res. 2013 Feb 1;319(3):113-21. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.10.011. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Exp Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23127514
-
LGR5/R-Spo1/Wnt3a axis promotes stemness and aggressive phenotype in hepatoblast-like hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines.Cell Signal. 2021 Jun;82:109972. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.109972. Epub 2021 Mar 6. Cell Signal. 2021. PMID: 33684507
-
Lgr5 in cancer biology: functional identification of Lgr5 in cancer progression and potential opportunities for novel therapy.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Jul 29;10(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1288-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31358061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atypical regulators of Wnt/β-catenin signaling as potential therapeutic targets in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Jun;242(11):1142-1149. doi: 10.1177/1535370217705865. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 28429652 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 5 predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018 Jul;25(5):904-908. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.12.014. Epub 2017 Dec 30. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30108439 Free PMC article.
-
Gpr97 Exacerbates AKI by Mediating Sema3A Signaling.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018 May;29(5):1475-1489. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2017080932. Epub 2018 Mar 12. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29531097 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of MicroRNA-216a Suppresses Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Glioma Cells by Targeting Leucine-Rich Repeat-Containing G Protein-Coupled Receptor 5.Oncol Res. 2017 Sep 21;25(8):1317-1327. doi: 10.3727/096504017X14874323871217. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Oncol Res. 2017. PMID: 28256193 Free PMC article.
-
The Pivotal Role of Long Noncoding RNA RAB5IF in the Proliferation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Via LGR5 Mediated β-Catenin and c-Myc Signaling.Biomolecules. 2019 Nov 8;9(11):718. doi: 10.3390/biom9110718. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31717443 Free PMC article.
-
LGR5 in Barrett's Esophagus and its Utility in Predicting Patients at Increased Risk of Advanced Neoplasia.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2020 Dec 22;12(1):e00272. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000272. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33464729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Sakamoto M, Effendi K, Masugi Y. Molecular diagnosis of multistage hepatocarcinogenesis. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2010;40:891–896. - PubMed
-
- Marrero JA, Fontana RJ, Barrat A, Askari F, Conjeevaram HS, Su GL, Lok AS. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of 7 staging systems in an American cohort. Hepatology. 2005;41:707–716. - PubMed
-
- Boyault S, Rickman DS, de Reyniès A, Balabaud C, Rebouissou S, Jeannot E, Hérault A, Saric J, Belghiti J, Franco D, Bioulac-Sage P, Laurent-Puig P, Zucman-Rossi J. Transcriptome classification of HCC is related to gene alterations and to new therapeutic targets. Hepatology. 2007;45:42–52. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

