A Triple Culture Model of the Blood-Brain Barrier Using Porcine Brain Endothelial cells, Astrocytes and Pericytes
- PMID: 26241648
- PMCID: PMC4524625
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134765
A Triple Culture Model of the Blood-Brain Barrier Using Porcine Brain Endothelial cells, Astrocytes and Pericytes
Abstract
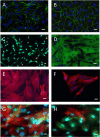
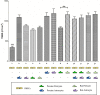
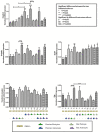
In vitro blood-brain barrier (BBB) models based on primary brain endothelial cells (BECs) cultured as monoculture or in co-culture with primary astrocytes and pericytes are useful for studying many properties of the BBB. The BECs retain their expression of tight junction proteins and efflux transporters leading to high trans-endothelial electric resistance (TEER) and low passive paracellular permeability. The BECs, astrocytes and pericytes are often isolated from small rodents. Larger species as cows and pigs however, reveal a higher yield, are readily available and have a closer resemblance to humans, which make them favorable high-throughput sources for cellular isolation. The aim of the present study has been to determine if the preferable combination of purely porcine cells isolated from the 6 months old domestic pigs, i.e. porcine brain endothelial cells (PBECs) in co-culture with porcine astrocytes and pericytes, would compare with PBECs co-cultured with astrocytes and pericytes isolated from newborn rats with respect to TEER value and low passive permeability. The astrocytes and pericytes were grown both as contact and non-contact co-cultures as well as in triple culture to examine their effects on the PBECs for barrier formation as revealed by TEER, passive permeability, and expression patterns of tight junction proteins, efflux transporters and the transferrin receptor. This syngenic porcine in vitro BBB model is comparable to triple cultures using PBECs, rat astrocytes and rat pericytes with respect to TEER formation, low passive permeability, and expression of hallmark proteins signifying the brain endothelium (tight junction proteins claudin 5 and occludin, the efflux transporters P-glycoprotein (PgP) and breast cancer related protein (BCRP), and the transferrin receptor).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
The blood-brain barrier studied in vitro across species.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 12;16(3):e0236770. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236770. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33711041 Free PMC article.
-
A new blood-brain barrier model using primary rat brain endothelial cells, pericytes and astrocytes.Neurochem Int. 2009 Mar-Apr;54(3-4):253-63. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2008.12.002. Epub 2008 Dec 7. Neurochem Int. 2009. PMID: 19111869
-
Transfection of brain capillary endothelial cells in primary culture with defined blood-brain barrier properties.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2015 Aug 7;12:19. doi: 10.1186/s12987-015-0015-9. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2015. PMID: 26246240 Free PMC article.
-
Brain endothelial cells and the glio-vascular complex.Cell Tissue Res. 2009 Jan;335(1):75-96. doi: 10.1007/s00441-008-0658-9. Epub 2008 Jul 16. Cell Tissue Res. 2009. PMID: 18633647 Review.
-
Blood-brain barrier biology and methodology.J Neurovirol. 1999 Dec;5(6):556-69. doi: 10.3109/13550289909021285. J Neurovirol. 1999. PMID: 10602397 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation methods and characterization of primary rat neurovascular cells.J Biol Eng. 2024 Jul 11;18(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13036-024-00434-3. J Biol Eng. 2024. PMID: 38992711 Free PMC article.
-
Phillyrin Prevents Neuroinflammation-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Damage Following Traumatic Brain Injury via Altering Microglial Polarization.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 20;12:719823. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.719823. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34744713 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Modeling of the Blood-Brain Barrier for the Study of Physiological Conditions and Alzheimer's Disease.Biomolecules. 2022 Aug 18;12(8):1136. doi: 10.3390/biom12081136. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36009030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flow induces barrier and glycocalyx-related genes and negative surface charge in a lab-on-a-chip human blood-brain barrier model.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2021 Sep;41(9):2201-2215. doi: 10.1177/0271678X21992638. Epub 2021 Feb 9. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2021. PMID: 33563079 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption in Herpes Simplex Encephalitis.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019 Jun;14(2):157-172. doi: 10.1007/s11481-018-9821-6. Epub 2018 Nov 19. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30456443 Review.
References
-
- Lichota J, Skjørringe T, Thomsen LB, Moos T. Macromolecular drug transport into the brain using targeted therapy. J Neurochem. 2010;113: 1–13. - PubMed
-
- Bauer HC, Bauer H, Lametschwandtner A, Amberger A, Ruiz P, Steiner M. Neovascularization and the appearance of morphological characteristics of the blood-brain barrier in the embryonic mouse central nervous system. Dev Brain Res. 1993;75: 269–78. - PubMed
-
- Abbott NJ, Rönnbäck L, Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7: 41–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

