miR-124 Regulates the Epithelial-Restricted with Serine Box/Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Axis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 26227488
- PMCID: PMC4596782
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-1071
miR-124 Regulates the Epithelial-Restricted with Serine Box/Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Axis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
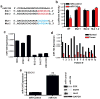
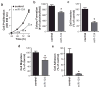
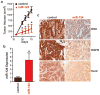
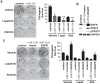
Epithelial-restricted with serine box (ESX), a member of the ETS transcription factor family, is elevated and regulates EGFR in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). However, the molecular mechanisms that contribute to ESX dysregulation remain to be elucidated. In this study, in silico analysis of the 3'-untranslated region (UTR) of ESX predicted two miR-124-binding sites. Delivery of miR-124 inhibited the 3'UTR ESX-driven reporter activity by 50% (P < 0.05) confirming ESX as a direct target of miR-124. Loss of miR-124 was found to be a frequent event in HNSCC. miR-124 expression was significantly depleted in the primary tumor compared with matched normal tissue in 100% (12/12) of HNSCC patients; relative mean miR-124 expression of 0.01197 and 0.00118 (P < 0.001, n = 12) in matched normal adjacent tissue and primary HNSCC tumor, respectively. Overexpression of miR-124 decreased ESX and EGFR levels in miR-124(low)/ESX(high)/EGFR(high) SCC15 HNSCC cells and reduced cell invasion, migration, proliferation, and colony formation. SCC15 cells with miR-124 restoration were less tumorigenic in vivo than miR-control SCC15 cells (70% inhibition, P < 0.01). Restoration of miR-124 in SCC15 cells enhanced the antiproliferative efficacy of the EGFR/Her2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Furthermore, recapitulation of EGFR in miR-124-overexpressing SCC15 cells was sufficient to completely block the antiproliferative effects of lapatinib and afatinib. Taken together, our work provides intriguing evidence that miR-124 is a novel therapeutic approach to reduce ESX/EGFR, and may be a tractable strategy to enhance the response rate of HNSCC patients to current anti-EGFR/Her2 therapies.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no competing financial interests in relation to the work described.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic and chemical targeting of epithelial-restricted with serine box reduces EGF receptor and potentiates the efficacy of afatinib.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Aug;12(8):1515-25. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-1110. Epub 2013 May 30. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 23723125 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-107 functions as a candidate tumor-suppressor gene in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by downregulation of protein kinase Cɛ.Oncogene. 2012 Sep 6;31(36):4045-53. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.565. Epub 2011 Dec 12. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 22158047 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated RET expression enhances EGFR activation and mediates EGFR inhibitor resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2016 Jul 10;377(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.04.023. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 27090738
-
Molecular targeted therapies in the management of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: recent developments and perspectives.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013 Mar;13(3):389-402. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23092267 Review.
-
Afatinib in the treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014 Jan;23(1):135-43. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2014.858696. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24266694 Review.
Cited by
-
Signature microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in laryngeal cancer recurrence identified using a competing endogenous RNA network.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Jun;19(6):4806-4818. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10143. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31059106 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-124 acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting the expression of sphingosine kinase 1 and its downstream signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 11;8(15):25005-25020. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15334. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28212569 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of LHX2 by miR-124 suppresses cellular migration and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer.Oncol Lett. 2017 Sep;14(3):3429-3436. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6607. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28927097 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNAs modulating glycolysis as non-invasive prognostic biomarkers of HNSCC.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021 May;278(5):1585-1594. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-06240-z. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 32737645
-
miR-124 modulates gefitinib resistance through SNAI2 and STAT3 in non-small cell lung cancer.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016 Dec;36(6):839-845. doi: 10.1007/s11596-016-1672-x. Epub 2016 Dec 7. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27924500
References
-
- Liu E, Thor A, He M, Barcos M, Ljung BM, Benz C. The HER2 (c-erbB-2) oncogene is frequently amplified in in situ carcinomas of the breast. Oncogene. 1992;7(5):1027–32. - PubMed
-
- Tymms MJ, Ng AY, Thomas RS, Schutte BC, Zhou J, Eyre HJ, et al. A novel epithelial-expressed ETS gene, ELF3: human and murine cDNA sequences, murine genomic organization, human mapping to 1q32.2 and expression in tissues and cancer. Oncogene. 1997;15(20):2449–62. - PubMed
-
- Schedin PJ, Eckel-Mahan KL, McDaniel SM, Prescott JD, Brodsky KS, Tentler JJ, et al. ESX induces transformation and functional epithelial to mesenchymal transition in MCF-12A mammary epithelial cells. Oncogene. 2004;23(9):1766–79. - PubMed
-
- Walker DM, Poczobutt JM, Gonzales MS, Horita H, Gutierrez-Hartmann A. ESE-1 is Required to Maintain the Transformed Phenotype of MCF-7 and ZR-75–1 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Open Cancer Journal. 2010;3:77–88.
-
- Benz CC, O’Hagan RC, Richter B, Scott GK, Chang CH, Xiong X, et al. HER2/Neu and the Ets transcription activator PEA3 are coordinately upregulated in human breast cancer. Oncogene. 1997;15(13):1513–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

