Tolerance and Cross-Tolerance following Toll-Like Receptor (TLR)-4 and -9 Activation Are Mediated by IRAK-M and Modulated by IL-7 in Murine Splenocytes
- PMID: 26218271
- PMCID: PMC4517781
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132921
Tolerance and Cross-Tolerance following Toll-Like Receptor (TLR)-4 and -9 Activation Are Mediated by IRAK-M and Modulated by IL-7 in Murine Splenocytes
Abstract
Objective: Immune suppression during critical illness predisposes to serious infections. We sought to determine the mechanisms regulating tolerance and cross-tolerance to common pro-inflammatory danger signals in a model that recapitulates the intact in vivo immune response.
Materials and methods: Flt3-expanded splenocytes obtained from wild-type or matching IRAK-M knockout (IRAK-M-/-), C57BL/6, male mice (8-10 weeks old) were treated repeatedly or alternately with either LPS or CpGA DNA, agonists of Toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 and -9, respectively, over successive 24-hour periods. Supernatants were collected following each 24-hour period with cytokine release (ELISA) and splenocyte IRAK-M expression (Western blot) determined. Tolerance and cross-tolerance were assessed in the absence or presence of programmed death receptor (PD)-1 blocking antibody or IL-7 pre-treatment.
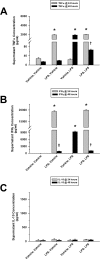
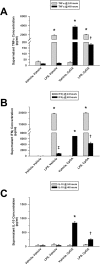
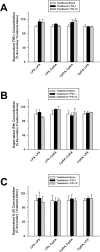
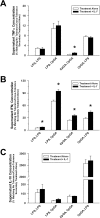
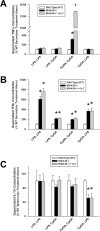
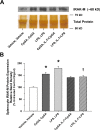
Main results: Splenocytes notably exhibited both tolerance and cross-tolerance to subsequent treatments with either LPS or CpGA DNA. The character of tolerance and cross-tolerance in this model was distinct following initial LPS or CpGA treatment in that TNFα and IFNγ release (not IL-10) were suppressed following LPS; whereas, initial CpGA treatment suppressed TNFα, IFNγ and IL-10 release in response to subsequent stimulation (LPS or CpGA). Tolerance and cross-tolerance were unrelated to IL-10 release or PD-1 but were attenuated in IRAK-M-/- splenocytes. IL-7 significantly suppressed IRAK-M expression and restored TNFα and IFNγ production without influencing IL-10 release.
Conclusions: In summary, acute immune tolerance and cross-tolerance in response to LPS or CpGA were distinct in that LPS selectively suppressed pro-inflammatory cytokine responses; whereas, CpGA suppressed both pro- and anti-inflammatory responses. The induction of tolerance and cross-tolerance in response to common danger signals was mechanistically unrelated to IL-10 or PD-1 but was directly influenced by IRAK-M expression. IL-7 reduced IRAK-M expression and attenuated immune tolerance induced by either LPS or CpGA, and thus may be useful for reversal of immune tolerance in the setting of critical illness.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Macrophage subsets exhibit distinct E. coli-LPS tolerisable cytokines associated with the negative regulators, IRAK-M and Tollip.PLoS One. 2019 May 23;14(5):e0214681. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214681. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31120887 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of IRAK-M is associated with lipopolysaccharide tolerance in a human endotoxemia model.J Immunol. 2007 Nov 15;179(10):7110-20. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.10.7110. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17982103 Clinical Trial.
-
Wear particles promote endotoxin tolerance in macrophages by inducing interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-M expression.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013 Mar;101(3):733-9. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.34375. Epub 2012 Aug 31. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013. PMID: 22941946
-
The interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinases: critical regulators of innate immune signalling.Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Dec 15;80(12):1981-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.06.020. Epub 2010 Jun 23. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20599782 Review.
-
Experimental and natural infections in MyD88- and IRAK-4-deficient mice and humans.Eur J Immunol. 2012 Dec;42(12):3126-35. doi: 10.1002/eji.201242683. Eur J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23255009 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Endotoxin Tolerance and Compensatory Anti-inflammatory Response Syndrome by Non-coding RNAs.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 20;9:2705. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02705. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30515175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Class A CpG Oligonucleotide Priming Rescues Mice from Septic Shock via Activation of Platelet-Activating Factor Acetylhydrolase.Front Immunol. 2017 Aug 30;8:1049. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01049. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28912777 Free PMC article.
-
K63-Linked Polyubiquitination on TRAF6 Regulates LPS-Mediated MAPK Activation, Cytokine Production, and Bacterial Clearance in Toll-Like Receptor 7/8 Primed Murine Macrophages.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 21;9:279. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00279. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29515583 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-Like Receptors Drive Specific Patterns of Tolerance and Training on Restimulation of Macrophages.Front Immunol. 2018 May 14;9:933. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00933. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29867935 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase-3 (IRAK3) function in modulating expression of inflammatory markers in cell culture models: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 31;15(12):e0244570. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244570. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33382782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dobrovolskaia MA, Medvedev AE, Thomas KE, Cuesta N, Toshchakov V, Ren T, et al. Induction of in vitro reprogramming by Toll-Like Receptor (TLR)2 and TLR4 agonists in murine macrophages: Effects of TLR “homotolerance” versus “heterotolerance” on NF-kappa B signaling pathway components. J Immunol. 2003; 170:508–519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

