Silencing the NR2B gene in rat ACC neurons by lentivirus-delivered shRNA alleviates pain-related aversion
- PMID: 26221210
- PMCID: PMC4509155
Silencing the NR2B gene in rat ACC neurons by lentivirus-delivered shRNA alleviates pain-related aversion
Abstract
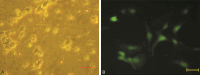
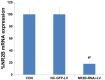
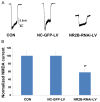
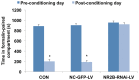
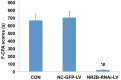
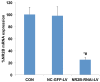
The N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor NR2B subunit on neurons in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) is implicated in the affective response to noxious stimuli. Selectively silencing this NR2B subunit in ACC neurons could therefore alleviate pain-related aversion. However, to date, there is no optimal approach to selectively silence the NR2B gene in ACC neurons. In the present study, we constructed lentiviral vectors and delivered shRNA (NR2B-RNAi-LV) to effectively silence the NR2B gene in ACC neurons. The use of lentivirus resulted in 95% transfection efficiency and 83% silencing of the NR2B gene in ACC neurons. Electrophysiological experiments showed that the total INMDA was similarly reduced by 48% in lentivirus-transfected ACC neurons. The biochemical and functional data demonstrated that lentiviral shRNA delivery produced a high transfection and silencing efficiency in the ACC neurons. SNI rats weighting 220-250 g were randomly divided into three groups: normal saline group (NS), lenti-siRNA/NC (LV-NC) group, and lenti-siRNA/NR2B (LV-NR2B) group, and conditioned place avoidance was conducted. The results indicated that NR2B-RNAi-LV decreased greatly the conditioning scores of F-CPA while NC-GFP-LV has no effects. NR2B mRNA expression in the NR2B-RNAi-LV group was significantly lower than that in the control group and NC-GFP-LV group. This novel approach of silencing the NR2B gene in ACC neuron could potentially be used to alleviate pain-related aversion.
Keywords: ACC; NR2B; RNA interference; gene silencing.
Figures



Similar articles
-
NMDA NR2A and NR2B receptors in the rostral anterior cingulate cortex contribute to pain-related aversion in male rats.Pain. 2009 Nov;146(1-2):183-93. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.07.027. Epub 2009 Aug 19. Pain. 2009. PMID: 19695778 Free PMC article.
-
[Construction of shRNA lentivirus vector on rat DREAM gene and its analgesic effect on CCI rats].Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2009 Aug;34(8):723-30. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2009. PMID: 19734578 Chinese.
-
Differential Role of Anterior Cingulate Cortical Glutamatergic Neurons in Pain-Related Aversion Learning and Nociceptive Behaviors in Male and Female Rats.Front Behav Neurosci. 2020 Aug 11;14:139. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2020.00139. eCollection 2020. Front Behav Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32848657 Free PMC article.
-
[Investigation of Lentiviral Vectors Based Integrin β8 RNAi System in Neonatal Rats' Brain].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018 May;49(3):325-330. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018. PMID: 30014628 Chinese.
-
Caveolin-1 in the anterior cingulate cortex modulates chronic neuropathic pain via regulation of NMDA receptor 2B subunit.J Neurosci. 2015 Jan 7;35(1):36-52. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1161-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25568101 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Potential of Combinative shRNA-Encoded Lentivirus-Mediated Gene Silencing to Accelerate Somatosensory Recovery After Spinal Cord Trauma.Neurotherapeutics. 2023 Mar;20(2):564-577. doi: 10.1007/s13311-022-01331-7. Epub 2022 Nov 18. Neurotherapeutics. 2023. PMID: 36401079 Free PMC article.
-
The Medial Prefrontal Cortex as a Central Hub for Mental Comorbidities Associated with Chronic Pain.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 13;21(10):3440. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103440. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32414089 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Koyama T, Tanaka YZ, Mikami A. Nociceptive neurons in the macaque anterior cingulate activate during anticipation of pain. Neuroreport. 1998;9:2663–2667. - PubMed
-
- Gao YJ, Ren WH, Zhang YQ, Zhao ZQ. Contributions of the anterior cingulate cortex and amygdala to pain-and fear-conditioned place avoidance in rats. Pain. 2004;110:343–353. - PubMed
-
- Higashi H, Tanaka E, Nishi S. Synaptic responses of guinea pig cingulate cortical neurons in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1991;65:822–833. - PubMed
-
- Wei F, Wang GD, Kerchner GA, Kim SJ, Xu HM, Chen ZF, Zhuo M. Genetic enhancement of inflammatory pain by forebrain NR2B overexpression. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4:164–169. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
