Signal Transduction Mechanisms of Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Emer ging Role of Lipin-1
- PMID: 26278388
- PMCID: PMC4879108
- DOI: 10.2174/1874467208666150817112109
Signal Transduction Mechanisms of Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Emer ging Role of Lipin-1
Abstract
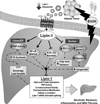
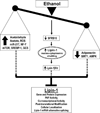
Lipin-1, a mammalian phosphatidic acid phosphatase (PAP), is a bi-functional molecule involved in various signaling pathways via its function as a PAP enzyme in the triglyceride synthesis pathway and in the nucleus as a transcriptional co-regulator. In the liver, lipin-1 is known to play a vital role in controlling the lipid metabolism and inflammation process at multiple regulatory levels. Alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) is one of the earliest forms of liver injury and approximately 8-20% of patients with simple steatosis can develop into more severe forms of liver injury, including steatohepatitis, fibrosis/ cirrhosis, and eventually hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The signal transduction mechanisms for alcohol-induced detrimental effects in liver involves alteration of complex and multiple signaling pathways largely governed by a central and upstream signaling system, namely, sirtuin 1 (SIRT1)-AMP activated kinase (AMPK) axis. Emerging evidence suggests a pivotal role of lipin-1 as a crucial downstream regulator of SIRT1-AMPK signaling system that is likely to be ultimately responsible for development and progression of AFLD. Several lines of evidence demonstrate that ethanol exposure significantly induces lipin-1 gene and protein expression levels in cultured hepatocytes and in the livers of rodents, induces lipin-1-PAP activity, impairs the functional activity of nuclear lipin-1, disrupts lipin-1 mRNA alternative splicing and induces lipin-1 nucleocytoplasmic shuttling. Such impairment in response to ethanol leads to derangement of hepatic lipid metabolism, and excessive production of inflammatory cytokines in the livers of the rodents and human alcoholics. This review summarizes current knowledge about the role of lipin-1 in the pathogenesis of AFLD and its potential signal transduction mechanisms.
Keywords: Lipin-1; alcoholic fatty liver disease; inflammation; lipid metabolism; signal transduction; transcriptional regulators.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.org.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Roles of silent information regulator 1-serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 10-lipin 1 axis in the pathogenesis of alcohol fatty liver disease.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Jun;242(11):1117-1125. doi: 10.1177/1535370217707729. Epub 2017 May 3. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 28467182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of lipin-1 in the pathogenesis of alcoholic fatty liver.Alcohol Alcohol. 2015 Mar;50(2):146-51. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agu102. Epub 2015 Jan 16. Alcohol Alcohol. 2015. PMID: 25595739 Review.
-
Deletion of SIRT1 from hepatocytes in mice disrupts lipin-1 signaling and aggravates alcoholic fatty liver.Gastroenterology. 2014 Mar;146(3):801-11. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.11.008. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Gastroenterology. 2014. PMID: 24262277 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of hepatic lipin-1 by ethanol: role of AMP-activated protein kinase/sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 signaling in mice.Hepatology. 2012 Feb;55(2):437-46. doi: 10.1002/hep.24708. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Hepatology. 2012. PMID: 21953514 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic Knockdown of Splicing Regulator Slu7 Ameliorates Inflammation and Attenuates Liver Injury in Ethanol-Fed Mice.Am J Pathol. 2018 Aug;188(8):1807-1819. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.05.004. Epub 2018 Jun 2. Am J Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29870742 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Allium victorialis L. Extracts Promote Activity of FXR to Ameliorate Alcoholic Liver Disease: Targeting Liver Lipid Deposition and Inflammation.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 8;12:738689. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.738689. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34690775 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Metabolism in Development and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 31;12(6):1419. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061419. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32486341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Roles of SIRT1 in Alcoholic Liver Disease.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Oct 17;16(16):3174-3183. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.49535. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33162823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Similarities and Differences: A Comparative Review of the Molecular Mechanisms and Effectors of NAFLD and AFLD.Front Physiol. 2021 Jul 30;12:710285. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.710285. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34393826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of silent information regulator 1-serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 10-lipin 1 axis in the pathogenesis of alcohol fatty liver disease.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Jun;242(11):1117-1125. doi: 10.1177/1535370217707729. Epub 2017 May 3. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 28467182 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- You M, Rogers CQ. Adiponectin: a key adipokine in alcoholic fatty liver. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2009;234:850–859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

