Prolyl isomerase Pin1 negatively regulates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) by associating with the CBS domain in the γ subunit
- PMID: 26276391
- PMCID: PMC4591812
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.658559
Prolyl isomerase Pin1 negatively regulates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) by associating with the CBS domain in the γ subunit
Abstract
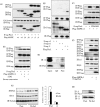
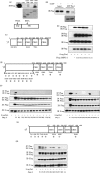
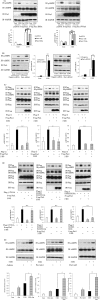
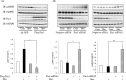
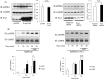
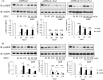
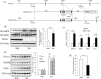
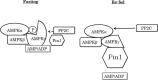
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) plays a critical role in metabolic regulation. In this study, first, it was revealed that Pin1 associates with any isoform of γ, but not with either the α or the β subunit, of AMPK. The association between Pin1 and the AMPK γ1 subunit is mediated by the WW domain of Pin1 and the Thr(211)-Pro-containing motif located in the CBS domain of the γ1 subunit. Importantly, overexpression of Pin1 suppressed AMPK phosphorylation in response to either 2-deoxyglucose or biguanide stimulation, whereas Pin1 knockdown by siRNAs or treatment with Pin1 inhibitors enhanced it. The experiments using recombinant Pin1, AMPK, LKB1, and PP2C proteins revealed that the protective effect of AMP against PP2C-induced AMPKα subunit dephosphorylation was markedly suppressed by the addition of Pin1. In good agreement with the in vitro data, the level of AMPK phosphorylation as well as the expressions of mitochondria-related genes, such as PGC-1α, which are known to be positively regulated by AMPK, were markedly higher with reduced triglyceride accumulation in the muscles of Pin1 KO mice as compared with controls. These findings suggest that Pin1 plays an important role in the pathogenic mechanisms underlying impaired glucose and lipid metabolism, functioning as a negative regulator of AMPK.
Keywords: AMP-activated kinase (AMPK); diabetes; energy metabolism; lipid metabolism; metabolic syndrome; muscle; prolyl isomerase.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The prolyl isomerase Pin1 interacts with and downregulates the activity of AMPK leading to induction of tumorigenicity of hepatocarcinoma cells.Mol Carcinog. 2013 Oct;52(10):813-23. doi: 10.1002/mc.21920. Epub 2012 Apr 30. Mol Carcinog. 2013. PMID: 22549912
-
Peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 associates with insulin receptor substrate-1 and enhances insulin actions and adipogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 10;286(23):20812-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.206904. Epub 2011 Mar 17. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21454638 Free PMC article.
-
The prolyl isomerase Pin1 regulates hypoxia-inducible transcription factor (HIF) activity.Cell Signal. 2014 Aug;26(8):1649-56. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.04.005. Epub 2014 Apr 12. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24726894
-
Prolyl isomerase Pin1 in metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells.Cancer Lett. 2020 Feb 1;470:106-114. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.10.043. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 31678165 Review.
-
The prolyl isomerase Pin1 in breast development and cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2003;5(2):76-82. doi: 10.1186/bcr572. Epub 2003 Jan 28. Breast Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12631385 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pin1 Plays Essential Roles in NASH Development by Modulating Multiple Target Proteins.Cells. 2019 Nov 29;8(12):1545. doi: 10.3390/cells8121545. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31795496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathological Role of Pin1 in the Development of DSS-Induced Colitis.Cells. 2021 May 17;10(5):1230. doi: 10.3390/cells10051230. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34067858 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and Pathogenic Roles of Prolyl Isomerase Pin1 in Metabolic Regulations via Multiple Signal Transduction Pathway Modulations.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 7;17(9):1495. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091495. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27618008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncogenic Hijacking of the PIN1 Signaling Network.Front Oncol. 2019 Feb 25;9:94. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00094. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30873382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prolyl isomerase Pin1 binds to and stabilizes acetyl CoA carboxylase 1 protein, thereby supporting cancer cell proliferation.Oncotarget. 2019 Feb 26;10(17):1637-1648. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26691. eCollection 2019 Feb 26. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 30899433 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kahn B. B., Alquier T., Carling D., Hardie D. G. (2005) AMP-activated protein kinase: ancient energy gauge provides clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab. 1, 15–25 - PubMed
-
- Hardie D. G. (2007) AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinases: conserved guardians of cellular energy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 774–785 - PubMed
-
- Hardie D. G., Carling D. (1997) The AMP-activated protein kinase: fuel gauge of the mammalian cell? Eur. J. Biochem. 246, 259–273 - PubMed
-
- Andersson U., Filipsson K., Abbott C. R., Woods A., Smith K., Bloom S. R., Carling D., Small C. J. (2004) AMP-activated protein kinase plays a role in the control of food intake. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 12005–12008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

