PDZ interaction of Vangl2 links PSD-95 and Prickle2 but plays only a limited role in the synaptic localisation of Vangl2
- PMID: 26257100
- PMCID: PMC4530445
- DOI: 10.1038/srep12916
PDZ interaction of Vangl2 links PSD-95 and Prickle2 but plays only a limited role in the synaptic localisation of Vangl2
Abstract
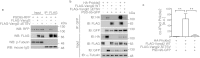
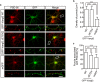
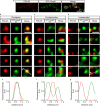
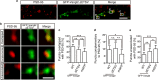
Postsynaptic density-95/Discs large/Zonula occludens-1 (PDZ) domain-mediated protein interactions play pivotal roles in various molecular biological events, including protein localisation, assembly, and signal transduction. Although the vertebrate regulator of planar cell polarity Van Gogh-like 2 (Vangl2) was recently described as a postsynaptic molecule with a PDZ-binding motif, the role of its PDZ interaction at the synapse is unknown. In this report, we demonstrate that the PDZ interaction was dispensable for the normal cluster formation of Vangl2 and not absolutely required for the synapse-associated localisation of Vangl2 in cultured hippocampal neurons. We further showed that the synaptic localisation of Vangl2 was categorised into two types: overlapping co-localisation with postsynaptic density (PSD)-95 or highly correlated but complementary pattern of association with PSD-95. Only the former was significantly sensitive to deletion of the PDZ-binding motif. In addition, the PDZ interaction enhanced the protein interactions between PSD-95 and Prickle2, which is another planar cell polarity factor that is localised at the postsynaptic density. Taken together with our recent report that the density of PSD-95 clusters was reduced in Vangl2-silenced neurons, these results suggest that Vangl2 determines the complex formation and clustering of postsynaptic molecules for synaptogenesis in mammalian brains.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vangl2, the planar cell polarity protein, is complexed with postsynaptic density protein PSD-95 [corrected].FEBS Lett. 2013 May 21;587(10):1453-9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.03.030. Epub 2013 Apr 6. FEBS Lett. 2013. PMID: 23567299
-
The planar cell polarity protein Vangl2 is involved in postsynaptic compartmentalization.Neurosci Lett. 2016 Jan 26;612:251-255. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.12.009. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Neurosci Lett. 2016. PMID: 26683906
-
The Wnt/planar cell polarity pathway component Vangl2 induces synapse formation through direct control of N-cadherin.Cell Rep. 2014 Mar 13;6(5):916-27. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.01.044. Epub 2014 Feb 27. Cell Rep. 2014. PMID: 24582966
-
Emerging roles of Dlg-like PDZ proteins in the organization of the NMDA-type glutamatergic synapse.J Biochem. 1998 Nov;124(5):869-75. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022200. J Biochem. 1998. PMID: 9792906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Syntenin: PDZ Protein Regulating Signaling Pathways and Cellular Functions.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 26;20(17):4171. doi: 10.3390/ijms20174171. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31454940 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prickle2 and Igsf9b Coordinately Regulate the Cytoarchitecture of the Axon Initial Segment.Cell Struct Funct. 2020 Sep 1;45(2):143-154. doi: 10.1247/csf.20028. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Cell Struct Funct. 2020. PMID: 32641624 Free PMC article.
-
The Planar Cell Polarity Transmembrane Protein Vangl2 Promotes Dendrite, Spine and Glutamatergic Synapse Formation in the Mammalian Forebrain.Mol Neuropsychiatry. 2016 Jul;2(2):107-14. doi: 10.1159/000446778. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Mol Neuropsychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27606324 Free PMC article.
-
Vangl as a Master Scaffold for Wnt/Planar Cell Polarity Signaling in Development and Disease.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 May 11;10:887100. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.887100. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35646914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt signaling networks in autism spectrum disorder and intellectual disability.J Neurodev Disord. 2016 Dec 5;8:45. doi: 10.1186/s11689-016-9176-3. eCollection 2016. J Neurodev Disord. 2016. PMID: 27980692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vangl2 interaction plays a role in the proteasomal degradation of Prickle2.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 27;9(1):2912. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39642-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30814664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Songyang Z. et al. Recognition of unique carboxyl-terminal motifs by distinct PDZ domains. Science 275, 73–77 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Kornau H. C., Schenker L. T., Kennedy M. B. & Seeburg P. H. Domain interaction between NMDA receptor subunits and the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95. Science 269, 1737–1740 (1995). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

