Isolation and characterization of an osmotic stress and ABA induced histone deacetylase in Arachis hygogaea
- PMID: 26217363
- PMCID: PMC4499716
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00512
Isolation and characterization of an osmotic stress and ABA induced histone deacetylase in Arachis hygogaea
Abstract
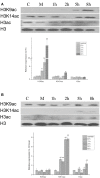
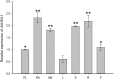
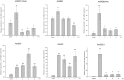
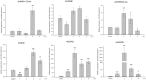
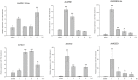
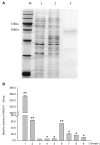
Histone acetylation, which together with histone methylation regulates gene activity in response to stress, is an important epigenetic modification. There is an increasing research focus on histone acetylation in crops, but there is no information to date in peanut (Arachis hypogaea). We showed that osmotic stress and ABA affect the acetylation of histone H3 loci in peanut seedlings by immunoblotting experiments. Using RNA-seq data for peanut, we found a RPD3/HDA1-like superfamily histone deacetylase (HDAC), termed AhHDA1, whose gene is up-regulated by PEG-induced water limitation and ABA signaling. We isolated and characterized AhHDA1 from A. hypogaea, showing that AhHDA1 is very similar to an Arabidopsis HDAC (AtHDA6) and, in recombinant form, possesses HDAC activity. To understand whether and how osmotic stress and ABA mediate the peanut stress response by epigenetics, the expression of AhHDA1 and stress-responsive genes following treatment with PEG, ABA, and the specific HDAC inhibitor trichostatin A (TSA) were analyzed. AhHDA1 transcript levels were enhanced by all three treatments, as was expression of peanut transcription factor genes, indicating that AhHDA1 might be involved in the epigenetic regulation of stress resistance genes that comprise the responses to osmotic stress and ABA.
Keywords: ABA; HDAC; RNA-seq; TSA; acetylation; epigenetics; osmotic stress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptome profiling reveals histone deacetylase 1 gene overexpression improves flavonoid, isoflavonoid, and phenylpropanoid metabolism in Arachis hypogaea hairy roots.PeerJ. 2021 Mar 16;9:e10976. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10976. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 33777524 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of AhDREB1, an AP2/ERF Transcription Factor Gene from Peanut, Is Affected by Histone Acetylation and Increases Abscisic Acid Sensitivity and Tolerance to Osmotic Stress in Arabidopsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 11;19(5):1441. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051441. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29751673 Free PMC article.
-
AhHDA1-mediated AhGLK1 promoted chlorophyll synthesis and photosynthesis regulates recovery growth of peanut leaves after water stress.Plant Sci. 2020 May;294:110461. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110461. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32234234
-
[Epigenetic mechanisms and alcohol use disorders: a potential therapeutic target].Biol Aujourdhui. 2017;211(1):83-91. doi: 10.1051/jbio/2017014. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Biol Aujourdhui. 2017. PMID: 28682229 Review. French.
-
Methylation hallmarks on the histone tail as a linker of osmotic stress and gene transcription.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Aug 10;13:967607. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.967607. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36035677 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The bHLH transcription factor AhbHLH112 improves the drought tolerance of peanut.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Nov 16;21(1):540. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03318-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 34784902 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Stress Responses and Phenotypic Plasticity in the Epigenomics Era: Perspectives on the Grapevine Scenario, a Model for Perennial Crop Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Feb 6;8:82. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00082. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28220131 Free PMC article.
-
Improved drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis by CRISPR/dCas9 fusion with a Histone AcetylTransferase.Sci Rep. 2019 May 30;9(1):8080. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44571-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31147630 Free PMC article.
-
Osmolarity controls the differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells into nucleus pulposus cells via histone demethylase KDM4B.Mol Cell Biochem. 2020 Sep;472(1-2):157-171. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03794-8. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32594337
-
Transcriptome profiling reveals histone deacetylase 1 gene overexpression improves flavonoid, isoflavonoid, and phenylpropanoid metabolism in Arachis hypogaea hairy roots.PeerJ. 2021 Mar 16;9:e10976. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10976. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 33777524 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

