GNL3L Is a Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Shuttling Protein: Role in Cell Cycle Regulation
- PMID: 26274615
- PMCID: PMC4537249
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135845
GNL3L Is a Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Shuttling Protein: Role in Cell Cycle Regulation
Abstract
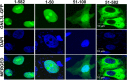
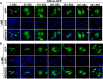
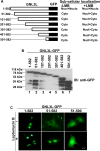
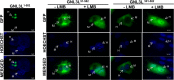
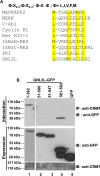
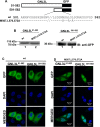
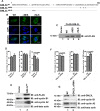
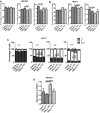
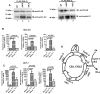
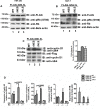
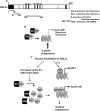
GNL3L is an evolutionarily conserved high molecular weight GTP binding nucleolar protein belonging to HSR1-MMR1 subfamily of GTPases. The present investigation reveals that GNL3L is a nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling protein and its export from the nucleus is sensitive to Leptomycin B. Deletion mutagenesis reveals that the C-terminal domain (amino acids 501-582) is necessary and sufficient for the export of GNL3L from the nucleus and the exchange of hydrophobic residues (M567, L570 and 572) within the C-terminal domain impairs this process. Results from the protein-protein interaction analysis indicate that GNL3L interaction with CRM1 is critical for its export from the nucleus. Ectopic expression of GNL3L leads to lesser accumulation of cells in the 'G2/M' phase of cell cycle whereas depletion of endogenous GNL3L results in 'G2/M' arrest. Interestingly, cell cycle analysis followed by BrdU labeling assay indicates that significantly increased DNA synthesis occurs in cells expressing nuclear export defective mutant (GNL3L∆NES) compared to the wild type or nuclear import defective GNL3L. Furthermore, increased hyperphosphorylation of Rb at Serine 780 and the upregulation of E2F1, cyclins A2 and E1 upon ectopic expression of GNL3L∆NES results in faster 'S' phase progression. Collectively, the present study provides evidence that GNL3L is exported from the nucleus in CRM1 dependent manner and the nuclear localization of GNL3L is important to promote 'S' phase progression during cell proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel lysine-rich domain and GTP binding motifs regulate the nucleolar retention of human guanine nucleotide binding protein, GNL3L.J Mol Biol. 2006 Dec 8;364(4):637-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.09.007. Epub 2006 Sep 8. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 17034816
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (ERK-2) mediated phosphorylation regulates nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling and cell growth control of Ras-associated tumor suppressor protein, RASSF2.Exp Cell Res. 2009 Oct 1;315(16):2775-90. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.06.013. Epub 2009 Jun 23. Exp Cell Res. 2009. PMID: 19555684
-
The homologous putative GTPases Grn1p from fission yeast and the human GNL3L are required for growth and play a role in processing of nucleolar pre-rRNA.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Jan;17(1):460-74. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-09-0848. Epub 2005 Oct 26. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16251348 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleostemin: a latecomer with new tricks.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Nov;41(11):2122-4. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.05.020. Epub 2009 Jun 6. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19501670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Classic "broken cell" techniques and newer live cell methods for cell cycle assessment.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 May 15;304(10):C927-38. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00006.2013. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23392113 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-Omics Analysis of GNL3L Expression, Prognosis, and Immune Value in Pan-Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 22;14(19):4595. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194595. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230520 Free PMC article.
-
Tough Way In, Tough Way Out: The Complex Interplay of Host and Viral Factors in Nucleocytoplasmic Trafficking during HIV-1 Infection.Viruses. 2022 Nov 12;14(11):2503. doi: 10.3390/v14112503. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36423112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between human nucleolar GNL1 and RPS20 is critical to modulate cell proliferation.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 30;8(1):11421. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29802-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30061673 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of GNL3L Alleviates the Progression of COPD Through Inhibiting the ATM/p53 Pathway.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023 Nov 18;18:2645-2659. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S424431. eCollection 2023. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023. PMID: 38022822 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing the oncogenic role of elevated GNL3L expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: insights into the STAT3 pathway.J Thorac Dis. 2024 Apr 30;16(4):2580-2590. doi: 10.21037/jtd-24-473. Epub 2024 Apr 29. J Thorac Dis. 2024. PMID: 38738247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caldon CE, Yoong P, March PE. Evolution of a molecular switch: universal bacterial GTPases regulate ribosome function. Mol. Microbiol. 2001; 41: 289–297. - PubMed
-
- Bourne HR, Sanders DA, McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991; 349: 117–127. - PubMed
-
- Leipe DD, Wolf YI, Koonin EV, Aravind L. Classification and Evolution of P-loop GTPases and Related ATPases. J. Mol.Biol. 2002; 317: 41–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

