Increasing the sensitivity of NMR diffusion measurements by paramagnetic longitudinal relaxation enhancement, with application to ribosome-nascent chain complexes
- PMID: 26253948
- PMCID: PMC4924603
- DOI: 10.1007/s10858-015-9968-x
Increasing the sensitivity of NMR diffusion measurements by paramagnetic longitudinal relaxation enhancement, with application to ribosome-nascent chain complexes
Abstract
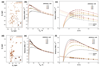
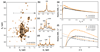
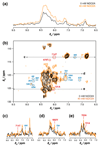
The translational diffusion of macromolecules can be examined non-invasively by stimulated echo (STE) NMR experiments to accurately determine their molecular sizes. These measurements can be important probes of intermolecular interactions and protein folding and unfolding, and are crucial in monitoring the integrity of large macromolecular assemblies such as ribosome-nascent chain complexes (RNCs). However, NMR studies of these complexes can be severely constrained by their slow tumbling, low solubility (with maximum concentrations of up to 10 μM), and short lifetimes resulting in weak signal, and therefore continuing improvements in experimental sensitivity are essential. Here we explore the use of the paramagnetic longitudinal relaxation enhancement (PLRE) agent NiDO2A on the sensitivity of (15)N XSTE and SORDID heteronuclear STE experiments, which can be used to monitor the integrity of these unstable complexes. We exploit the dependence of the PLRE effect on the gyromagnetic ratio and electronic relaxation time to accelerate recovery of (1)H magnetization without adversely affecting storage on N z during diffusion delays or introducing significant transverse relaxation line broadening. By applying the longitudinal relaxation-optimized SORDID pulse sequence together with NiDO2A to 70S Escherichia coli ribosomes and RNCs, NMR diffusion sensitivity enhancements of up to 4.5-fold relative to XSTE are achieved, alongside ~1.9-fold improvements in two-dimensional NMR sensitivity, without compromising the sample integrity. We anticipate these results will significantly advance the use of NMR to probe dynamic regions of ribosomes and other large, unstable macromolecular assemblies.
Keywords: Diffusion NMR spectroscopy; NMR sensitivity enhancement; Paramagnetic longitudinal relaxation enhancement; Ribosome–nascent chain complex.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A strategy for co-translational folding studies of ribosome-bound nascent chain complexes using NMR spectroscopy.Nat Protoc. 2016 Aug;11(8):1492-507. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2016.101. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Nat Protoc. 2016. PMID: 27466710
-
Probing the dynamic stalk region of the ribosome using solution NMR.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 19;9(1):13528. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49190-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31537834 Free PMC article.
-
Solid-state NMR enhanced by dynamic nuclear polarization as a novel tool for ribosome structural biology.J Biomol NMR. 2013 Jun;56(2):85-93. doi: 10.1007/s10858-013-9721-2. Epub 2013 May 21. J Biomol NMR. 2013. PMID: 23689811
-
Detection of intermolecular NOE interactions in large protein complexes.Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2016 Nov;97:40-56. doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2016.08.002. Epub 2016 Aug 18. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2016. PMID: 27888839 Review.
-
Protein folding by NMR.Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2017 May;100:52-77. doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2016.10.002. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2017. PMID: 28552172 Review.
Cited by
-
Obtaining Hydrodynamic Radii of Intrinsically Disordered Protein Ensembles by Pulsed Field Gradient NMR Measurements.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2141:285-302. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0524-0_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32696363
-
The ribosome and its role in protein folding: looking through a magnifying glass.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2017 Jun 1;73(Pt 6):509-521. doi: 10.1107/S2059798317007446. Epub 2017 May 31. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2017. PMID: 28580913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimal design of adaptively sampled NMR experiments for measurement of methyl group dynamics with application to a ribosome-nascent chain complex.J Magn Reson. 2021 May;326:106937. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2021.106937. Epub 2021 Feb 18. J Magn Reson. 2021. PMID: 33706222 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between nascent proteins and the ribosome surface inhibit co-translational folding.Nat Chem. 2021 Dec;13(12):1214-1220. doi: 10.1038/s41557-021-00796-x. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Nat Chem. 2021. PMID: 34650236 Free PMC article.
-
The ribosome lowers the entropic penalty of protein folding.Nature. 2024 Sep;633(8028):232-239. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07784-4. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Nature. 2024. PMID: 39112704 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Augustyniak R, Ferrage F, Paquin R, Lequin O, Bodenhausen G. J Biomol NMR. 2011;50:209. - PubMed
-
- Augustyniak R, Ferrage F, Damblon C, Bodenhausen G, Pelupessy P. Chem Commun (Camb) 2012;48:5307. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin AJ, Anthony-Cahill SJ, Knowles TPJ, Lippens G, Christo-doulou J, Barker PD, Dobson CM. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2008;47:3385. - PubMed
-
- Bernini A, Venditti V, Spiga O, Niccolai N. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2009;54:278.
-
- Bertini I, Luchinat C, Parigi G. Solution NMR of paramagnetic molecules: applications to metallobiomolecules and models. Elsevier; Amsterdam: 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

