miRegulome: a knowledge-base of miRNA regulomics and analysis
- PMID: 26243198
- PMCID: PMC4525332
- DOI: 10.1038/srep12832
miRegulome: a knowledge-base of miRNA regulomics and analysis
Abstract
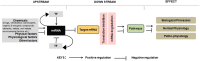
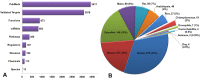
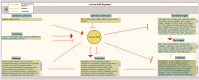
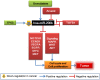
miRNAs regulate post transcriptional gene expression by targeting multiple mRNAs and hence can modulate multiple signalling pathways, biological processes, and patho-physiologies. Therefore, understanding of miRNA regulatory networks is essential in order to modulate the functions of a miRNA. The focus of several existing databases is to provide information on specific aspects of miRNA regulation. However, an integrated resource on the miRNA regulome is currently not available to facilitate the exploration and understanding of miRNA regulomics. miRegulome attempts to bridge this gap. The current version of miRegulome v1.0 provides details on the entire regulatory modules of miRNAs altered in response to chemical treatments and transcription factors, based on validated data manually curated from published literature. Modules of miRegulome (upstream regulators, downstream targets, miRNA regulated pathways, functions, diseases, etc) are hyperlinked to an appropriate external resource and are displayed visually to provide a comprehensive understanding. Four analysis tools are incorporated to identify relationships among different modules based on user specified datasets. miRegulome and its tools are helpful in understanding the biology of miRNAs and will also facilitate the discovery of biomarkers and therapeutics. With added features in upcoming releases, miRegulome will be an essential resource to the scientific community.
Availability: http://bnet.egr.vcu.edu/miRegulome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of miRNA-mRNA regulatory modules by exploring collective group relationships.BMC Genomics. 2016 Jan 11;17 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):7. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2300-z. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26817421 Free PMC article.
-
miReg: a resource for microRNA regulation.J Integr Bioinform. 2010 Aug 6;7(1). doi: 10.2390/biecoll-jib-2010-144. J Integr Bioinform. 2010. PMID: 20693604
-
AtmiRNET: a web-based resource for reconstructing regulatory networks of Arabidopsis microRNAs.Database (Oxford). 2015 May 13;2015:bav042. doi: 10.1093/database/bav042. Print 2015. Database (Oxford). 2015. PMID: 25972521 Free PMC article.
-
RegNetwork: an integrated database of transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulatory networks in human and mouse.Database (Oxford). 2015 Sep 30;2015:bav095. doi: 10.1093/database/bav095. Print 2015. Database (Oxford). 2015. PMID: 26424082 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of cardiovascular microRNA targetomes.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011 Nov;51(5):674-81. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.08.017. Epub 2011 Aug 24. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21888912 Review.
Cited by
-
DISMIRA: Prioritization of disease candidates in miRNA-disease associations based on maximum weighted matching inference model and motif-based analysis.BMC Genomics. 2015;16 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):S12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-16-S5-S12. Epub 2015 May 26. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26040329 Free PMC article.
-
miRsig: a consensus-based network inference methodology to identify pan-cancer miRNA-miRNA interaction signatures.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 3;7:39684. doi: 10.1038/srep39684. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28045122 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Prioritization Method in Identifying Recurrent Venous Thromboembolism-Related Genes.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 6;11(4):e0153006. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153006. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27050193 Free PMC article.
-
Linking common non-coding RNAs of human lung cancer and M. tuberculosis.Bioinformation. 2018 Jun 30;14(6):337-345. doi: 10.6026/97320630014337. eCollection 2018. Bioinformation. 2018. PMID: 30237679 Free PMC article.
-
DES-ncRNA: A knowledgebase for exploring information about human micro and long noncoding RNAs based on literature-mining.RNA Biol. 2017 Jul 3;14(7):963-971. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1312243. Epub 2017 Apr 7. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 28387604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Filipowicz W., Bhattacharyya S. N. & Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet 9, 102–114 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Yokoi T. & Nakajima M. Toxicological implications of modulation of gene expression by microRNAs. Toxicol Sci 123, 1–14 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Krek A. et al. Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet 37, 495–500 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Hossain M. M., Salilew-Wondim D., Schellander K. & Tesfaye D. The role of microRNAs in mammalian oocytes and embryos. Anim Reprod Sci 134, 36–44 (2012). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

