Cooperative target mRNA destabilization and translation inhibition by miR-58 microRNA family in C. elegans
- PMID: 26232411
- PMCID: PMC4617964
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.183160.114
Cooperative target mRNA destabilization and translation inhibition by miR-58 microRNA family in C. elegans
Abstract
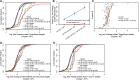
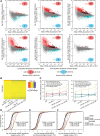
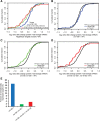
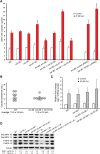
In animals, microRNAs frequently form families with related sequences. The functional relevance of miRNA families and the relative contribution of family members to target repression have remained, however, largely unexplored. Here, we used the Caenorhabditis elegans miR-58 miRNA family, composed primarily of the four highly abundant members miR-58.1, miR-80, miR-81, and miR-82, as a model to investigate the redundancy of miRNA family members and their impact on target expression in an in vivo setting. We found that miR-58 family members repress largely overlapping sets of targets in a predominantly additive fashion. Progressive deletions of miR-58 family members lead to cumulative up-regulation of target protein and RNA levels. Phenotypic defects could only be observed in the family quadruple mutant, which also showed the strongest change in target protein levels. Interestingly, although the seed sequences of miR-80 and miR-58.1 differ in a single nucleotide, predicted canonical miR-80 targets were efficiently up-regulated in the mir-58.1 single mutant, indicating functional redundancy of distinct members of this miRNA family. At the aggregate level, target binding leads mainly to mRNA degradation, although we also observed some degree of translational inhibition, particularly in the single miR-58 family mutants. These results provide a framework for understanding how miRNA family members interact to regulate target mRNAs.
© 2015 Subasic et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Degradome sequencing reveals an endogenous microRNA target in C. elegans.FEBS Lett. 2013 Apr 2;587(7):964-9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.02.029. Epub 2013 Feb 26. FEBS Lett. 2013. PMID: 23485825
-
HRPK-1, a conserved KH-domain protein, modulates microRNA activity during Caenorhabditis elegans development.PLoS Genet. 2019 Oct 4;15(10):e1008067. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008067. eCollection 2019 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31584932 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation.Cell. 2005 Aug 26;122(4):553-63. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.07.031. Cell. 2005. PMID: 16122423
-
Translational control of endogenous microRNA target genes in C. elegans.Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2010;50:21-40. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-03103-8_2. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2010. PMID: 19841879 Review.
-
MicroRNAs, mRNAs, and translation.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:531-5. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.043. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381336 Review.
Cited by
-
MINA-1 and WAGO-4 are part of regulatory network coordinating germ cell death and RNAi in C. elegans.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Oct;26(10):2157-2178. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0291-z. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 30728462 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-type-specific profiling of loaded miRNAs from Caenorhabditis elegans reveals spatial and temporal flexibility in Argonaute loading.Nat Commun. 2021 Apr 13;12(1):2194. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22503-7. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33850152 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing the Presence of a Symbolic Sequence Representing Multiple Nucleotides Based on K-Means Clustering of Oligonucleotides.Molecules. 2019 Jan 18;24(2):348. doi: 10.3390/molecules24020348. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30669407 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs cooperate in apoptosis regulation during C. elegans development.Genes Dev. 2017 Jan 15;31(2):209-222. doi: 10.1101/gad.288555.116. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Genes Dev. 2017. PMID: 28167500 Free PMC article.
-
sta-1 is repressed by mir-58 family in Caenorhabditis elegans.Worm. 2016 Sep 21;5(4):e1238560. doi: 10.1080/21624054.2016.1238560. eCollection 2016. Worm. 2016. PMID: 28090395 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
