Dual targeting of the chemokine receptors CXCR4 and ACKR3 with novel engineered chemokines
- PMID: 26216880
- PMCID: PMC4566214
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.675108
Dual targeting of the chemokine receptors CXCR4 and ACKR3 with novel engineered chemokines
Abstract
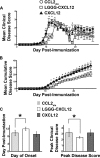
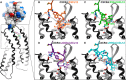
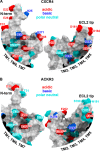
The chemokine CXCL12 and its G protein-coupled receptors CXCR4 and ACKR3 are implicated in cancer and inflammatory and autoimmune disorders and are targets of numerous antagonist discovery efforts. Here, we describe a series of novel, high affinity CXCL12-based modulators of CXCR4 and ACKR3 generated by selection of N-terminal CXCL12 phage libraries on live cells expressing the receptors. Twelve of 13 characterized CXCL12 variants are full CXCR4 antagonists, and four have Kd values <5 nm. The new variants also showed high affinity for ACKR3. The variant with the highest affinity for CXCR4, LGGG-CXCL12, showed efficacy in a murine model for multiple sclerosis, demonstrating translational potential. Molecular modeling was used to elucidate the structural basis of binding and antagonism of selected variants and to guide future designs. Together, this work represents an important step toward the development of therapeutics targeting CXCR4 and ACKR3.
Keywords: ACKR3; C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR-4); CXCL12; G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR); SDF-1a; chemokine; chemokine receptors; experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE); phage display; signaling.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential activity and selectivity of N-terminal modified CXCL12 chemokines at the CXCR4 and ACKR3 receptors.J Leukoc Biol. 2020 Jun;107(6):1123-1135. doi: 10.1002/JLB.2MA0320-383RR. Epub 2020 May 6. J Leukoc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32374043 Free PMC article.
-
The chemokine X-factor: Structure-function analysis of the CXC motif at CXCR4 and ACKR3.J Biol Chem. 2020 Oct 2;295(40):13927-13939. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014244. Epub 2020 Aug 11. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32788219 Free PMC article.
-
Partial agonist activity of α1-adrenergic receptor antagonists for chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 and atypical chemokine receptor 3.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 24;13(9):e0204041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204041. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30248140 Free PMC article.
-
Role and implications of the CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in atherosclerosis: still a debate.Ann Med. 2021 Dec;53(1):1598-1612. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2021.1974084. Ann Med. 2021. PMID: 34494495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between CXCL12/CXCR4/ACKR3 and the STAT3 Pathway.Cells. 2024 Jun 13;13(12):1027. doi: 10.3390/cells13121027. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38920657 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chemokines and their receptors: insights from molecular modeling and crystallography.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2016 Oct;30:27-37. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2016.07.006. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27459124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational design of dynamic receptor-peptide signaling complexes applied to chemotaxis.Nat Commun. 2023 May 19;14(1):2875. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38491-9. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37208363 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of CC Chemokine Receptor 5 with a Potent Chemokine Antagonist Reveals Mechanisms of Chemokine Recognition and Molecular Mimicry by HIV.Immunity. 2017 Jun 20;46(6):1005-1017.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.05.002. Immunity. 2017. PMID: 28636951 Free PMC article.
-
Latest update on chemokine receptors as therapeutic targets.Biochem Soc Trans. 2021 Jun 30;49(3):1385-1395. doi: 10.1042/BST20201114. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021. PMID: 34060588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemokine-Driven Migration of Pro-Inflammatory CD4+ T Cells in CNS Autoimmune Disease.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 16;13:817473. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.817473. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35250997 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bleul C. C., Farzan M., Choe H., Parolin C., Clark-Lewis I., Sodroski J., Springer T. A. (1996) The lymphocyte chemoattractant SDF-1 is a ligand for LESTR/fusin and blocks HIV-1 entry. Nature 382, 829–833 - PubMed
-
- Hori T., Sakaida H., Sato A., Nakajima T., Shida H., Yoshie O., Uchiyama T. (1998) Detection and delineation of CXCR-4 (fusin) as an entry and fusion cofactor for T cell-tropic HIV-1 by three different monoclonal antibodies. J. Immunol. 160, 180–188 - PubMed
-
- Sun Y., Cheng Z., Ma L., Pei G. (2002) β-Arrestin2 is critically involved in CXCR4-mediated chemotaxis, and this is mediated by its enhancement of p38 MAPK activation. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 49212–49219 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

