Phase II study of an AKT inhibitor MK2206 in patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoma
- PMID: 26213141
- PMCID: PMC5278973
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.13603
Phase II study of an AKT inhibitor MK2206 in patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoma
Abstract
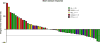
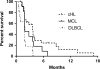
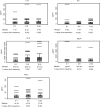
We conducted a phase II study of the AKT inhibitor, MK2206 in patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoma of any histology excluding Burkitt lymphoma or lymphoblastic lymphoma. MK-2206 was administered orally at 200 mg once weekly in 28-d cycles up to 12 cycles in the absence of progression or significant toxicity. The dose was adjusted based on tolerance. A total of 59 patients were enrolled. The final doses patients received were 300 mg (n = 33), 250 mg (n = 2), 200 mg (n = 16) and 135 mg (n = 8). Based on intent-to-treat analysis, objective response was observed in 8 (14%) patients (2 complete response and 6 partial response), with median response duration of 5·8 months. The overall response rate was 20% in 25 patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Rash was the most common toxicity (any grade 53%, Grade 3 in 15%) and was observed in a dose-dependent manner. The correlative cytokine analysis showed paradoxical increase in several cytokines, which may be explained by negative feedback mechanism induced by the on-target effect of AKT inhibitor. Our data demonstrate that MK2206 has a favourable safety profile with a modest activity in patients with relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma. The future studies should explore mechanism-based combinations (clinicaltrials.gov NCT01258998).
Keywords: AKT; clinical trials; lymphoma; target therapy.
© 2015 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
statements Authors disclosed no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ENGAGE- 501: phase II study of entinostat (SNDX-275) in relapsed and refractory Hodgkin lymphoma.Haematologica. 2016 Aug;101(8):968-75. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2016.142406. Epub 2016 May 5. Haematologica. 2016. PMID: 27151994 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I trial of high-dose clofarabine, etoposide, and cyclophosphamide and autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in patients with primary refractory and relapsed and refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011 Jul;17(7):987-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2010.10.016. Epub 2010 Oct 20. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011. PMID: 20965266 Clinical Trial.
-
A phase II study to assess the safety and efficacy of the dual mTORC1/2 inhibitor vistusertib in relapsed, refractory DLBCL.Hematol Oncol. 2019 Oct;37(4):352-359. doi: 10.1002/hon.2662. Epub 2019 Sep 9. Hematol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31385336 Clinical Trial.
-
Outcome analysis of high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation in adolescent and young adults with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma.Ann Hematol. 2016 Sep;95(9):1521-35. doi: 10.1007/s00277-016-2736-5. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Ann Hematol. 2016. PMID: 27376363
-
Treatment of relapsed aggressive lymphomas: regimens with and without high-dose therapy and stem cell rescue.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2002 May;49 Suppl 1:S13-20. doi: 10.1007/s00280-002-0447-1. Epub 2002 Apr 12. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12042984 Review.
Cited by
-
AKT in cancer: new molecular insights and advances in drug development.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016 Oct;82(4):943-56. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13021. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27232857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small-molecule HDAC and Akt inhibitors suppress tumor growth and enhance immunotherapy in multiple myeloma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Mar 23;40(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01909-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33757580 Free PMC article.
-
Combined BCL-2 and PI3K/AKT Pathway Inhibition in KMT2A-Rearranged Acute B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 10;24(2):1359. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021359. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674872 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic Signaling Pathways and Pathway-Based Therapeutic Biomarkers in Lymphoid Malignancies.Crit Rev Oncog. 2017;22(5-6):527-557. doi: 10.1615/CritRevOncog.2017020816. Crit Rev Oncog. 2017. PMID: 29604930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reactive intermediates in copanlisib metabolism identified by LC-MS/MS: phase I metabolic profiling.RSC Adv. 2019 Feb 21;9(11):6409-6418. doi: 10.1039/c8ra10322d. eCollection 2019 Feb 18. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35517257 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bertacchini J, Guida M, Accordi B, Mediani L, Martelli AM, Barozzi P, Petricoin E, 3rd, Liotta L, Milani G, Giordan M, Luppi M, Forghieri F, De Pol A, Cocco L, Basso G, Marmiroli S. Feedbacks and adaptive capabilities of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis in acute myeloid leukemia revealed by pathway selective inhibition and phosphoproteome analysis. Leukemia. 2014;28:2197–2205. - PubMed
-
- Biondo A, Yap TA, Yan L, Patnaik A, Fearen I, Baird RD, Papadopoulos KP, Delgado LM, Taylor A, Lupinacci L, Blackman SC, Decordova S, Tall M, Heaton S, Garrett MD, Sullivan D, Bono JSD, Tolcher AW. Phase I clinical trial of an allosteric AKT inhibitor, MK-2206, using a once weekly (QW) dose regimen in patients with advanced solid tumors. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2011;29 abstr 3037. - PubMed
-
- Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME, Gascoyne RD, Specht L, Horning SJ, Coiffier B, Fisher RI, Hagenbeek A, Zucca E, Rosen ST, Stroobants S, Lister TA, Hoppe RT, Dreyling M, Tobinai K, Vose JM, Connors JM, Federico M, Diehl V. Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2007;25:579–586. - PubMed
-
- Dreyling M, Morschhauser F, Bron D, Bouabdallah K, Vitolo U, Linton K, Van Den Neste E, Mappa S, Giurescu M, Childs BH, Zinzani PL. Preliminary results of a phase II study of single agent Bay 80-6946, a novel PI3K inhibitor, in patients with relapsed/refractory, indolent or aggressive lymphoma. Blood. 2013;122 abstr 87.
-
- Engelman JA. Targeting PI3K signalling in cancer: opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2009;9:550–562. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

